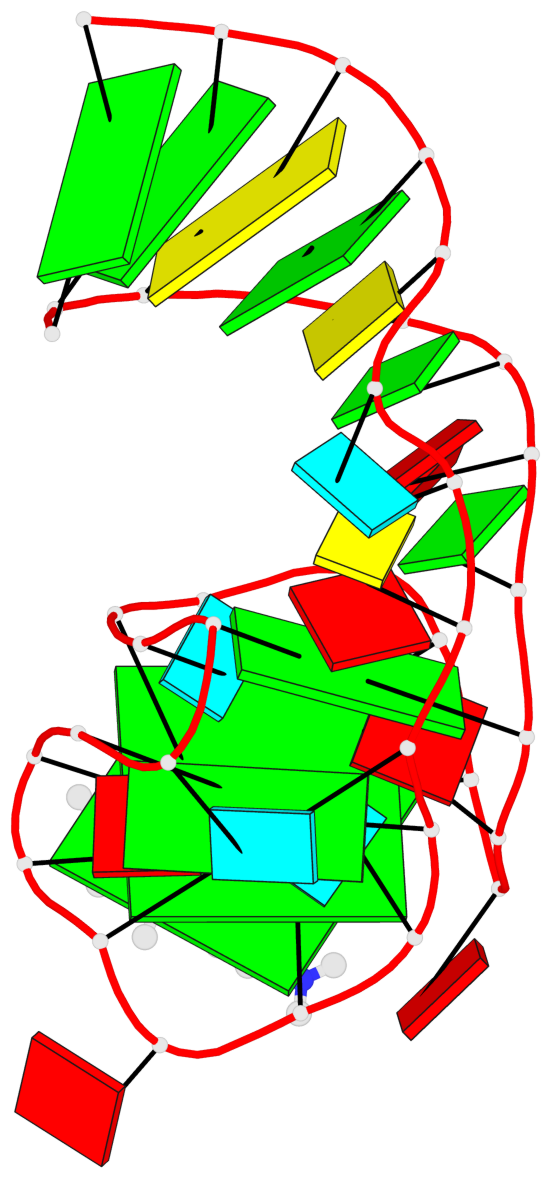
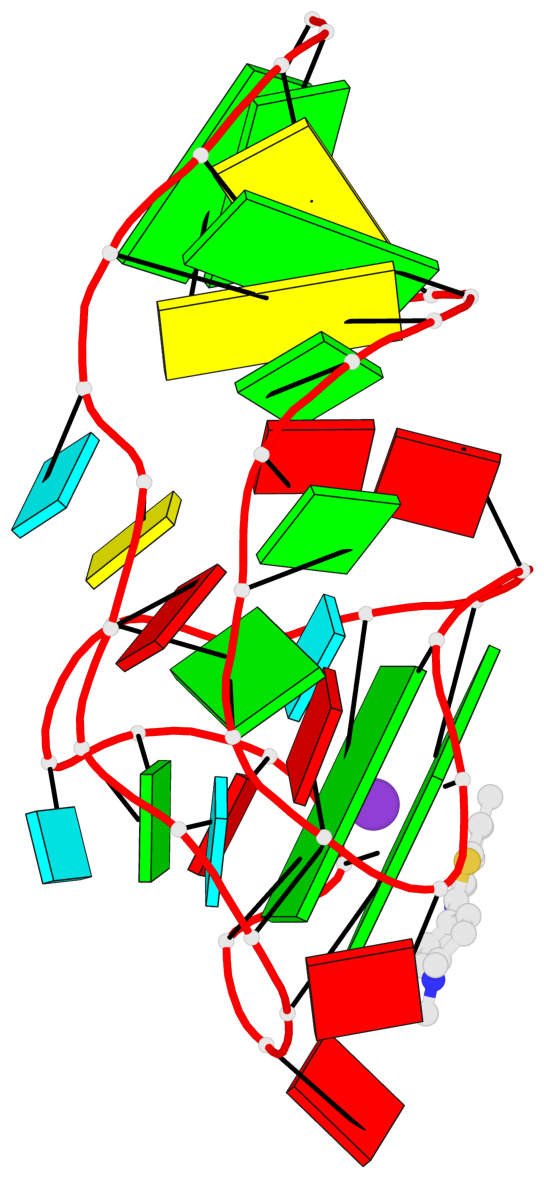
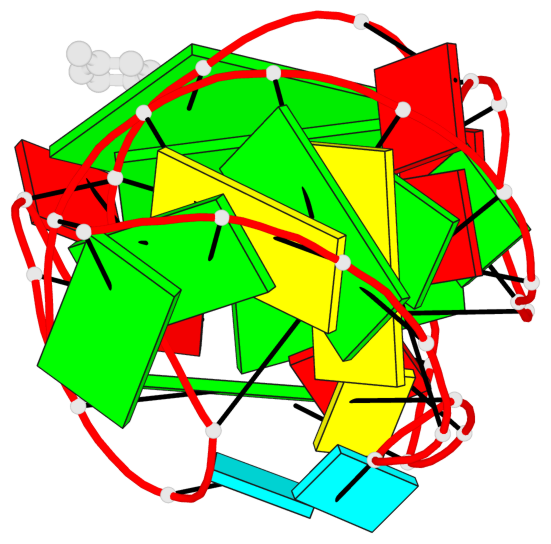
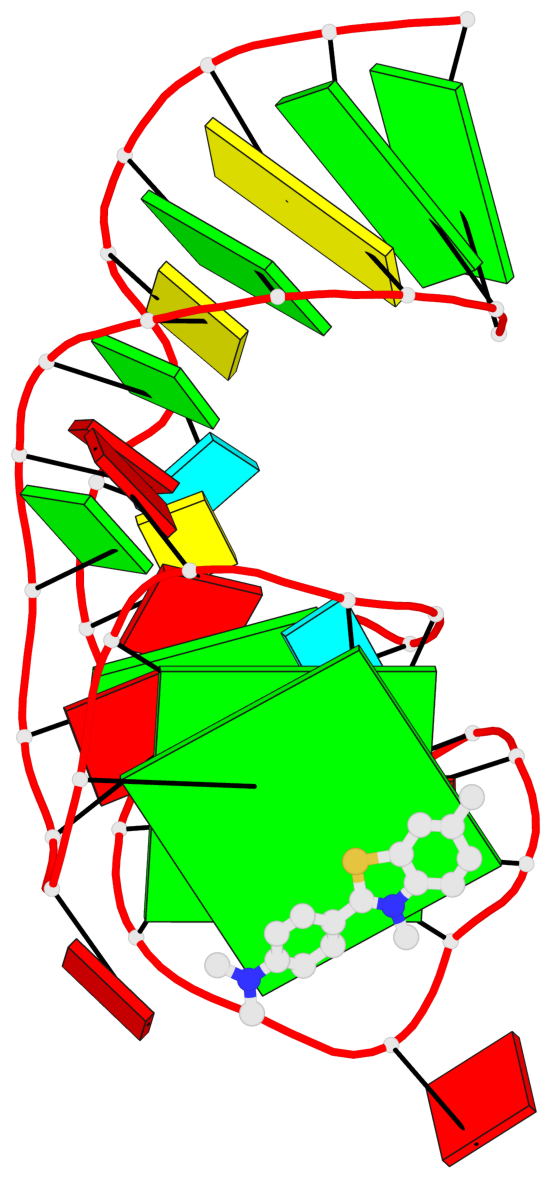
Detailed DSSR results for the G-quadruplex: PDB entry 6e81
Created and maintained by Xiang-Jun Lu <xiangjun@x3dna.org>
Citation: Please cite the NAR'20 DSSR-PyMOL schematics paper and/or the NAR'15 DSSR method paper.
Summary information
- PDB id
- 6e81
- Class
- RNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.721 Å)
- Summary
- Crystal structure of the corn aptamer in complex with tht
- Reference
- Sjekloca L, Ferre-D'Amare AR (2019): "Binding between G Quadruplexes at the Homodimer Interface of the Corn RNA Aptamer Strongly Activates Thioflavin T Fluorescence." Cell Chem Biol, 26, 1159. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2019.04.012.
- Abstract
- Thioflavin T (ThT) is widely used for the detection of amyloids. Many unrelated DNAs and RNAs that contain G-quadruplex motifs also bind ThT and strongly activate its fluorescence. To elucidate the structural basis of ThT binding to G quadruplexes and its fluorescence turn-on, we determined its co-crystal structure with the homodimeric RNA Corn, which contains two G quadruplexes. We found that two ThT molecules bind in the dimer interface, constrained by a G quartet from each protomer into a maximally fluorescent planar conformation. The unliganded Corn homodimer crystal structure reveals a collapsed fluorophore-binding site. In solution, Corn must fluctuate between this and an open, binding-competent conformation. A co-crystal structure with another benzothiazole derivate, thiazole orange (TO), also shows binding at the Corn homodimer interface. As the bound ThT and TO make no interactions with the RNA backbone, their Corn co-crystal structures likely explain their fluorescence activation upon sequence-independent DNA and RNA G-quadruplex binding.
- G4 notes
- 2 G-tetrads, 1 G4 helix, 1 G4 stem, 2(-P-P-P), parallel(4+0), UUUU
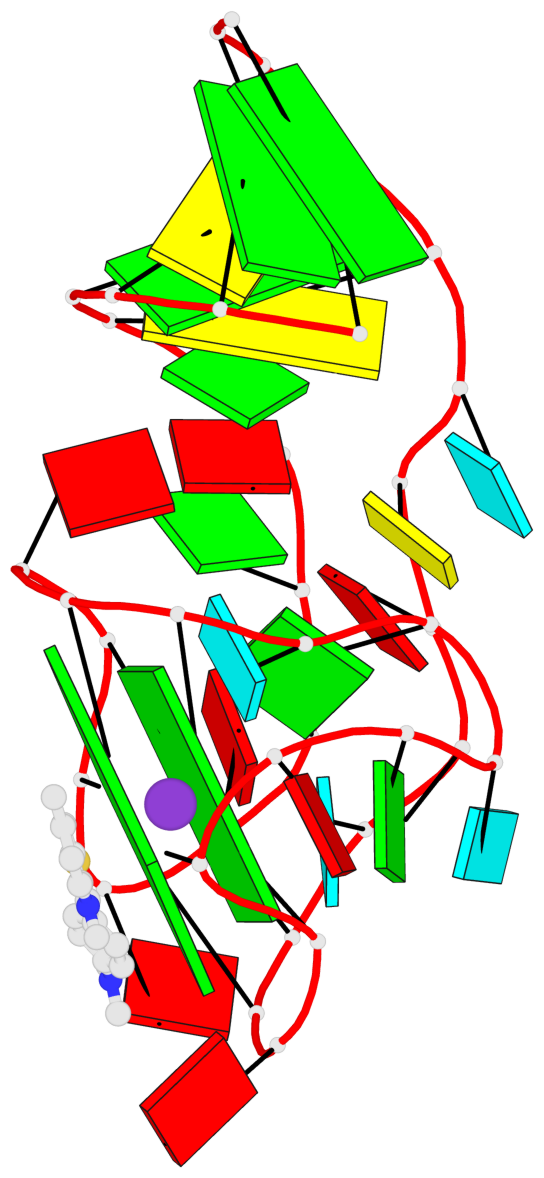
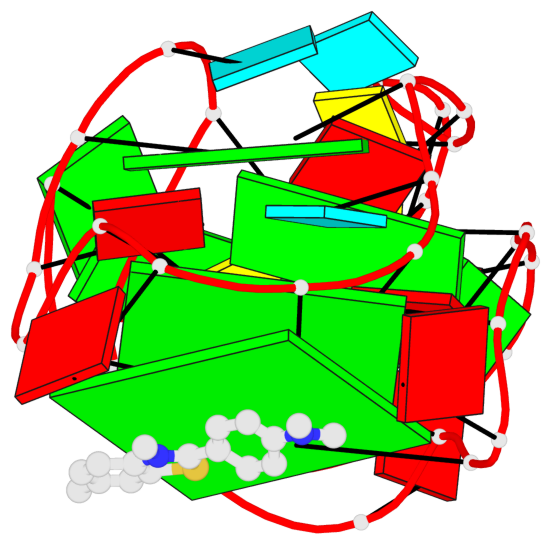
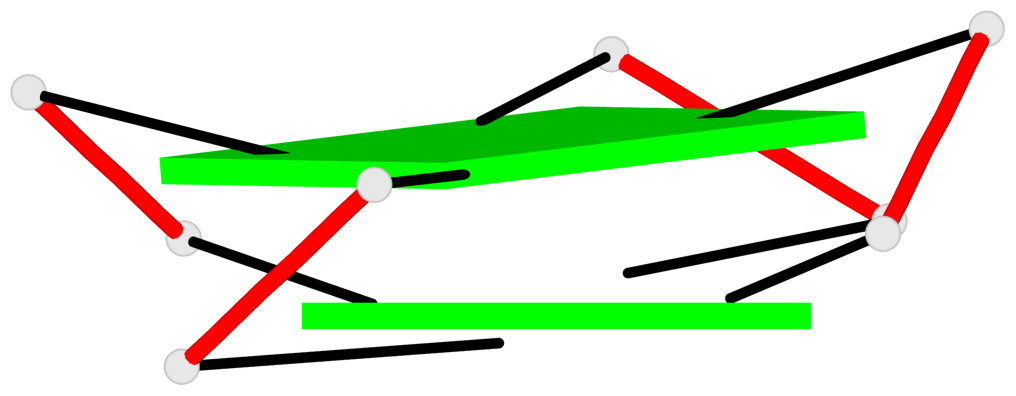
Base-block schematics in six views
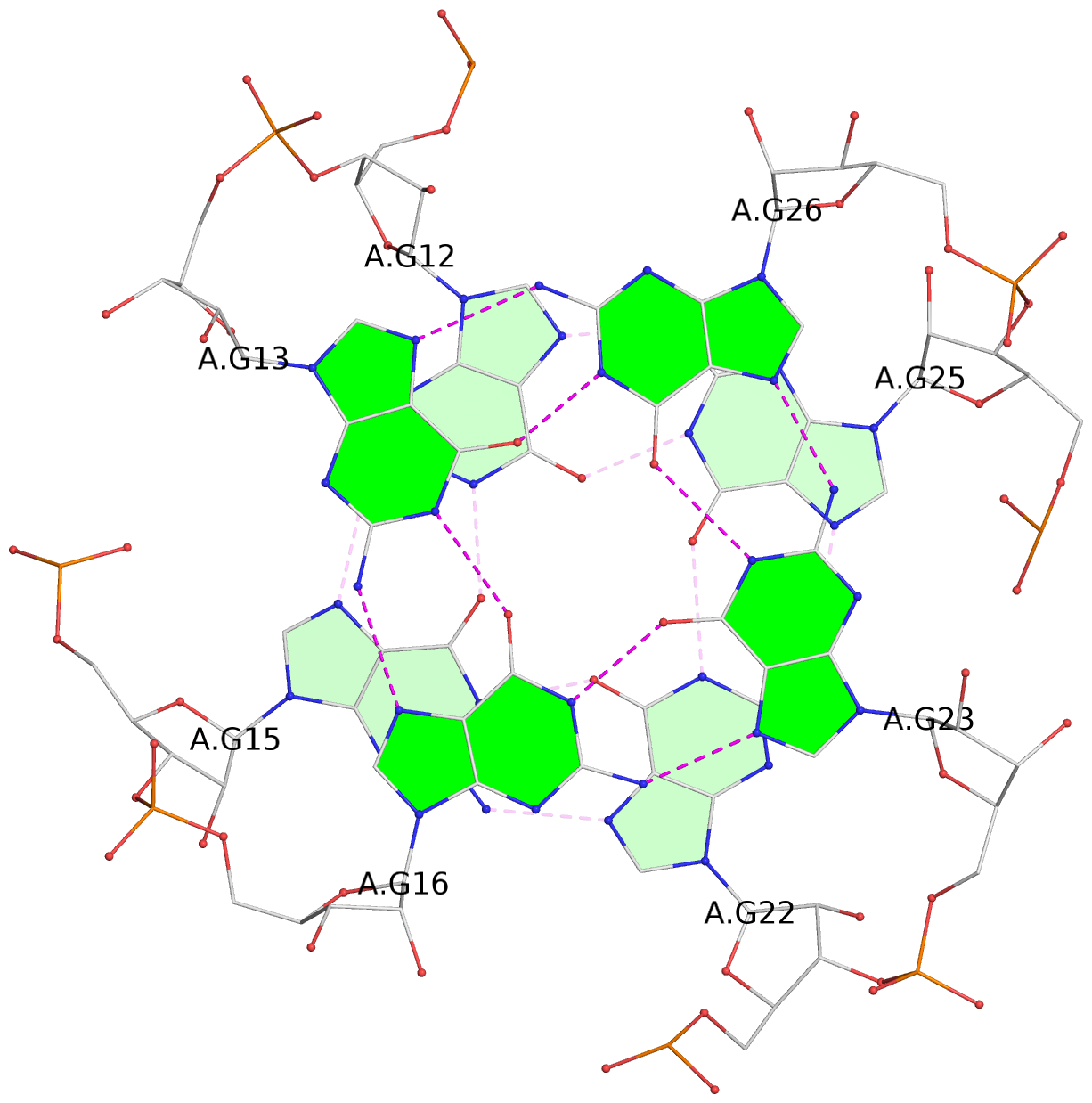
List of 2 G-tetrads
1 glyco-bond=---- sugar=-333 groove=---- planarity=0.300 type=other nts=4 GGGG A.G12,A.G15,A.G22,A.G25 2 glyco-bond=---- sugar=-3-3 groove=---- planarity=0.117 type=planar nts=4 GGGG A.G13,A.G16,A.G23,A.G26
List of 1 G4-helix
In DSSR, a G4-helix is defined by stacking interactions of G-tetrads, regardless of backbone connectivity, and may contain more than one G4-stem.
Helix#1, 2 G-tetrad layers, INTRA-molecular, with 1 stem
List of 1 G4-stem
In DSSR, a G4-stem is defined as a G4-helix with backbone connectivity. Bulges are also allowed along each of the four strands.