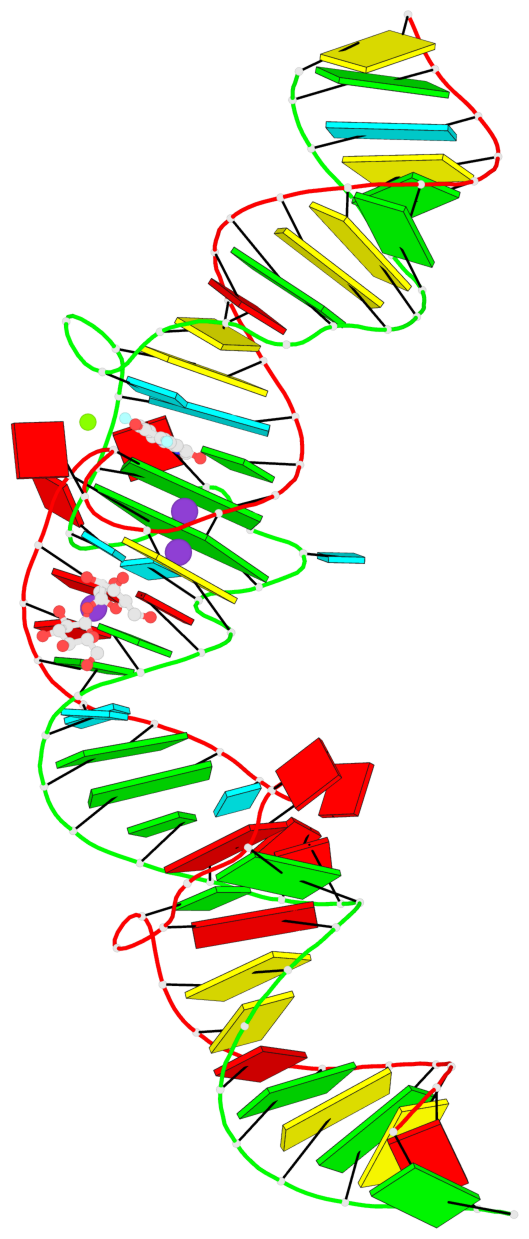
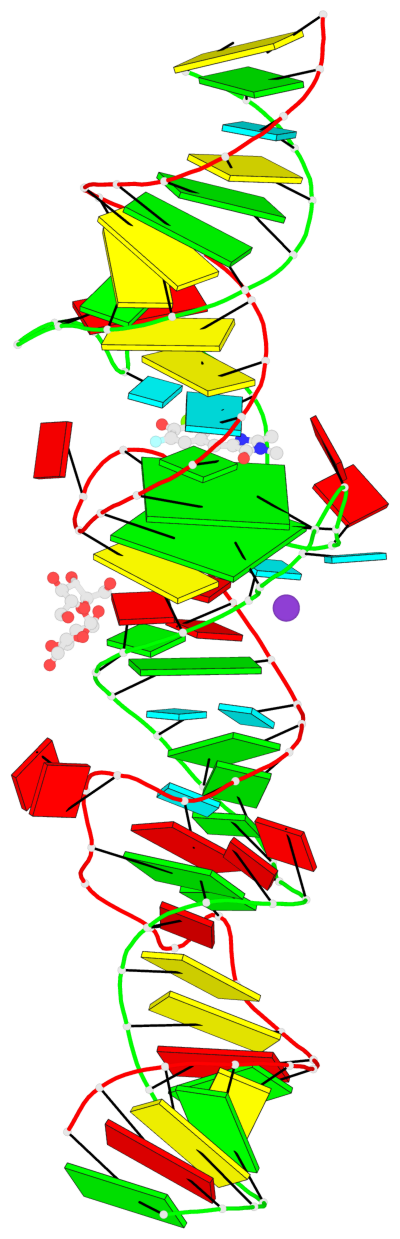
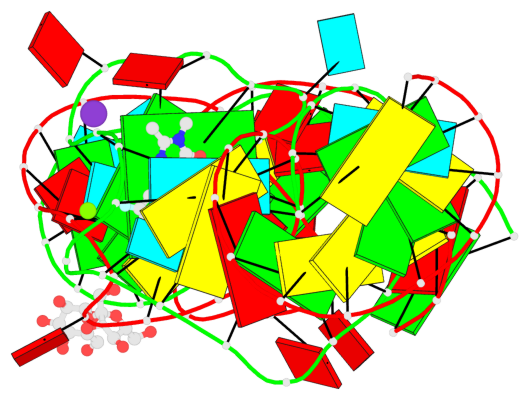
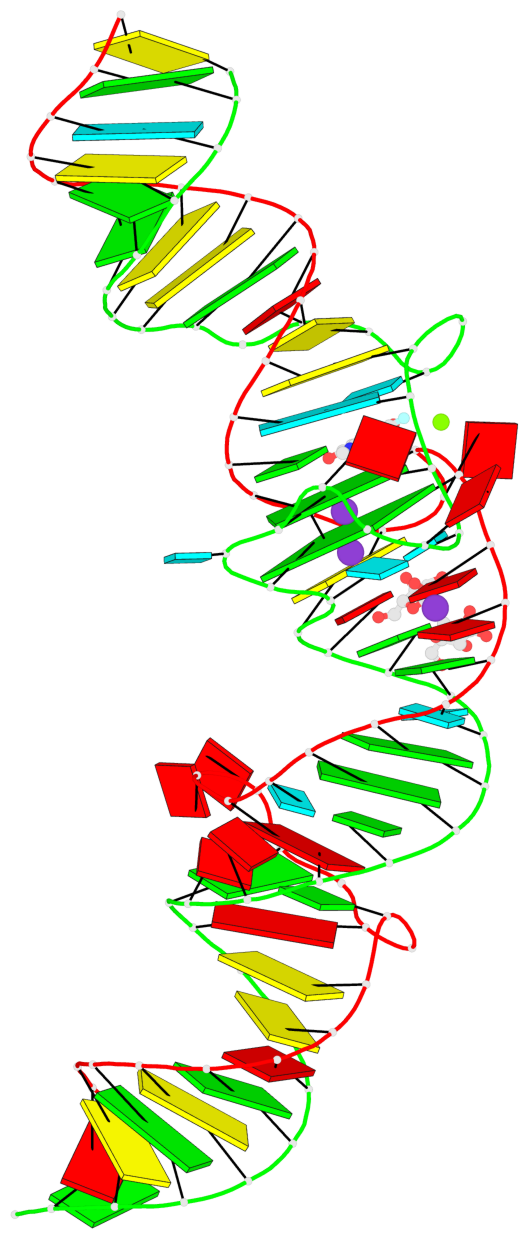
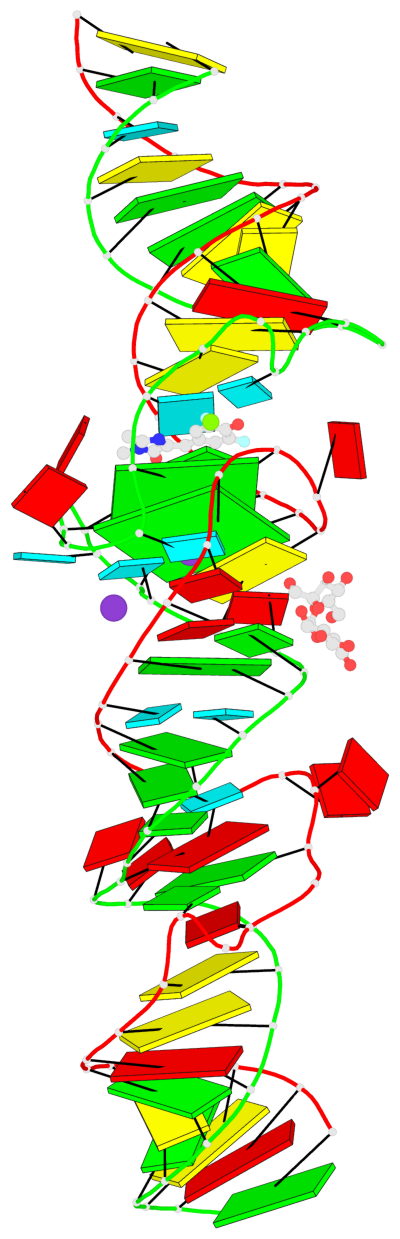
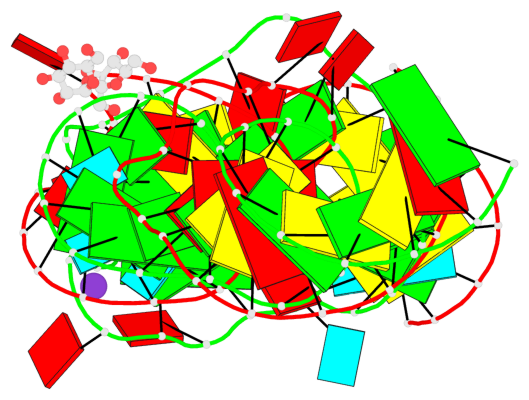
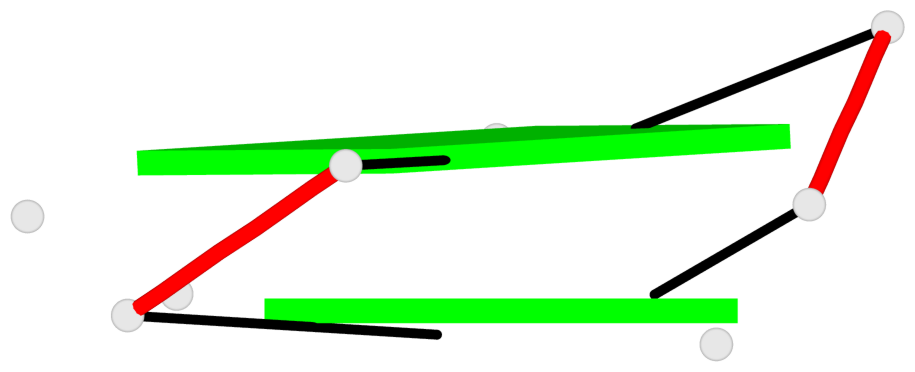
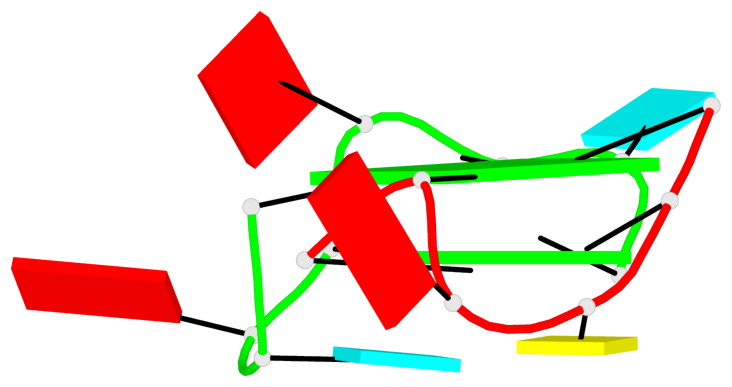
Detailed DSSR results for the G-quadruplex: PDB entry 4ts2
Created and maintained by Xiang-Jun Lu <xiangjun@x3dna.org>
Citation: Please cite the NAR'20 DSSR-PyMOL schematics paper and/or the NAR'15 DSSR method paper.
Summary information
- PDB id
- 4ts2
- Class
- RNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.884 Å)
- Summary
- Crystal structure of the spinach RNA aptamer in complex with dfhbi, magnesium ions
- Reference
- Warner KD, Chen MC, Song W, Strack RL, Thorn A, Jaffrey SR, Ferre-D'Amare AR (2014): "Structural basis for activity of highly efficient RNA mimics of green fluorescent protein." Nat.Struct.Mol.Biol., 21, 658-663. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2865.
- Abstract
- GFP and its derivatives revolutionized the study of proteins. Spinach is a recently reported in vitro-evolved RNA mimic of GFP, which as genetically encoded fusions makes possible live-cell, real-time imaging of biological RNAs without resorting to large RNA-binding protein-GFP fusions. To elucidate the molecular basis of Spinach fluorescence, we solved the cocrystal structure of Spinach bound to its cognate exogenous chromophore, showing that Spinach activates the small molecule by immobilizing it between a base triple, a G-quadruplex and an unpaired G. Mutational and NMR analyses indicate that the G-quadruplex is essential for Spinach fluorescence, is also present in other fluorogenic RNAs and may represent a general strategy for RNAs to induce fluorescence of chromophores. The structure guided the design of a miniaturized 'Baby Spinach', and it provides a foundation for structure-driven design and tuning of fluorescent RNAs.
- G4 notes
- 2 G-tetrads, 1 G4 helix, 1 G4 stem, (2+2), UUDD
Base-block schematics in six views
List of 2 G-tetrads
1 glyco-bond=--s- sugar=-33. groove=-wn- planarity=0.335 type=other nts=4 GGGG X.G25,X.G29,Y.G72,Y.G68 2 glyco-bond=--ss sugar=-3-3 groove=-w-n planarity=0.180 type=other nts=4 GGGG X.G26,X.G30,Y.G70,Y.G65
List of 1 G4-helix
In DSSR, a G4-helix is defined by stacking interactions of G-tetrads, regardless of backbone connectivity, and may contain more than one G4-stem.
Helix#1, 2 G-tetrad layers, inter-molecular, with 1 stem
List of 1 G4-stem
In DSSR, a G4-stem is defined as a G4-helix with backbone connectivity. Bulges are also allowed along each of the four strands.