Detailed DSSR results for the G-quadruplex: PDB entry 1c34
Created and maintained by Xiang-Jun Lu <xiangjun@x3dna.org>
Citation: Please cite the NAR'20 DSSR-PyMOL schematics paper and/or the NAR'15 DSSR method paper.
Summary information
- PDB id
- 1c34
- Class
- DNA
- Method
- NMR
- Summary
- Solution structure of a quadruplex forming DNA and its intermidiate
- Reference
- Marathias VM, Bolton PH (2000): "Structures of the potassium-saturated, 2:1, and intermediate, 1:1, forms of a quadruplex DNA." Nucleic Acids Res., 28, 1969-1977. doi: 10.1093/nar/28.9.1969.
- Abstract
- Potassium can stabilize the formation of chair- or edge-type quadruplex DNA structures and appears to be the only naturally occurring cation that can do so. As quadruplex DNAs may be important in the structure of telomere, centromere, triplet repeat and other DNAs, information about the details of the potassium-quadruplex DNA interactions are of interest. The structures of the 1:1 and the fully saturated, 2:1, potassium-DNA complexes of d(GGTTGGTGTGGTTGG) have been determined using the combination of experimental NMR results and restrained molecular dynamics simulations. The refined structures have been used to model the interactions at the potassium binding sites. Comparison of the 1:1 and 2:1 potassium:DNA structures indicates how potassium binding can determine the folding pattern of the DNA. In each binding site potassium interacts with the carbonyl oxygens of both the loop thymine residues and the guanine residues of the adjacent quartet.
- G4 notes
- 2 G-tetrads, 1 G4 helix, 1 G4 stem, 2(+Ln+Lw+Lx), (2+2), UDUD
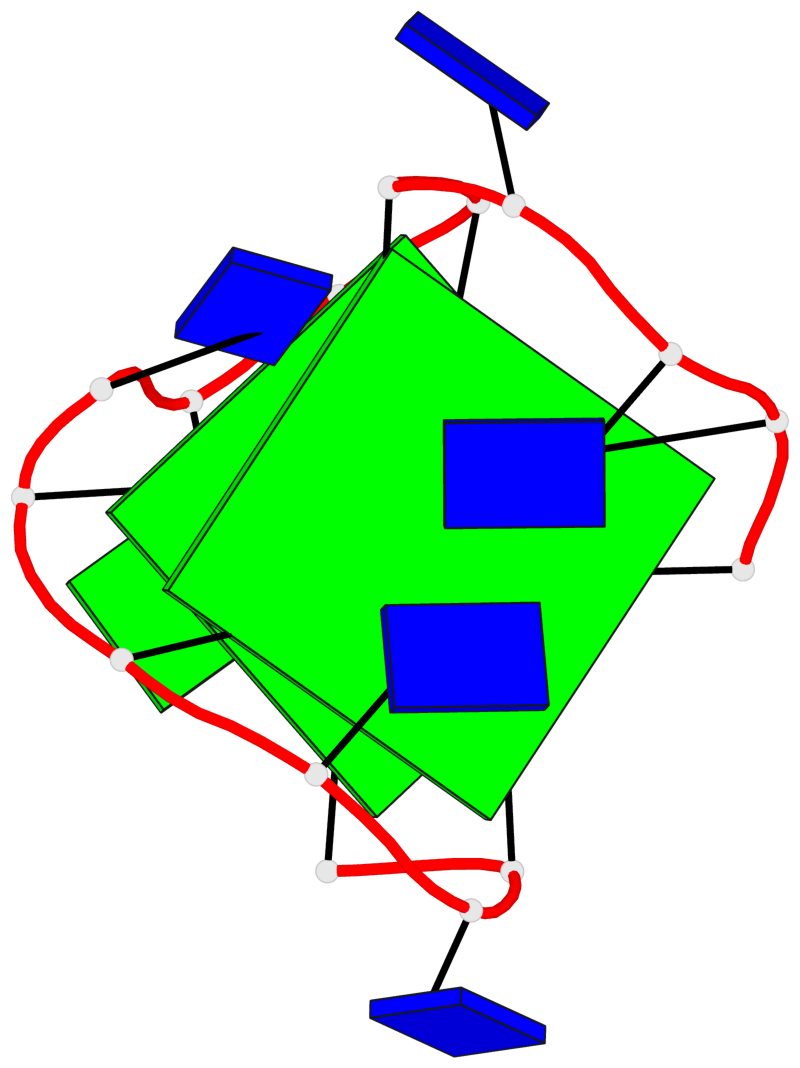
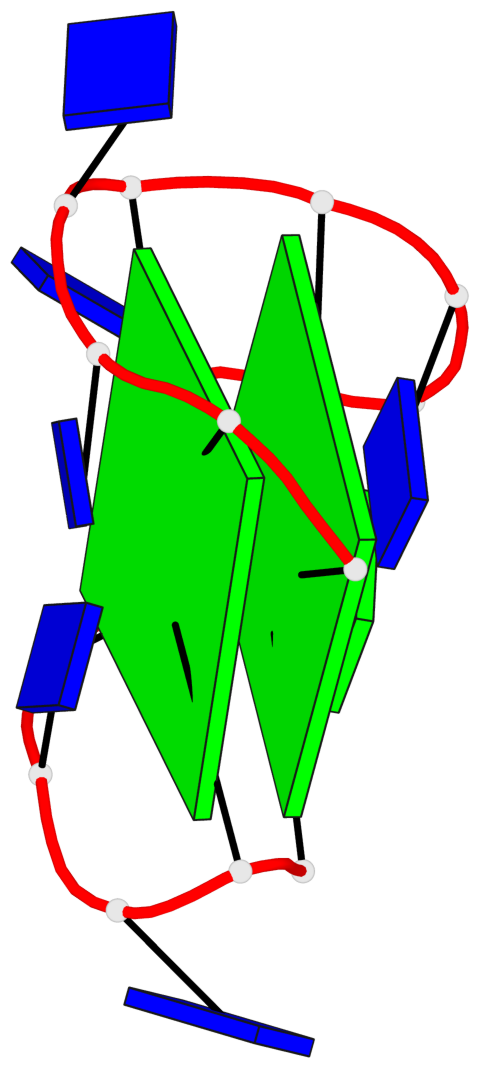
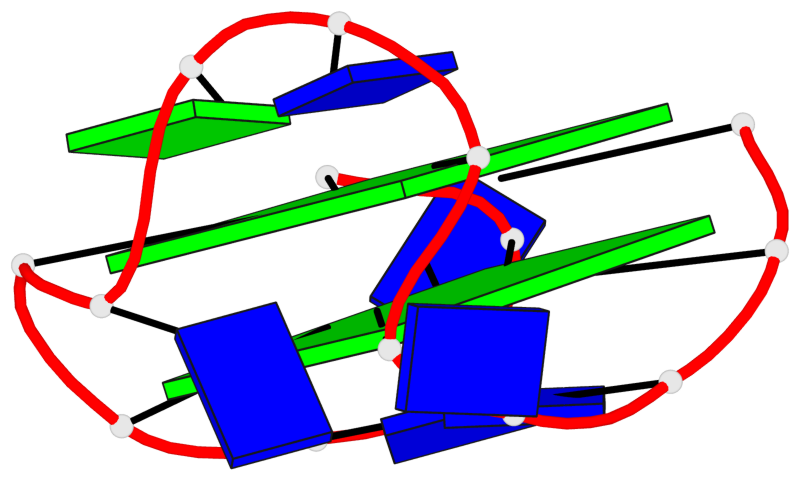
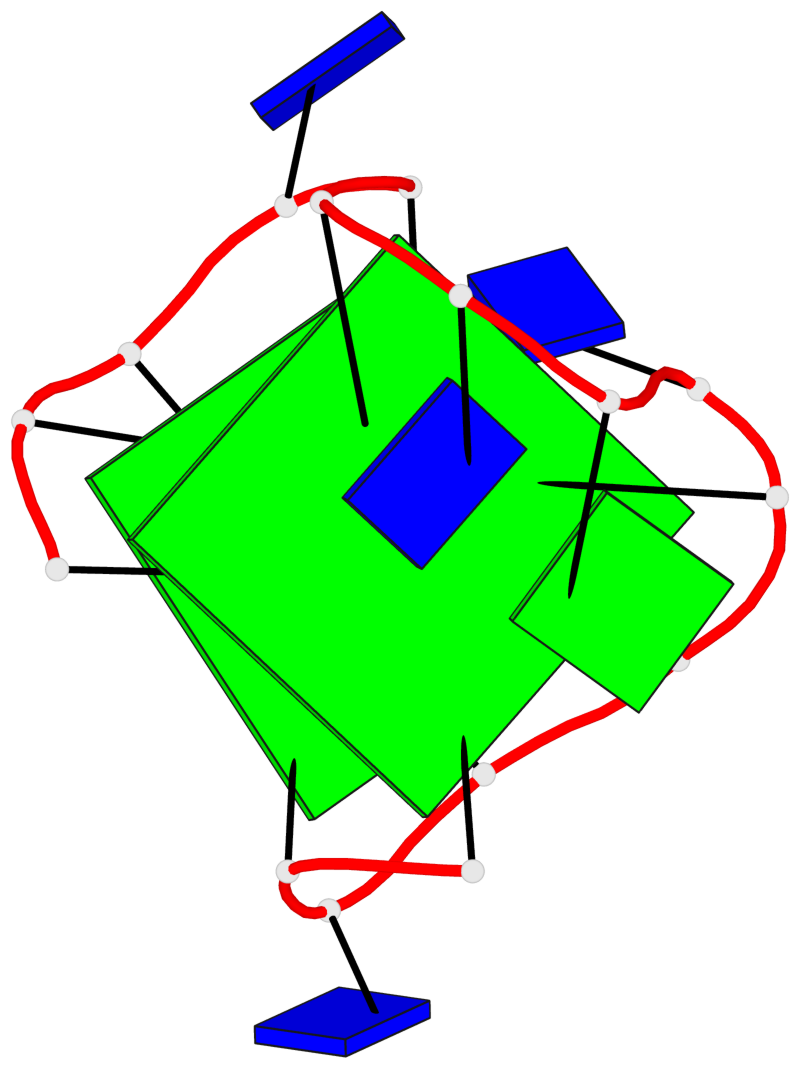
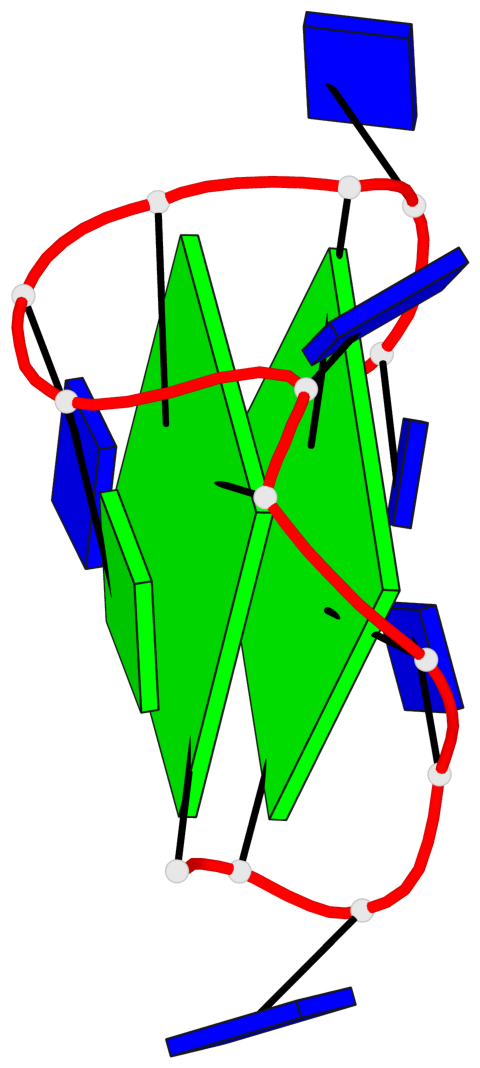
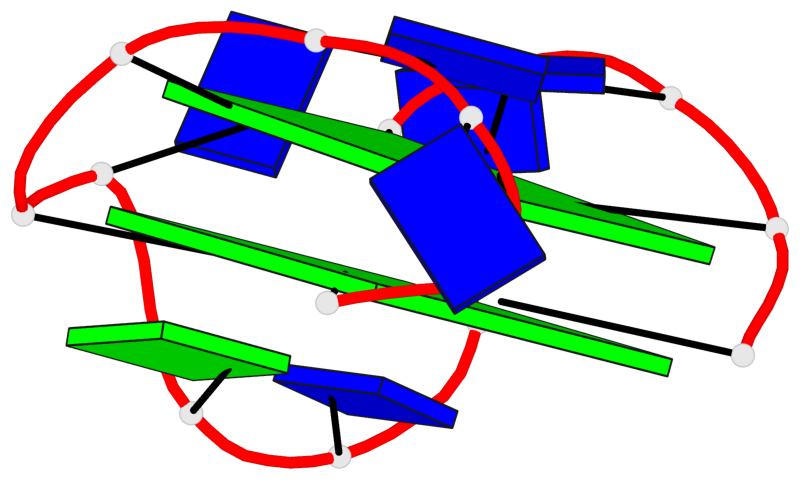
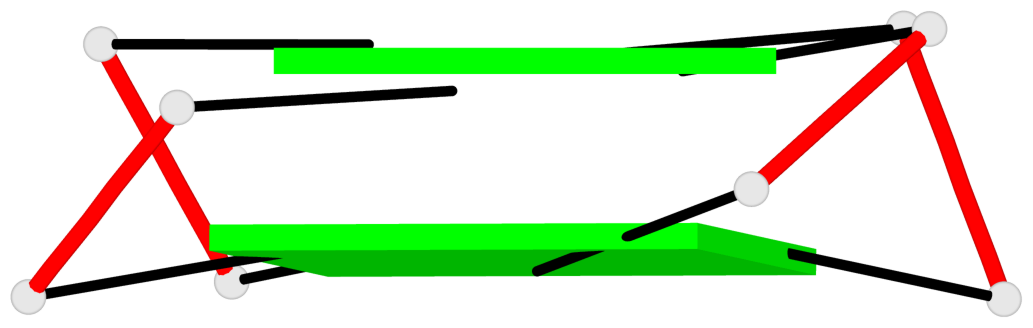
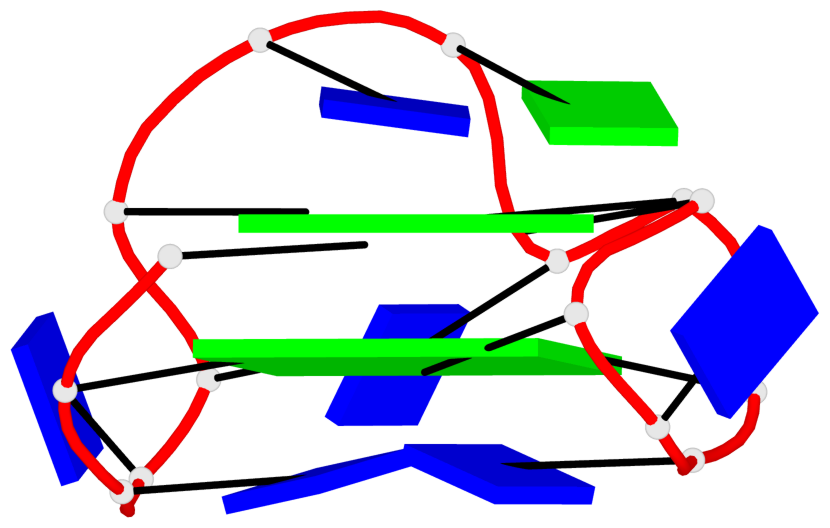
Base-block schematics in six views
List of 2 G-tetrads
1 glyco-bond=s-s- sugar=---- groove=wnwn planarity=0.491 type=other nts=4 GGGG A.DG1,A.DG15,A.DG10,A.DG6 2 glyco-bond=---s sugar=---- groove=--wn planarity=0.613 type=other nts=4 GGGG A.DG2,A.DG14,A.DG11,A.DG5
List of 1 G4-helix
In DSSR, a G4-helix is defined by stacking interactions of G-tetrads, regardless of backbone connectivity, and may contain more than one G4-stem.
Helix#1, 2 G-tetrad layers, INTRA-molecular, with 1 stem
List of 1 G4-stem
In DSSR, a G4-stem is defined as a G4-helix with backbone connectivity. Bulges are also allowed along each of the four strands.