Detailed DSSR results for the G-quadruplex: PDB entry 7wgw
Created and maintained by Xiang-Jun Lu <xiangjun@x3dna.org>
Citation: Please cite the NAR'20 DSSR-PyMOL schematics paper and/or the NAR'15 DSSR method paper.
Summary information
- PDB id
- 7wgw
- Class
- DNA
- Method
- NMR
- Summary
- NMR solution structure of a cgmp fill-in vacancy g-quadruplex formed in the oxidized blm gene promoter
- Reference
- Wang KB, Liu Y, Li Y, Dickerhoff J, Li J, Yang MH, Yang D, Kong LY (2022): "Oxidative Damage Induces a Vacancy G-Quadruplex That Binds Guanine Metabolites: Solution Structure of a cGMP Fill-in Vacancy G-Quadruplex in the Oxidized BLM Gene Promoter." J.Am.Chem.Soc., 144, 6361-6372. doi: 10.1021/jacs.2c00435.
- Abstract
- Guanine (G)-oxidation to 8-oxo-7,8-dihydroguanine (OG) by reactive oxygen species in genomic DNA has been implicated with various human diseases. G-quadruplex (G4)-forming sequences in gene promoters are highly susceptible to G-oxidation, which can subsequently cause gene activation. However, the underlying G4 structural changes that result from OG modifications remain poorly understood. Herein, we investigate the effect of G-oxidation on the BLM gene promoter G4. For the first time, we show that OG can induce a G-vacancy-containing G4 (vG4), which can be filled in and stabilized by guanine metabolites and derivatives. We determined the NMR solution structure of the cGMP-fill-in oxidized BLM promoter vG4. This is the first complex structure of an OG-induced vG4 from a human gene promoter sequence with a filled-in guanine metabolite. The high-resolution structure elucidates the structural features of the specific 5'-end cGMP-fill-in for the OG-induced vG4. Interestingly, the OG is removed from the G-core and becomes part of the 3'-end capping structure. A series of guanine metabolites and derivatives are evaluated for fill-in activity to the oxidation-induced vG4. Significantly, cellular guanine metabolites, such as cGMP and GTP, can bind and stabilize the OG-induced vG4, suggesting their potential regulatory role in response to oxidative damage in physiological and pathological processes. Our work thus provides exciting insights into how oxidative damage and cellular metabolites may work together through a G4-based epigenetic feature for gene regulation. Furthermore, the NMR structure can guide the rational design of small-molecule inhibitors that specifically target the oxidation-induced vG4s.
- G4 notes
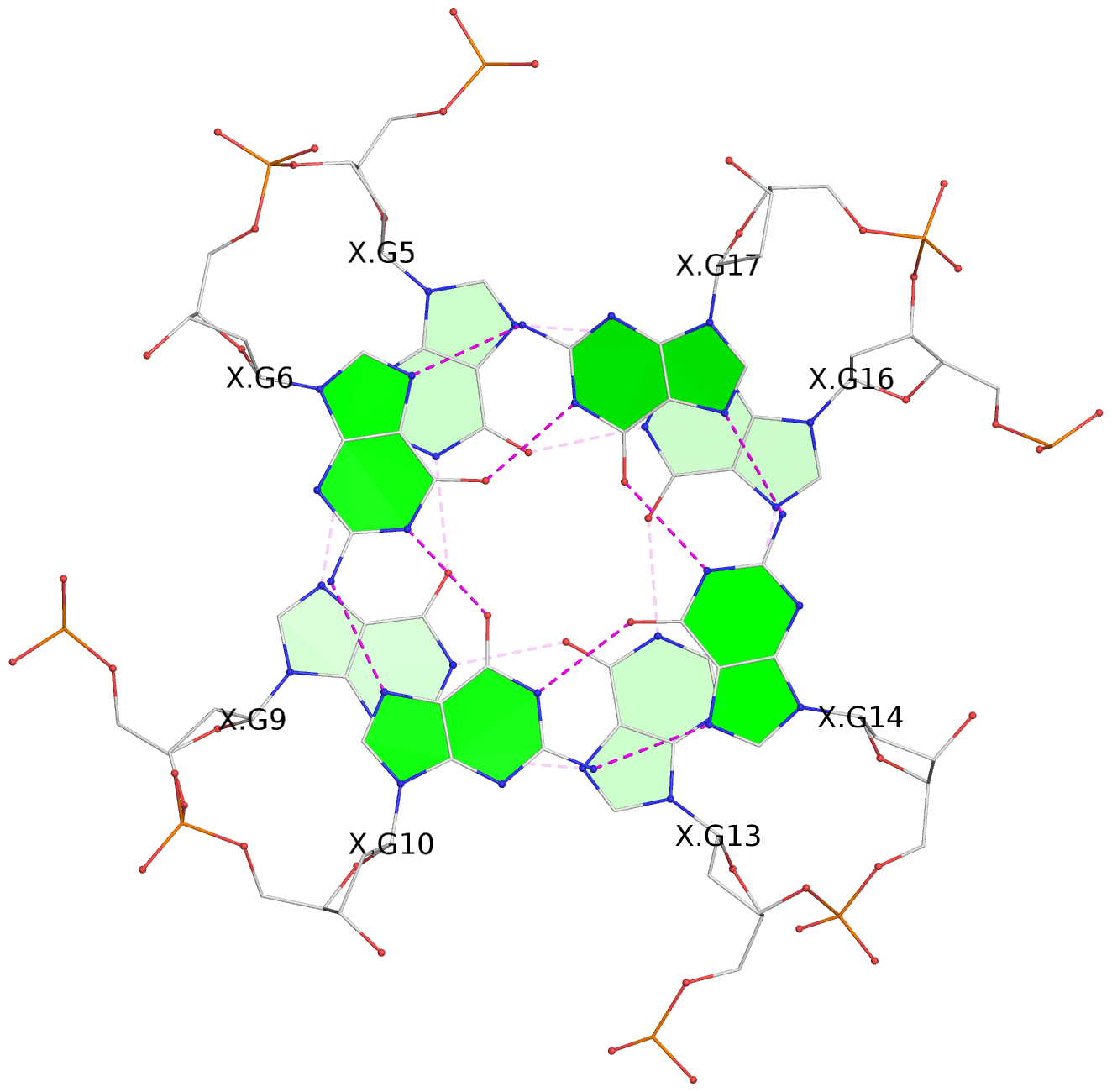
- 3 G-tetrads, 1 G4 helix, 1 G4 stem, 2(-P-P-P), parallel(4+0), UUUU
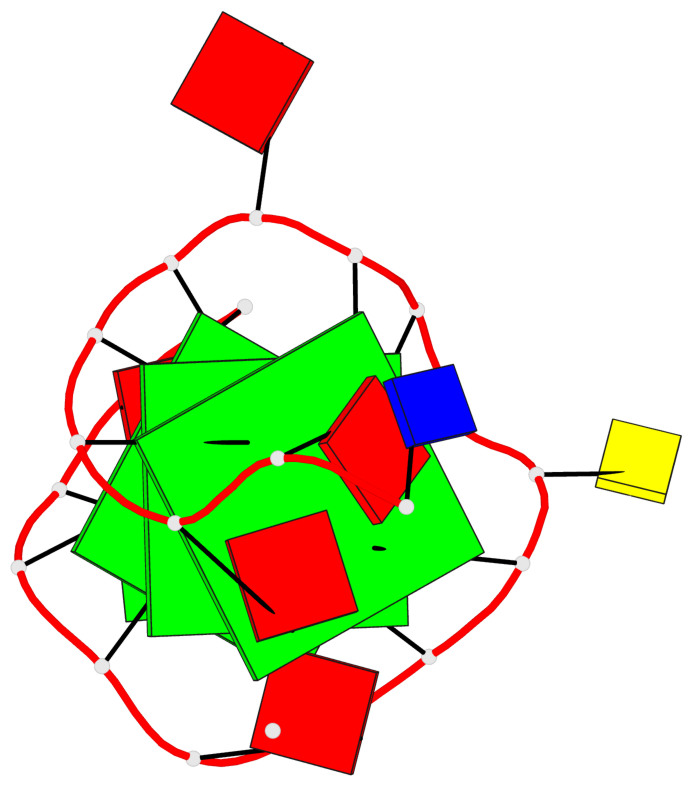
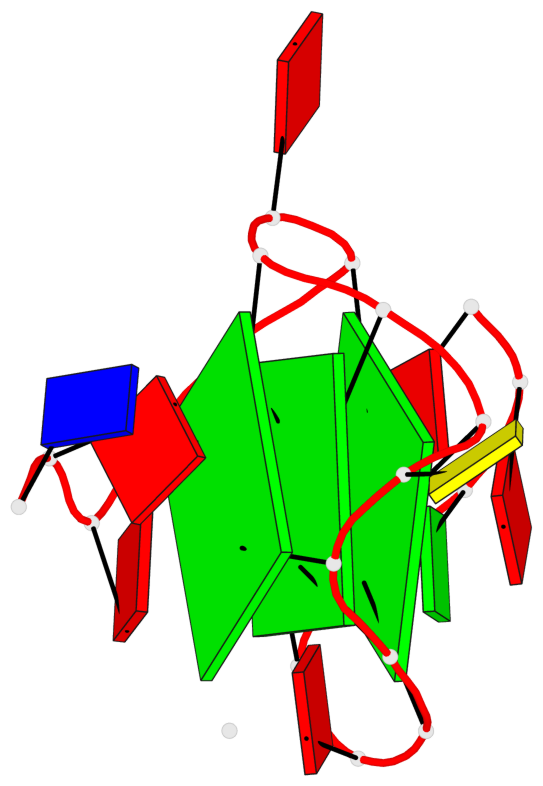
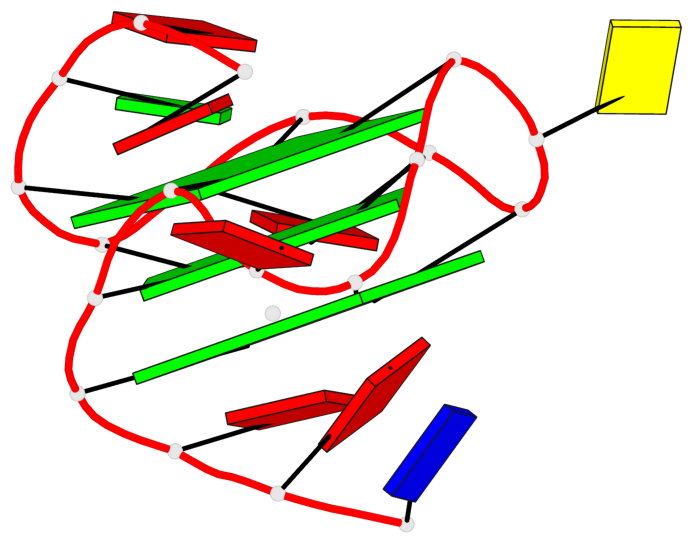
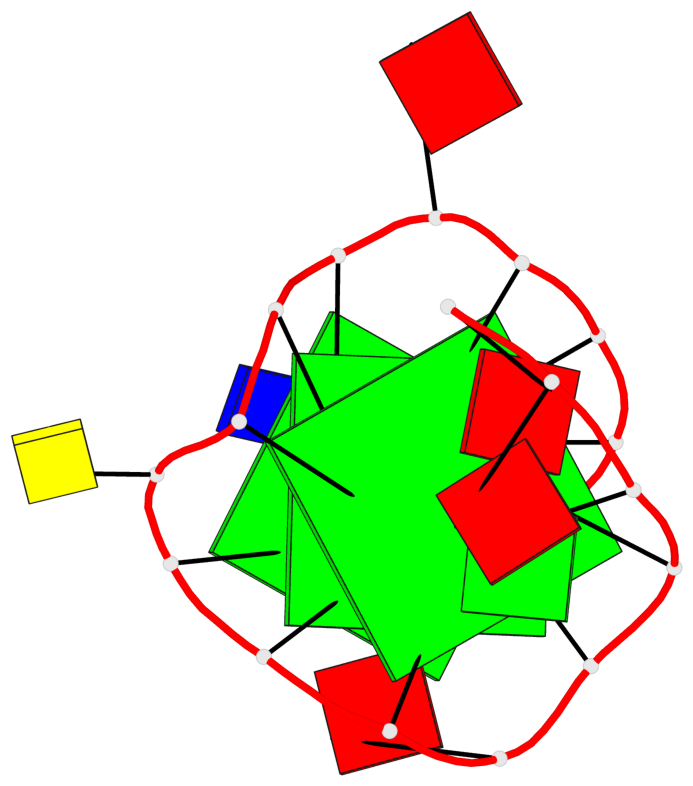
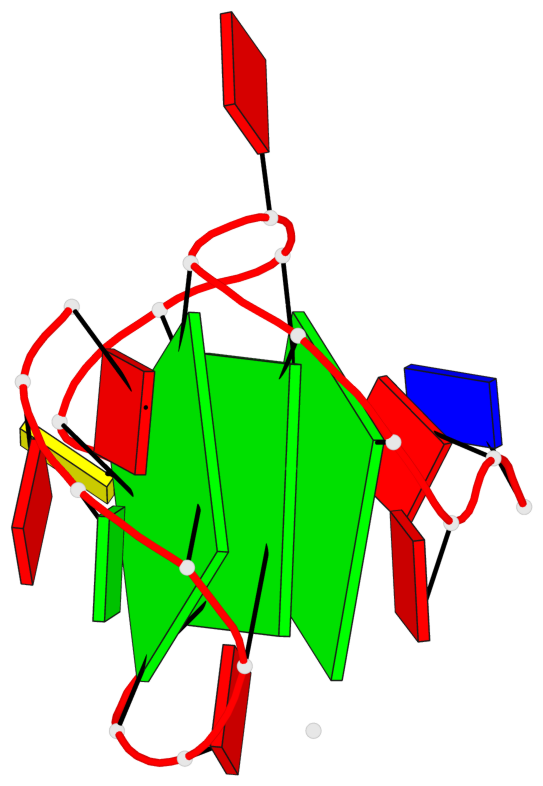
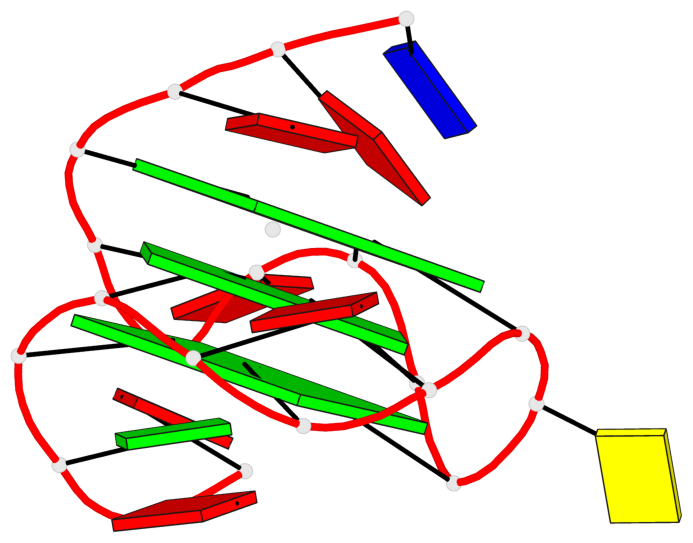
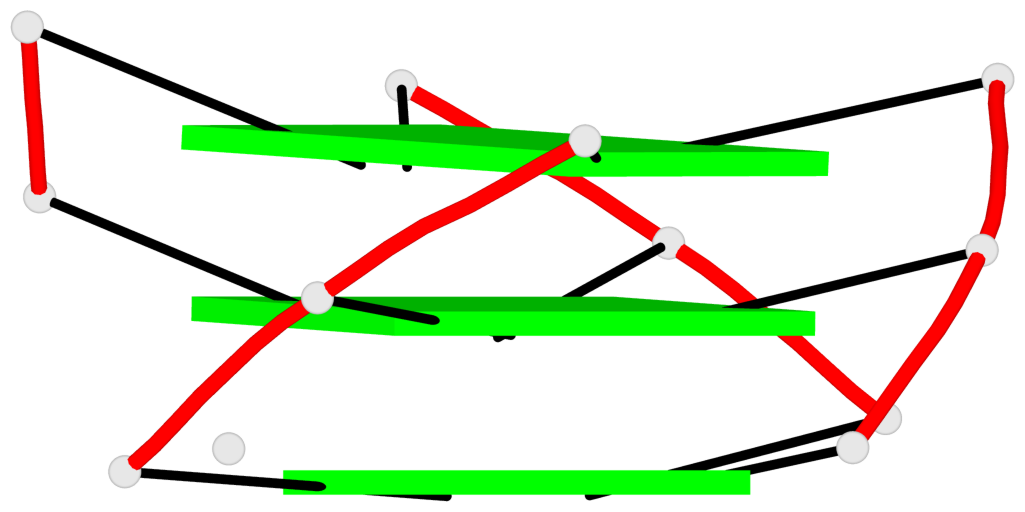
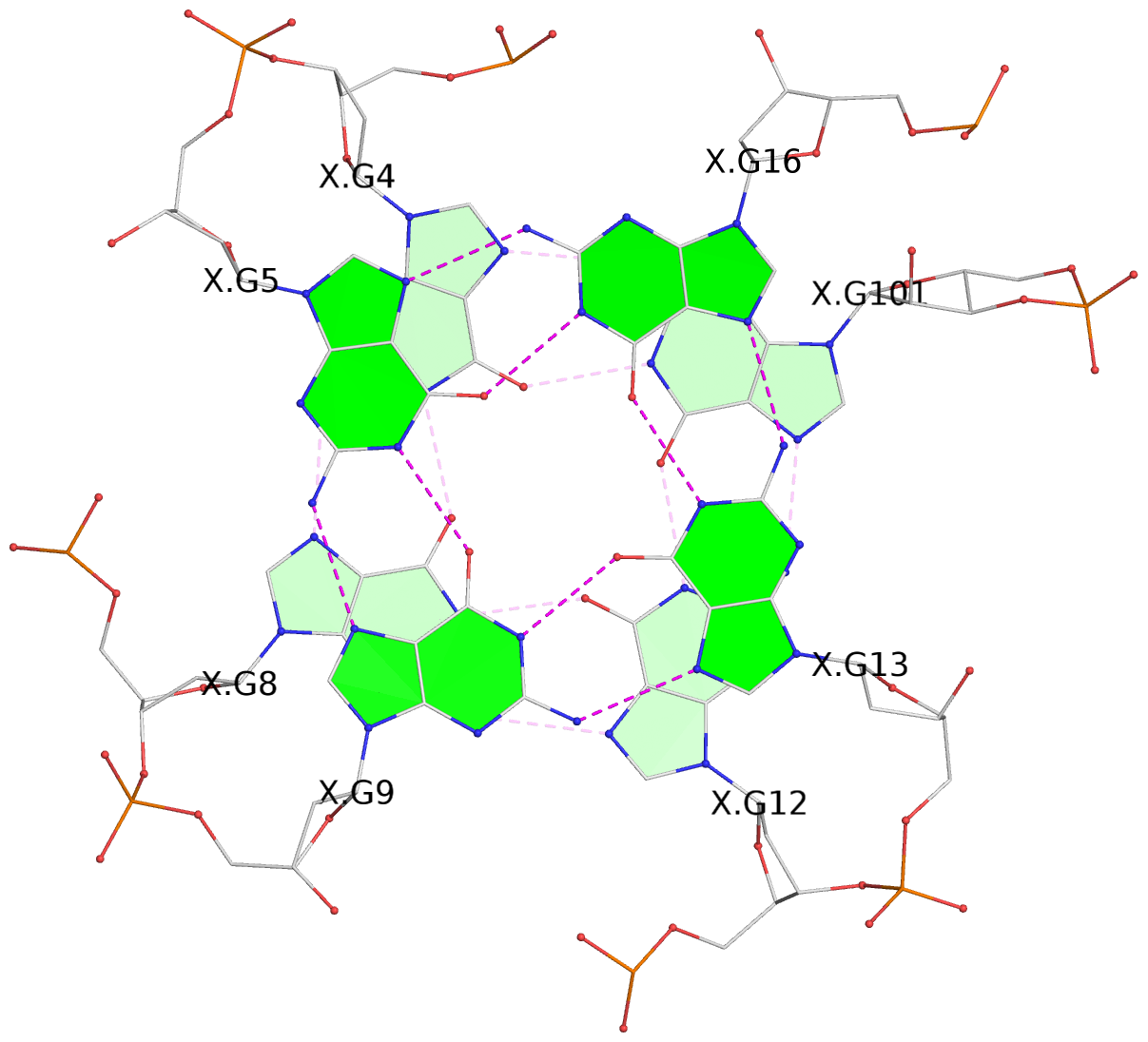
Base-block schematics in six views
List of 3 G-tetrads
1 glyco-bond=---- sugar=---3 groove=---- planarity=0.265 type=saddle nts=4 GGGg X.DG4,X.DG8,X.DG12,X.PCG101 2 glyco-bond=---- sugar=---- groove=---- planarity=0.298 type=bowl nts=4 GGGG X.DG5,X.DG9,X.DG13,X.DG16 3 glyco-bond=---- sugar=---- groove=---- planarity=0.419 type=bowl nts=4 GGGG X.DG6,X.DG10,X.DG14,X.DG17
List of 1 G4-helix
In DSSR, a G4-helix is defined by stacking interactions of G-tetrads, regardless of backbone connectivity, and may contain more than one G4-stem.
Helix#1, 3 G-tetrad layers, INTRA-molecular, with 1 stem
List of 1 G4-stem
In DSSR, a G4-stem is defined as a G4-helix with backbone connectivity. Bulges are also allowed along each of the four strands.