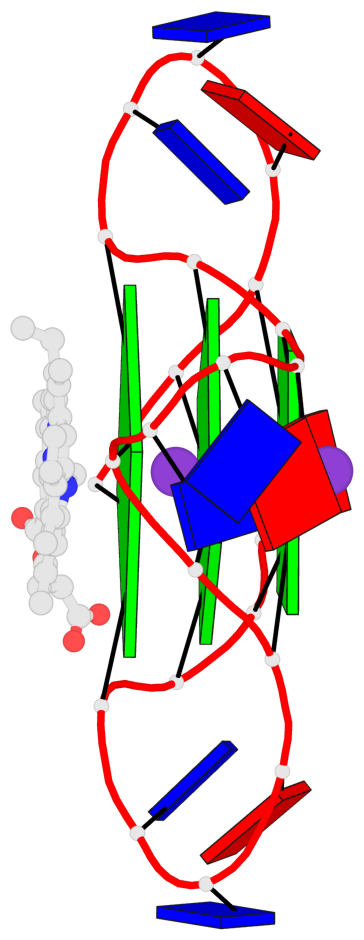
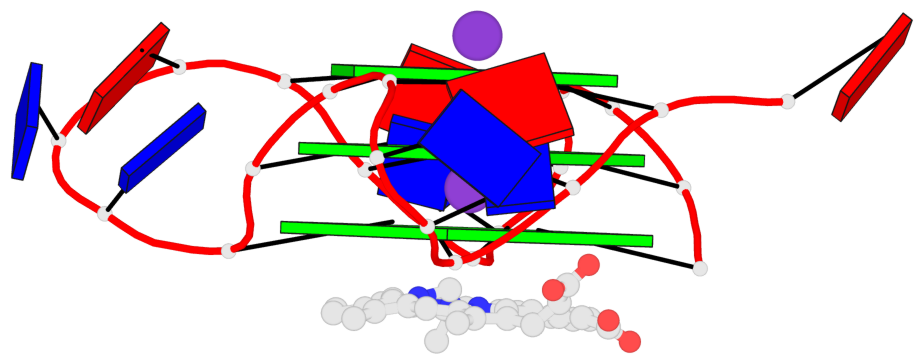
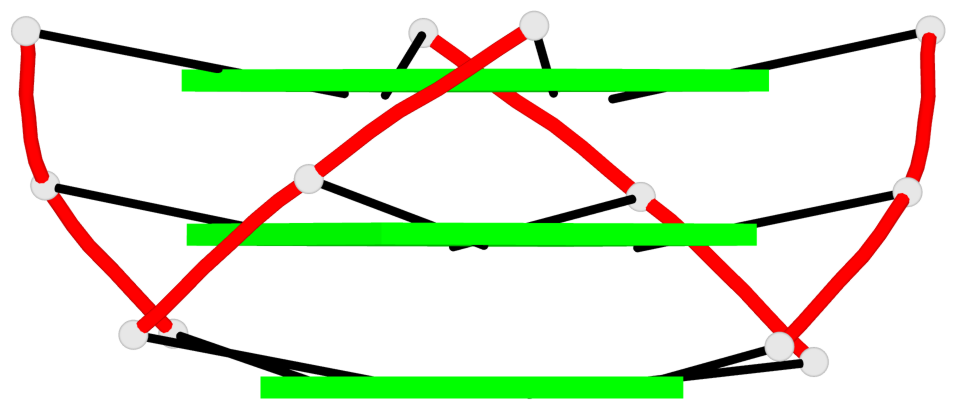
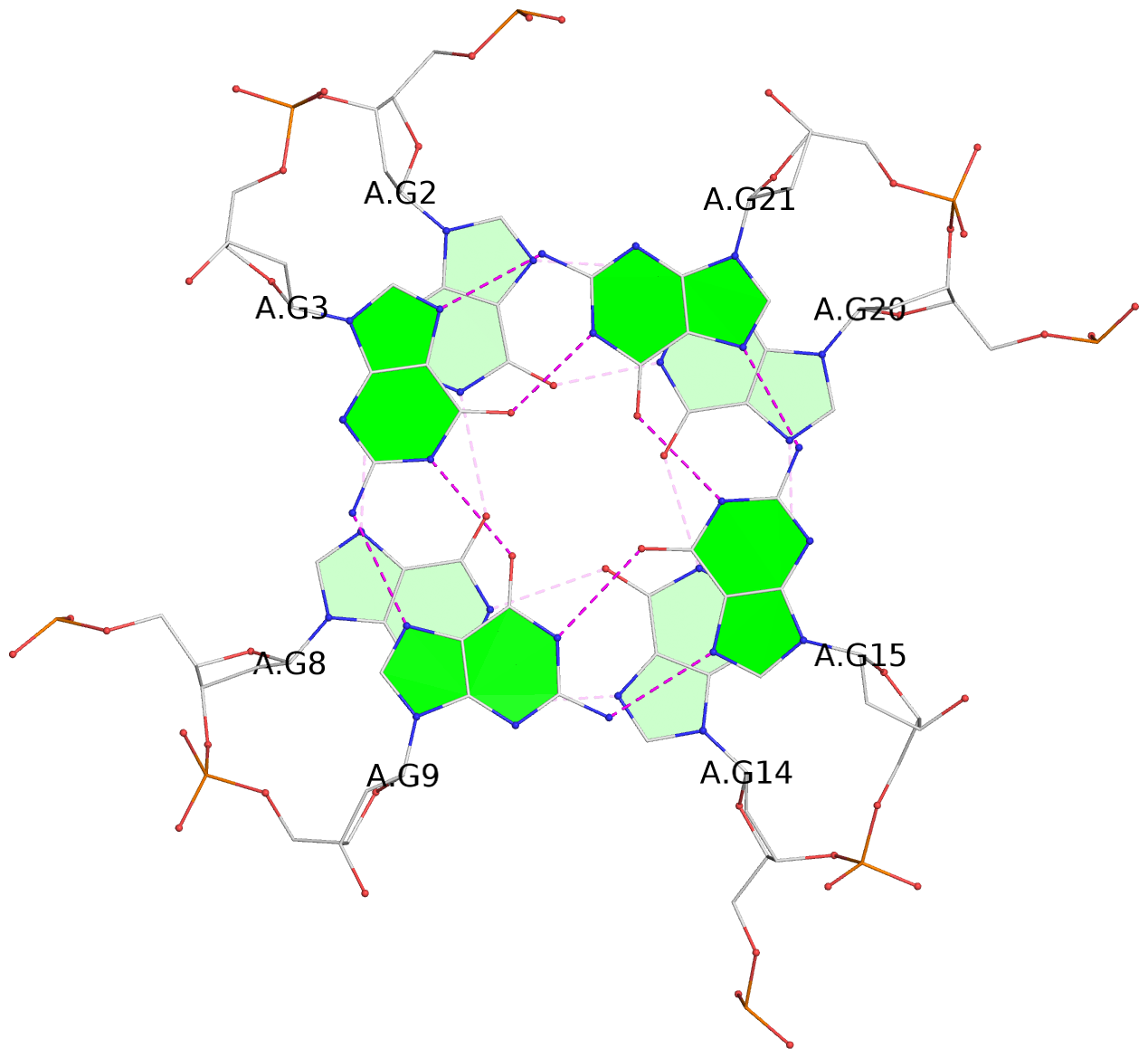
Detailed DSSR results for the G-quadruplex: PDB entry 4g0f
Created and maintained by Xiang-Jun Lu <xiangjun@x3dna.org>
Citation: Please cite the NAR'20 DSSR-PyMOL schematics paper and/or the NAR'15 DSSR method paper.
Summary information
- PDB id
- 4g0f
- Class
- DNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.15 Å)
- Summary
- Crystal structure of the complex of a human telomeric repeat g-quadruplex and n-methyl mesoporphyrin ix (p6)
- Reference
- Nicoludis JM, Miller ST, Jeffrey PD, Barrett SP, Rablen PR, Lawton TJ, Yatsunyk LA (2012): "Optimized End-Stacking Provides Specificity of N-Methyl Mesoporphyrin IX for Human Telomeric G-Quadruplex DNA." J.Am.Chem.Soc., 134, 20446-20456. doi: 10.1021/ja3088746.
- Abstract
- N-methyl mesoporphyrin IX (NMM) is exceptionally selective for G-quadruplexes (GQ) relative to duplex DNA and, as such, has found a wide range of applications in biology and chemistry. In addition, NMM is selective for parallel versus antiparallel GQ folds, as was recently demonstrated in our laboratory. Here, we present the X-ray crystal structure of a complex between NMM and human telomeric DNA dAGGG(TTAGGG)(3), Tel22, determined in two space groups, P2(1)2(1)2 and P6, at 1.65 and 2.15 Å resolution, respectively. The former is the highest resolution structure of the human telomeric GQ DNA reported to date. The biological unit contains a Tel22 dimer of 5'-5' stacked parallel-stranded quadruplexes capped on both ends with NMM, supporting the spectroscopically determined 1:1 stoichiometry. NMM is capable of adjusting its macrocycle geometry to closely match that of the terminal G-tetrad required for efficient π-π stacking. The out-of-plane N-methyl group of NMM fits perfectly into the center of the parallel GQ core where it aligns with potassium ions. In contrast, the interaction of the N-methyl group with duplex DNA or antiparallel GQ would lead to steric clashes that prevent NMM from binding to these structures, thus explaining its unique selectivity. On the basis of the biochemical data, binding of NMM to Tel22 does not rely on relatively nonspecific electrostatic interactions, which characterize most canonical GQ ligands, but rather it is hydrophobic in nature. The structural features observed in the NMM-Tel22 complex described here will serve as guidelines for developing new quadruplex ligands that have excellent affinity and precisely defined selectivity.
- G4 notes
- 3 G-tetrads, 1 G4 helix, 1 G4 stem, 3(-P-P-P), parallel(4+0), UUUU
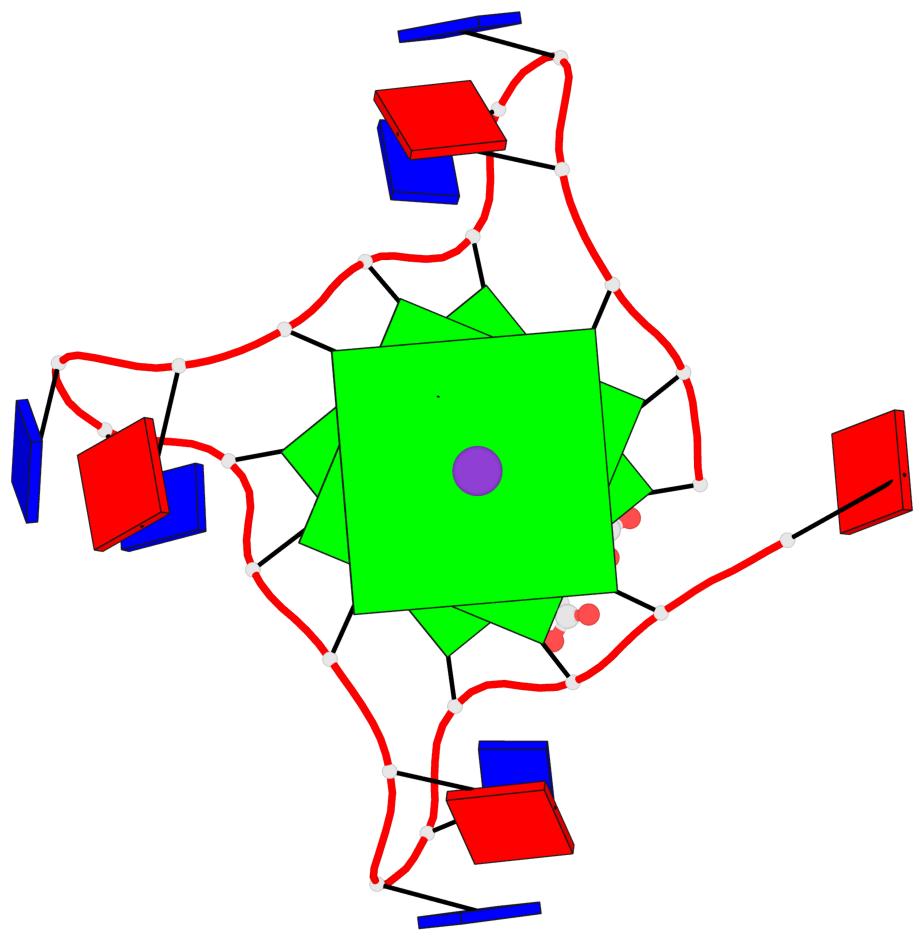
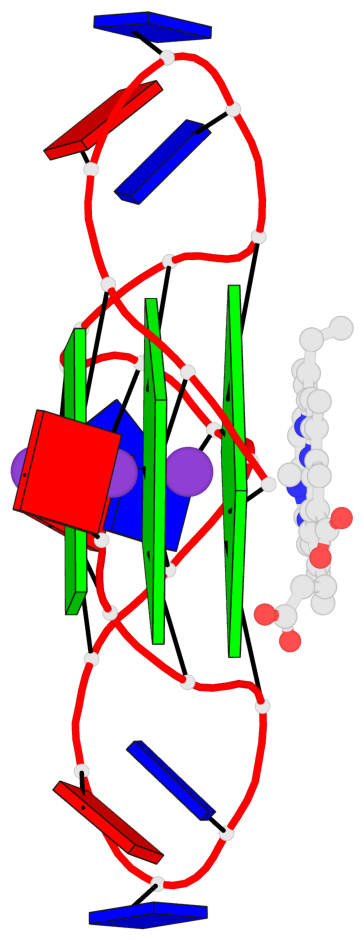
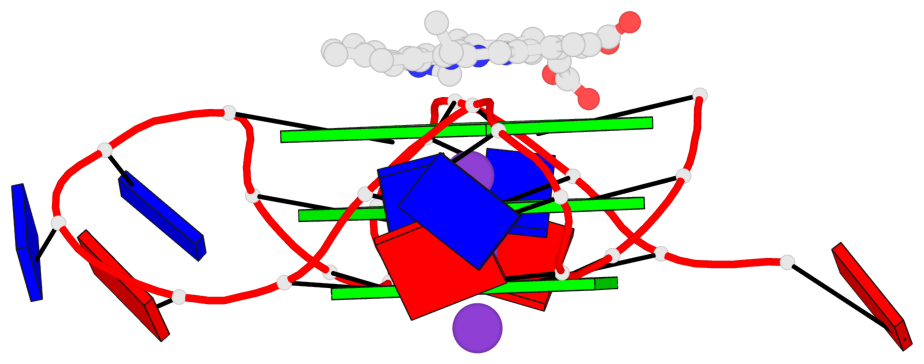
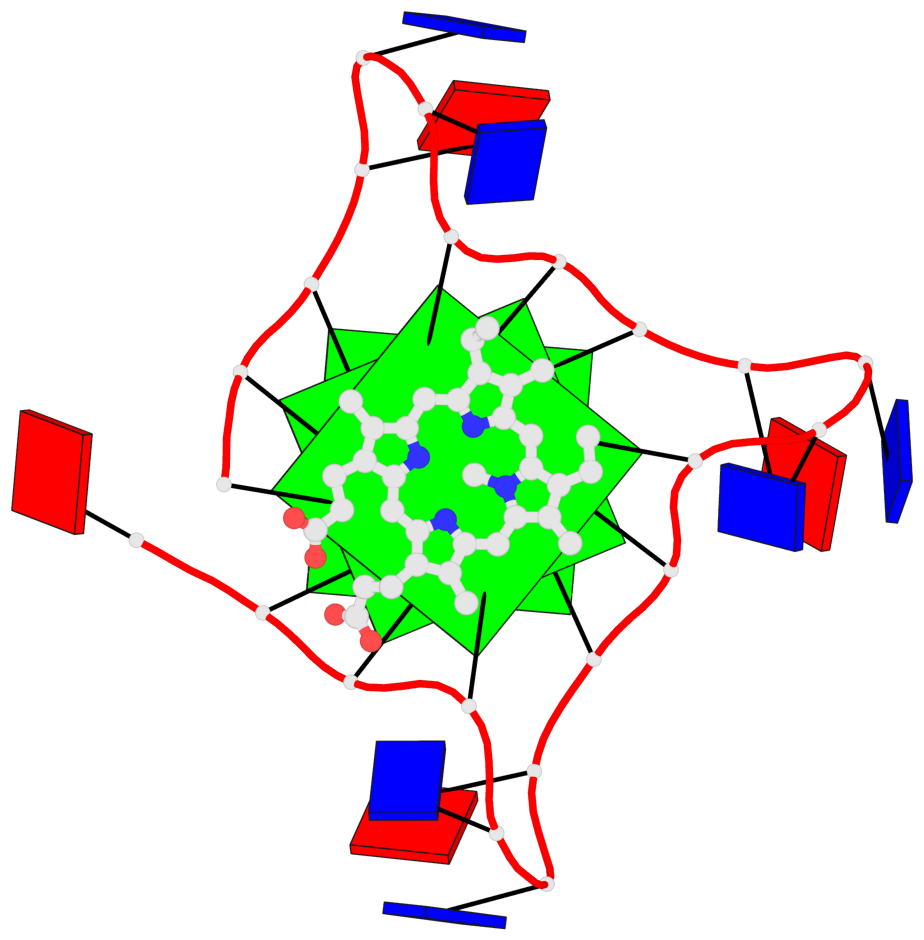
Base-block schematics in six views
List of 3 G-tetrads
1 glyco-bond=---- sugar=.--- groove=---- planarity=0.084 type=planar nts=4 GGGG A.DG2,A.DG8,A.DG14,A.DG20 2 glyco-bond=---- sugar=---- groove=---- planarity=0.212 type=bowl nts=4 GGGG A.DG3,A.DG9,A.DG15,A.DG21 3 glyco-bond=---- sugar=---- groove=---- planarity=0.305 type=bowl nts=4 GGGG A.DG4,A.DG10,A.DG16,A.DG22
List of 1 G4-helix
In DSSR, a G4-helix is defined by stacking interactions of G-tetrads, regardless of backbone connectivity, and may contain more than one G4-stem.
Helix#1, 3 G-tetrad layers, INTRA-molecular, with 1 stem
List of 1 G4-stem
In DSSR, a G4-stem is defined as a G4-helix with backbone connectivity. Bulges are also allowed along each of the four strands.