Detailed DSSR results for the G-quadruplex: PDB entry 1xav
Created and maintained by Xiang-Jun Lu <xiangjun@x3dna.org>
Citation: Please cite the NAR'20 DSSR-PyMOL schematics paper and/or the NAR'15 DSSR method paper.
Summary information
- PDB id
- 1xav
- Class
- DNA
- Method
- NMR
- Summary
- Major g-quadruplex structure formed in human c-myc promoter, a monomeric parallel-stranded quadruplex
- Reference
- Ambrus A, Chen D, Dai J, Jones RA, Yang D (2005): "Solution structure of the biologically relevant G-Quadruplex element in the human c-MYC promoter. Implications for G-quadruplex stabilization." Biochemistry, 44, 2048-2058. doi: 10.1021/bi048242p.
- Abstract
- The nuclease hypersensitivity element III(1) (NHE III(1)) of the c-MYC promoter strongly controls the transcriptional activity of the c-MYC oncogene. The purine-rich strand of the NHE III(1) element has been shown to be a silencer element for c-MYC transcription upon formation of a G-quadruplex structure. We have determined the predominant G-quadruplex structure of this silencer element in potassium solution by NMR. The G-quadruplex structure adopts an intramolecular parallel-stranded quadruplex conformation with three guanine tetrads and three side loops, including two single-nucleotide side loops and one double-nucleotide side loop, that connect the four guanine strands. The three side loops are very stable and well-defined. The 3'-flanking sequence forms a stable fold-back stacking conformation capping the top end of the G-quadruplex structure. The 5'-flanking A and G bases cap the bottom end of the G-quadruplex, with the adenine stacking very well with the bottom tetrad. This paper reports the first solution structure of a G-quadruplex found to form in the promoter region of an oncogene (c-MYC). This G-quadruplex structure is extremely stable, with a similar melting temperature (>85 degrees C) to that of the wild-type 27-mer purine-rich NHE III(1) sequence of the c-MYC promoter. This predominant quadruplex structure has been shown to be biologically relevant, and the structural information revealed in this research provides an important basis for the design of new drug candidates that specifically target the c-MYC G-quadruplex structure and modulate gene expression.
- G4 notes
- 3 G-tetrads, 1 G4 helix, 1 G4 stem, 3(-P-P-P), parallel(4+0), UUUU
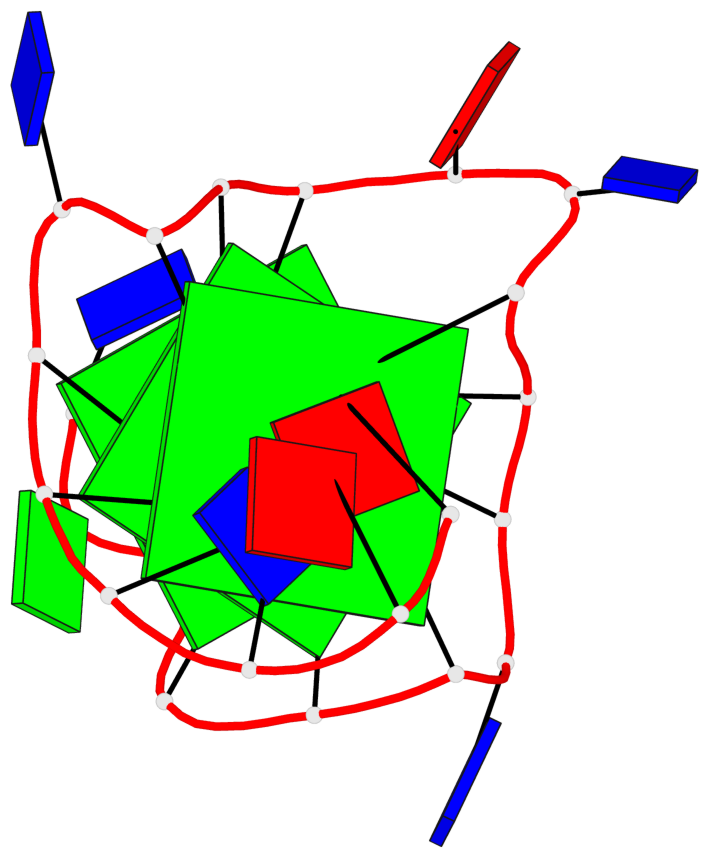
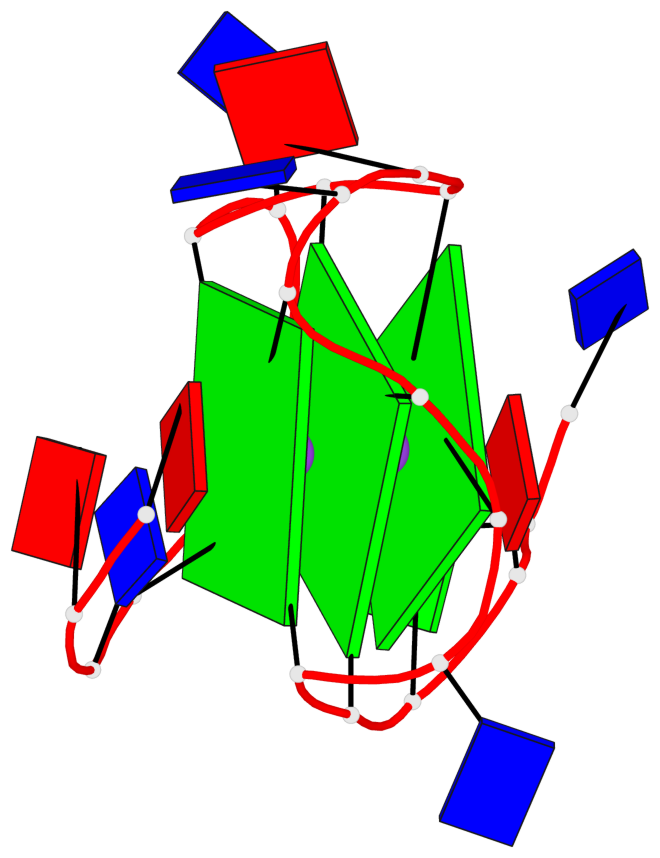
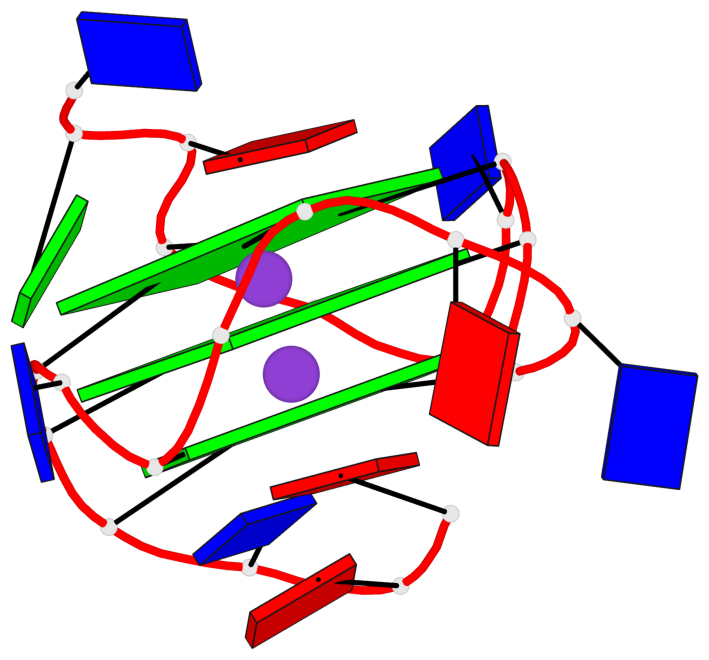
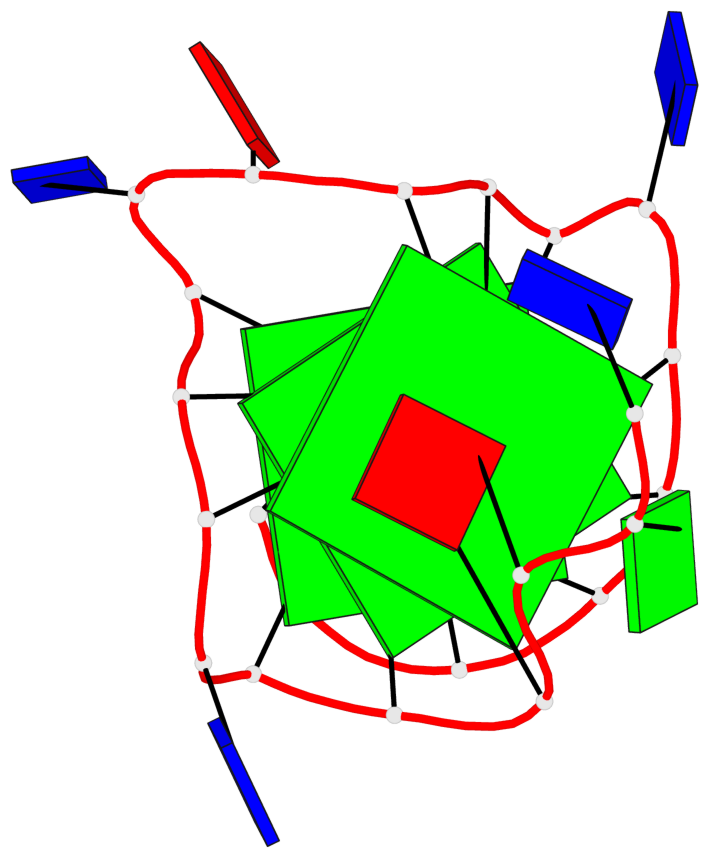
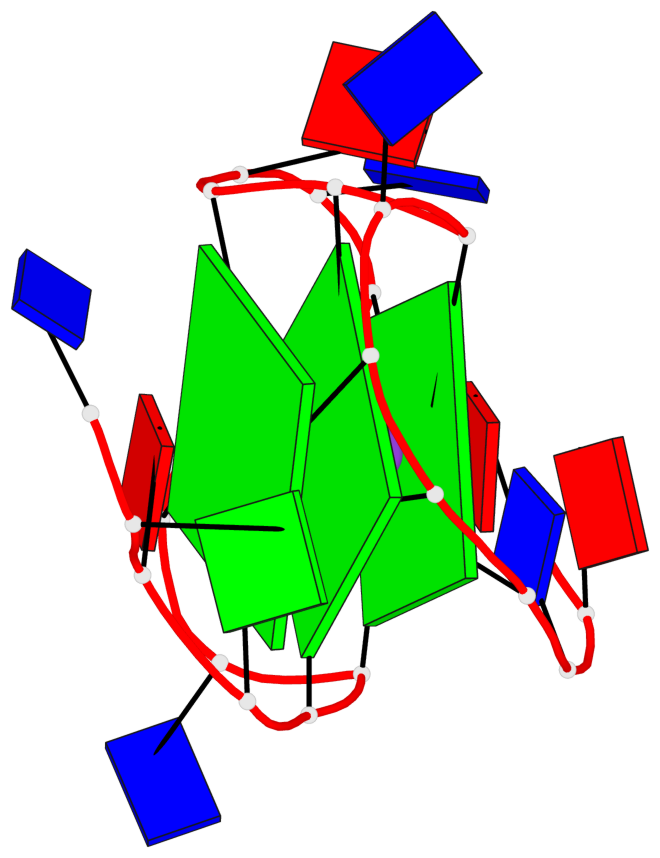
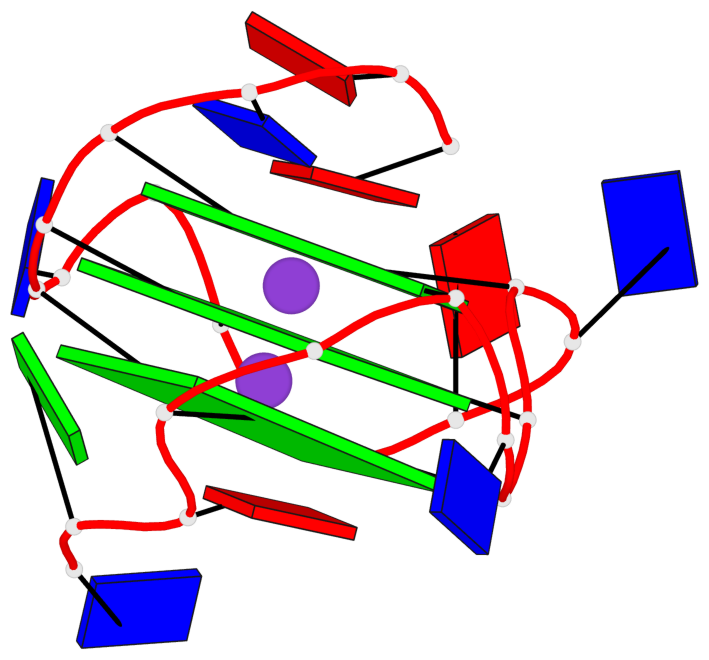
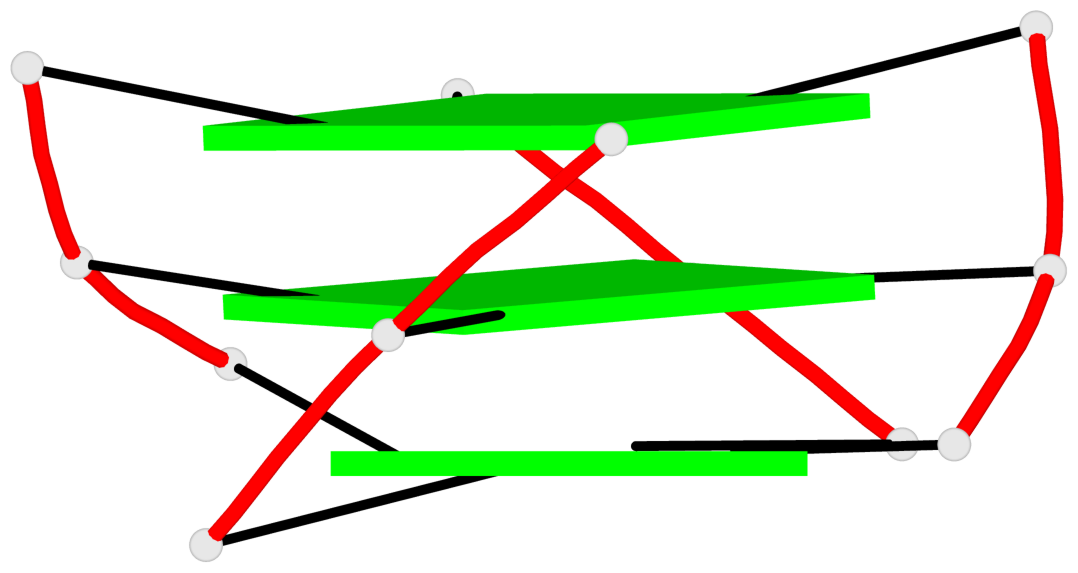
Base-block schematics in six views
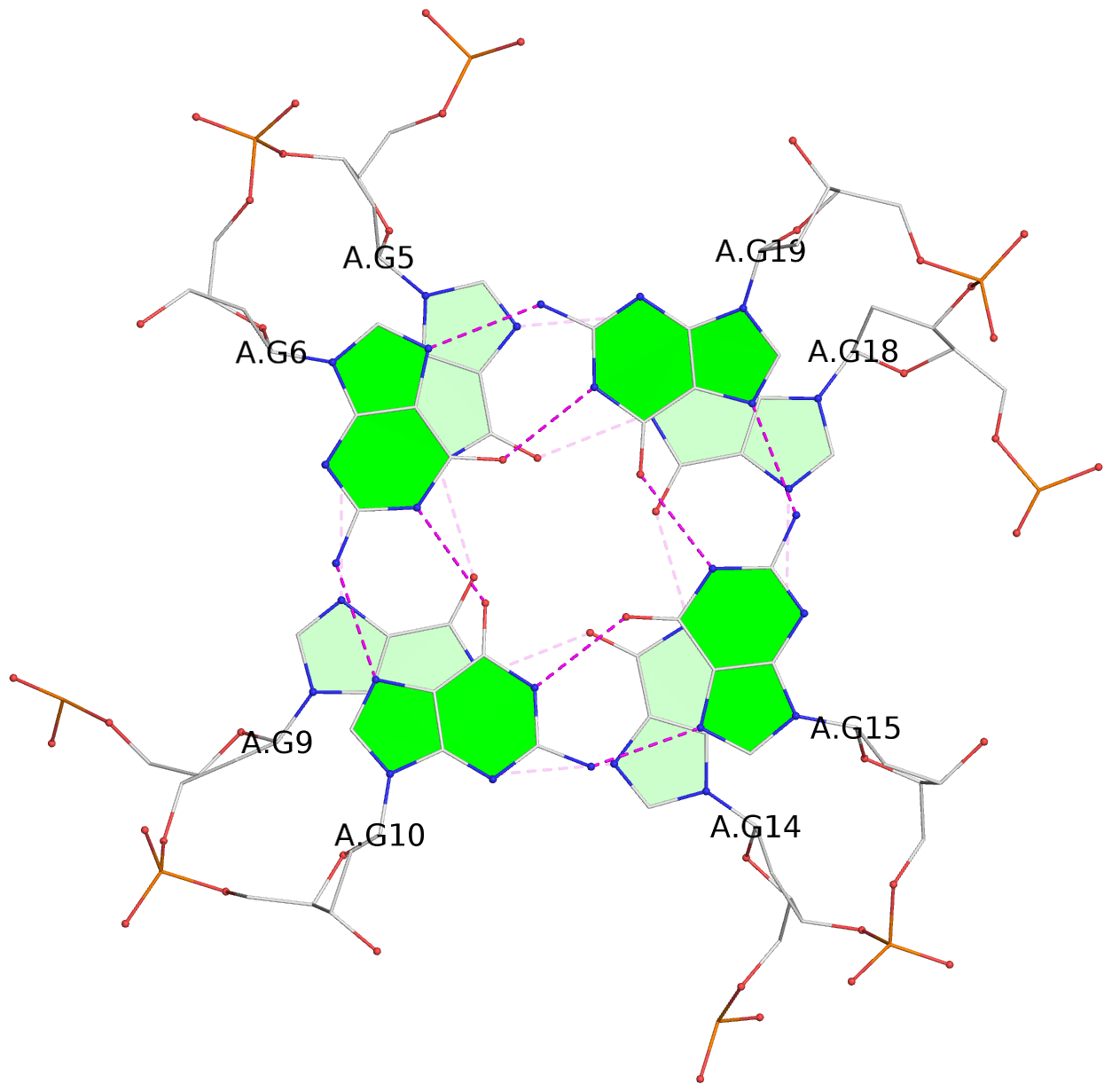
List of 3 G-tetrads
1 glyco-bond=---- sugar=---. groove=---- planarity=0.251 type=other nts=4 GGGG A.DG4,A.DG8,A.DG13,A.DG17 2 glyco-bond=---- sugar=-..3 groove=---- planarity=0.171 type=other nts=4 GGGG A.DG5,A.DG9,A.DG14,A.DG18 3 glyco-bond=---- sugar=---- groove=---- planarity=0.190 type=other nts=4 GGGG A.DG6,A.DG10,A.DG15,A.DG19
List of 1 G4-helix
In DSSR, a G4-helix is defined by stacking interactions of G-tetrads, regardless of backbone connectivity, and may contain more than one G4-stem.
Helix#1, 3 G-tetrad layers, INTRA-molecular, with 1 stem
List of 1 G4-stem
In DSSR, a G4-stem is defined as a G4-helix with backbone connectivity. Bulges are also allowed along each of the four strands.