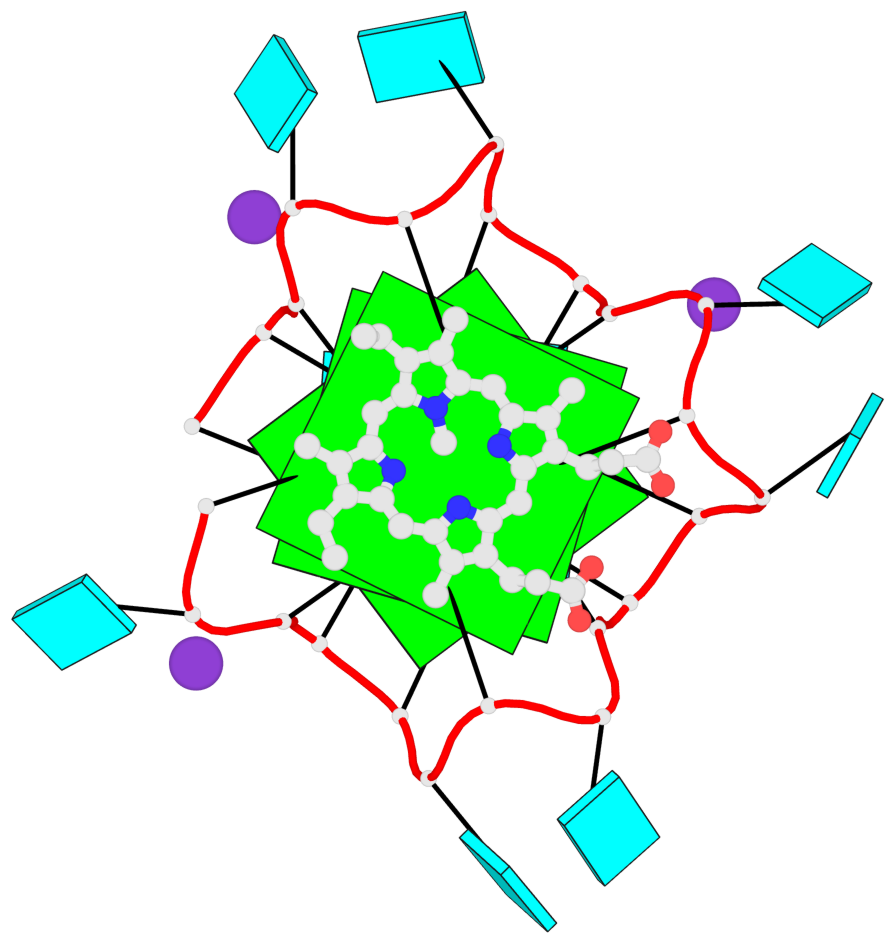
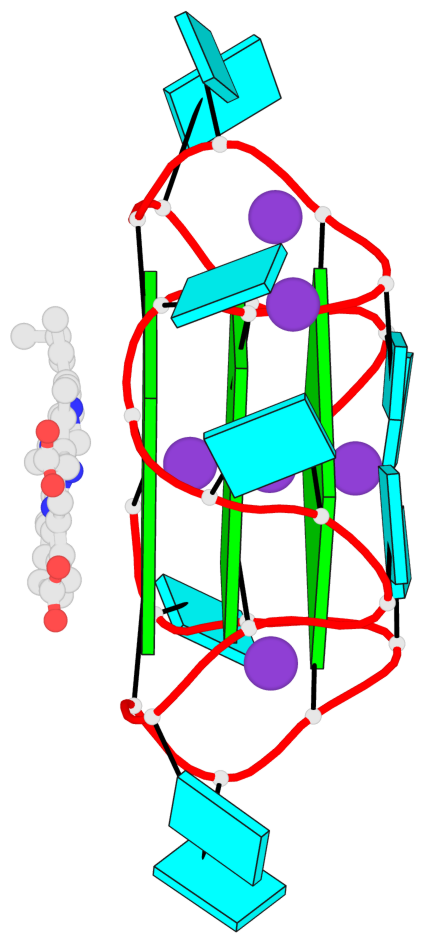
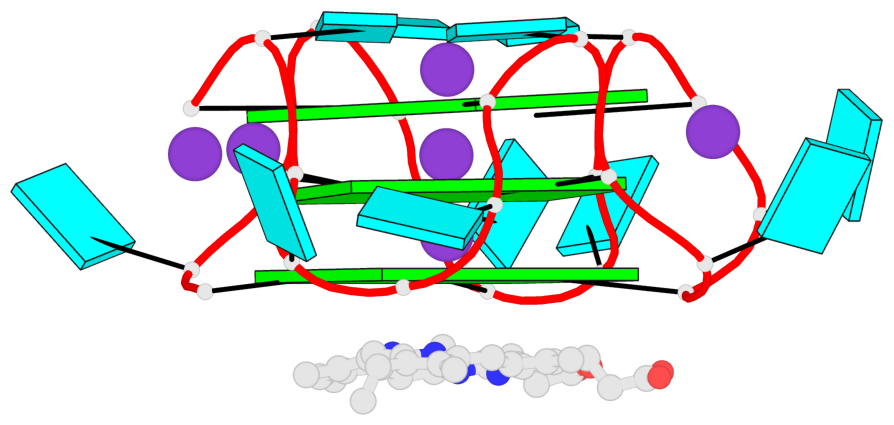
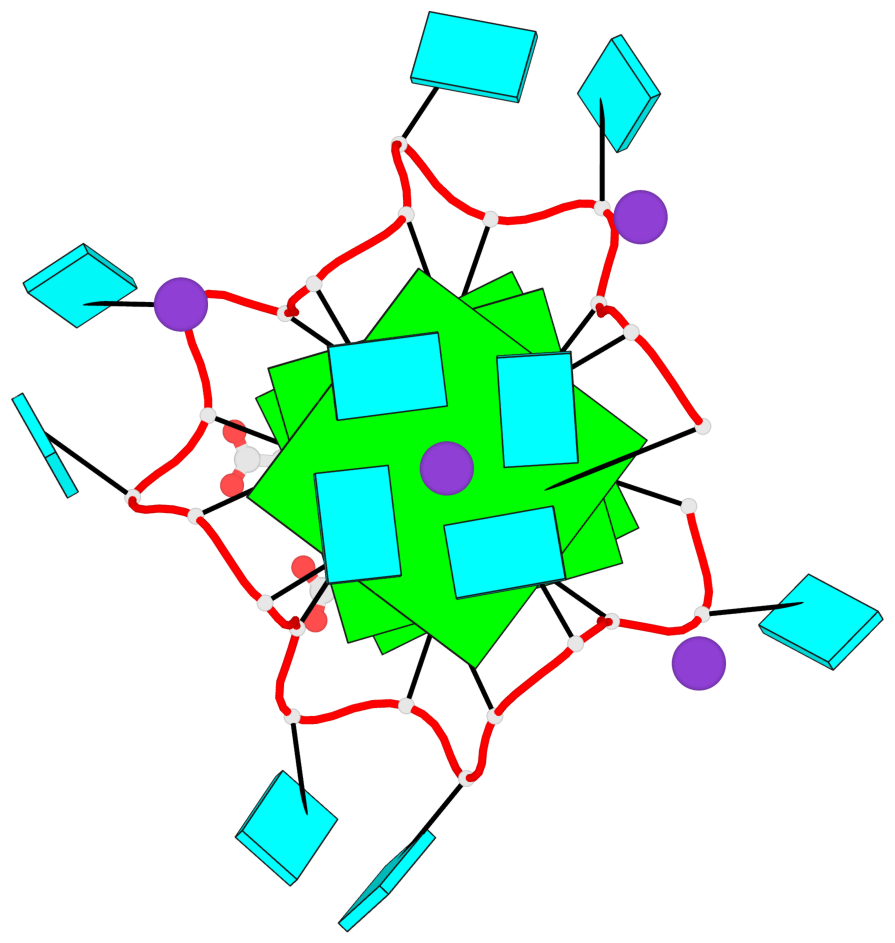
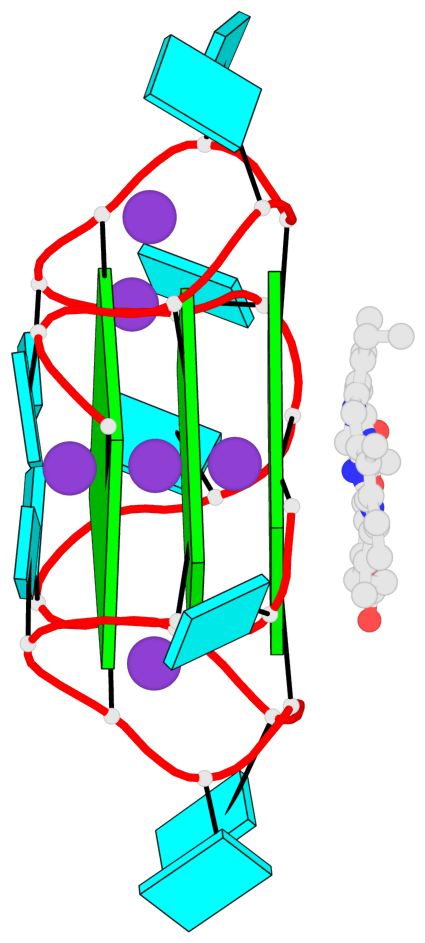
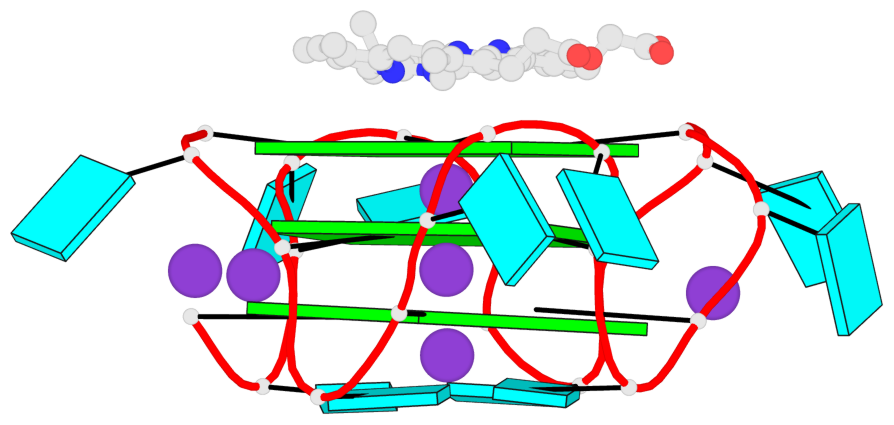
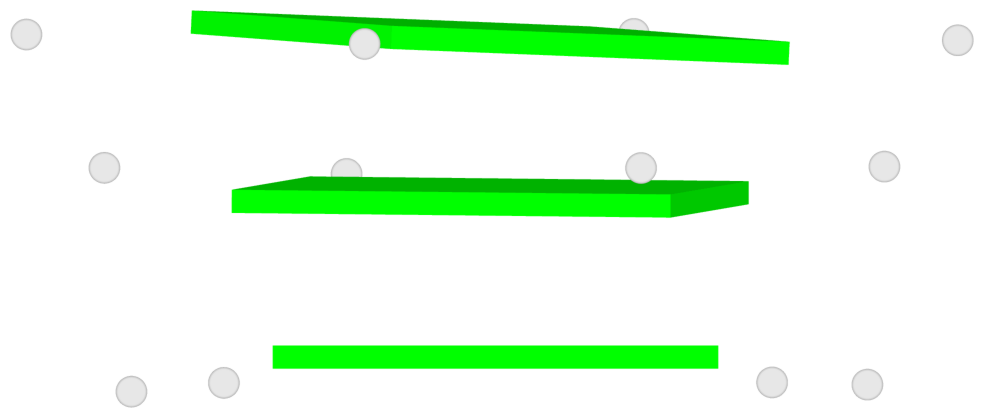
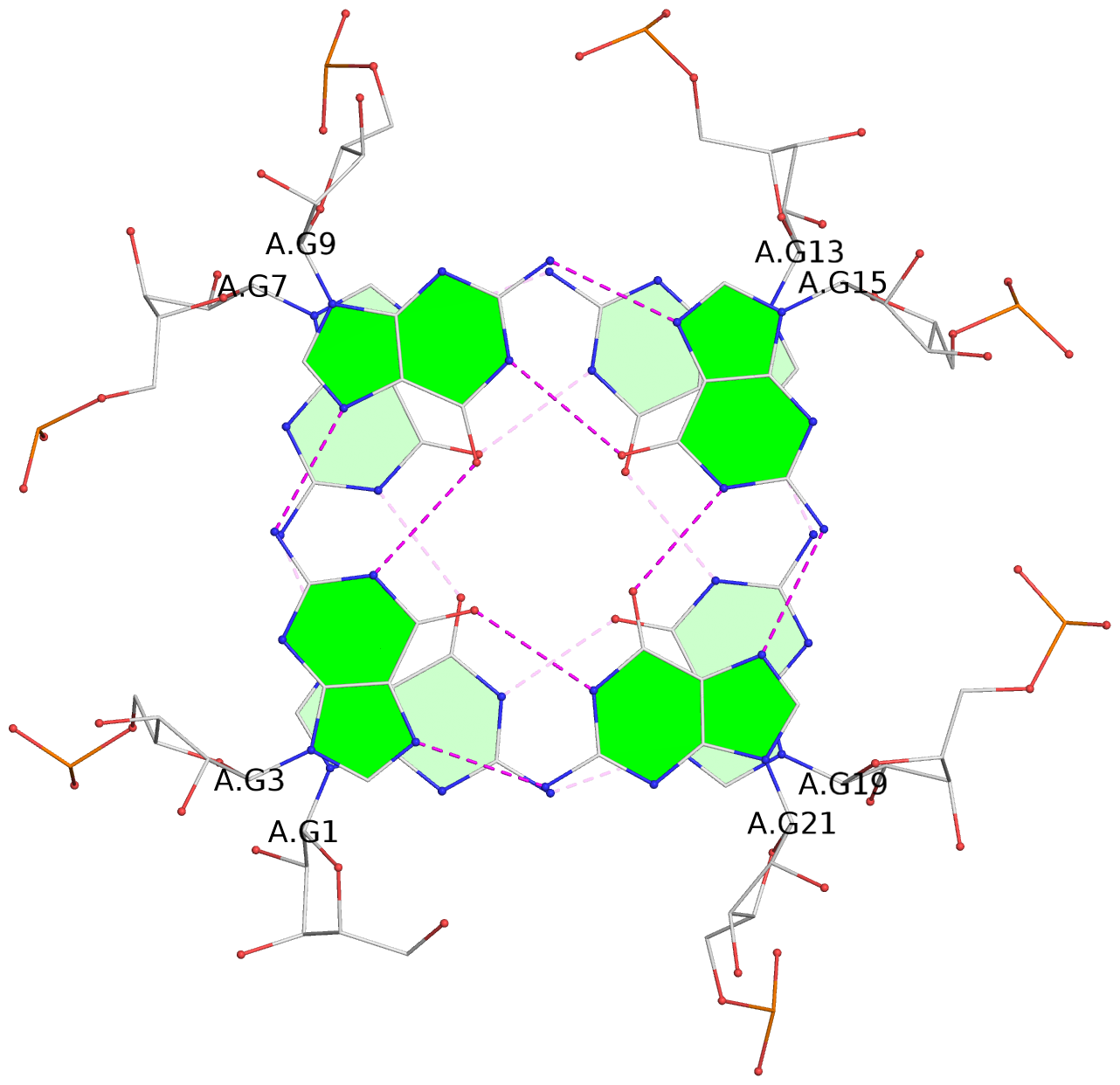
Detailed DSSR results for the G-quadruplex: PDB entry 7mkt
Created and maintained by Xiang-Jun Lu <xiangjun@x3dna.org>
Citation: Please cite the NAR'20 DSSR-PyMOL schematics paper and/or the NAR'15 DSSR method paper.
Summary information
- PDB id
- 7mkt
- Class
- RNA
- Method
- X-ray (1.97 Å)
- Summary
- Crystal structure of r(gu)11g-nmm complex
- Reference
- Roschdi S, Yan J, Nomura Y, Escobar CA, Petersen RJ, Bingman CA, Tonelli M, Vivek R, Montemayor EJ, Wickens M, Kennedy SG, Butcher SE (2022): "An atypical RNA quadruplex marks RNAs as vectors for gene silencing." Nat.Struct.Mol.Biol., 29, 1113-1121. doi: 10.1038/s41594-022-00854-z.
- Abstract
- The addition of poly(UG) ('pUG') repeats to 3' termini of mRNAs drives gene silencing and transgenerational epigenetic inheritance in the metazoan Caenorhabditis elegans. pUG tails promote silencing by recruiting an RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRP) that synthesizes small interfering RNAs. Here we show that active pUG tails require a minimum of 11.5 repeats and adopt a quadruplex (G4) structure we term the pUG fold. The pUG fold differs from known G4s in that it has a left-handed backbone similar to Z-RNA, no consecutive guanosines in its sequence, and three G quartets and one U quartet stacked non-sequentially. The compact pUG fold binds six potassium ions and brings the RNA ends into close proximity. The biological importance of the pUG fold is emphasized by our observations that porphyrin molecules bind to the pUG fold and inhibit both gene silencing and binding of RdRP. Moreover, specific 7-deaza substitutions that disrupt the pUG fold neither bind RdRP nor induce RNA silencing. These data define the pUG fold as a previously unrecognized RNA structural motif that drives gene silencing. The pUG fold can also form internally within larger RNA molecules. Approximately 20,000 pUG-fold sequences are found in noncoding regions of human RNAs, suggesting that the fold probably has biological roles beyond gene silencing.
- G4 notes
- 3 G-tetrads, 1 G4 helix
Base-block schematics in six views
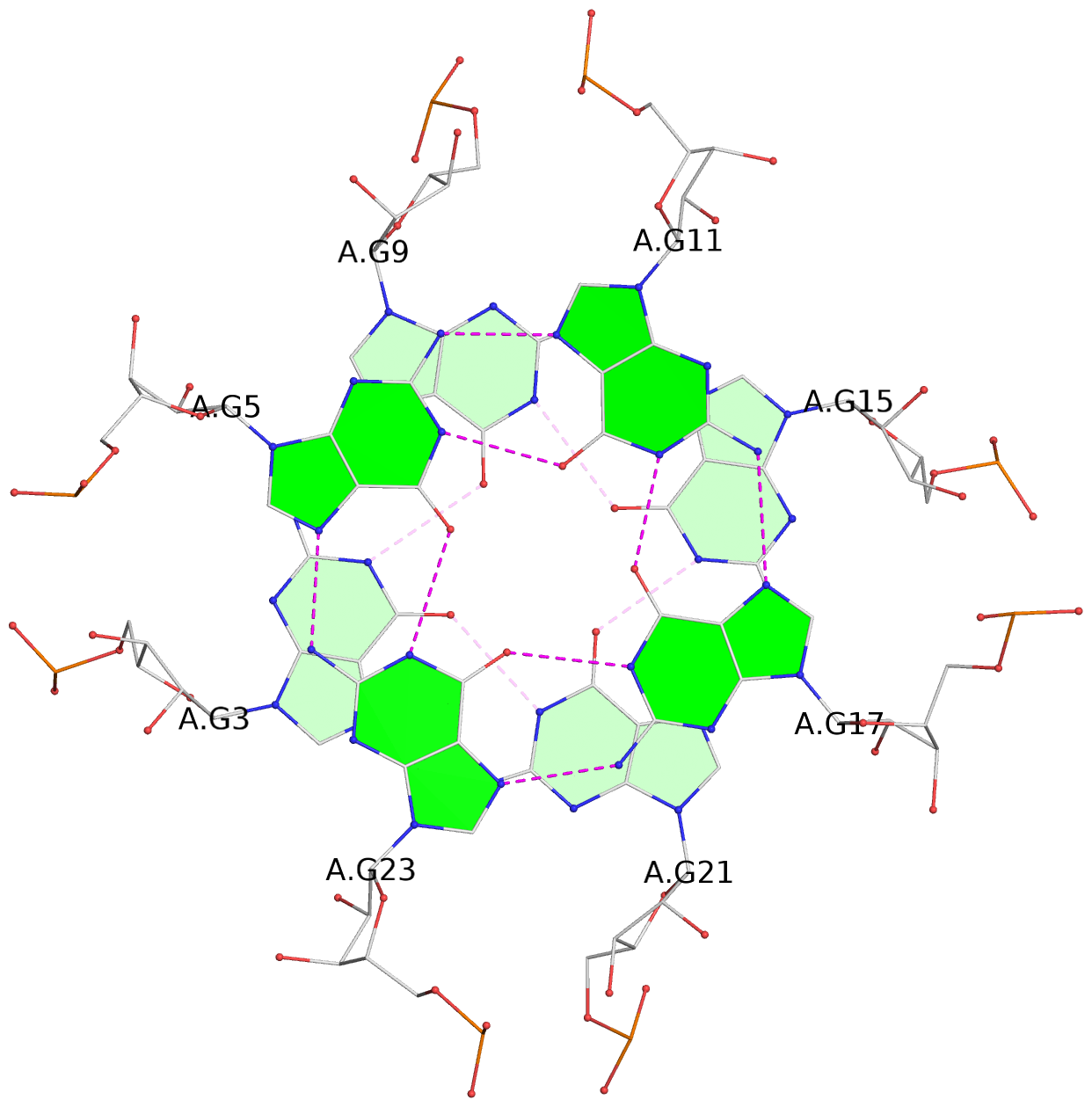
List of 3 G-tetrads
1 glyco-bond=ssss sugar=---- groove=---- planarity=0.069 type=planar nts=4 GGGG A.G1,A.G7,A.G13,A.G19 2 glyco-bond=ssss sugar=3333 groove=---- planarity=0.102 type=planar nts=4 GGGG A.G3,A.G21,A.G15,A.G9 3 glyco-bond=---- sugar=---- groove=---- planarity=0.197 type=other nts=4 GGGG A.G5,A.G11,A.G17,A.G23
List of 1 G4-helix
In DSSR, a G4-helix is defined by stacking interactions of G-tetrads, regardless of backbone connectivity, and may contain more than one G4-stem.