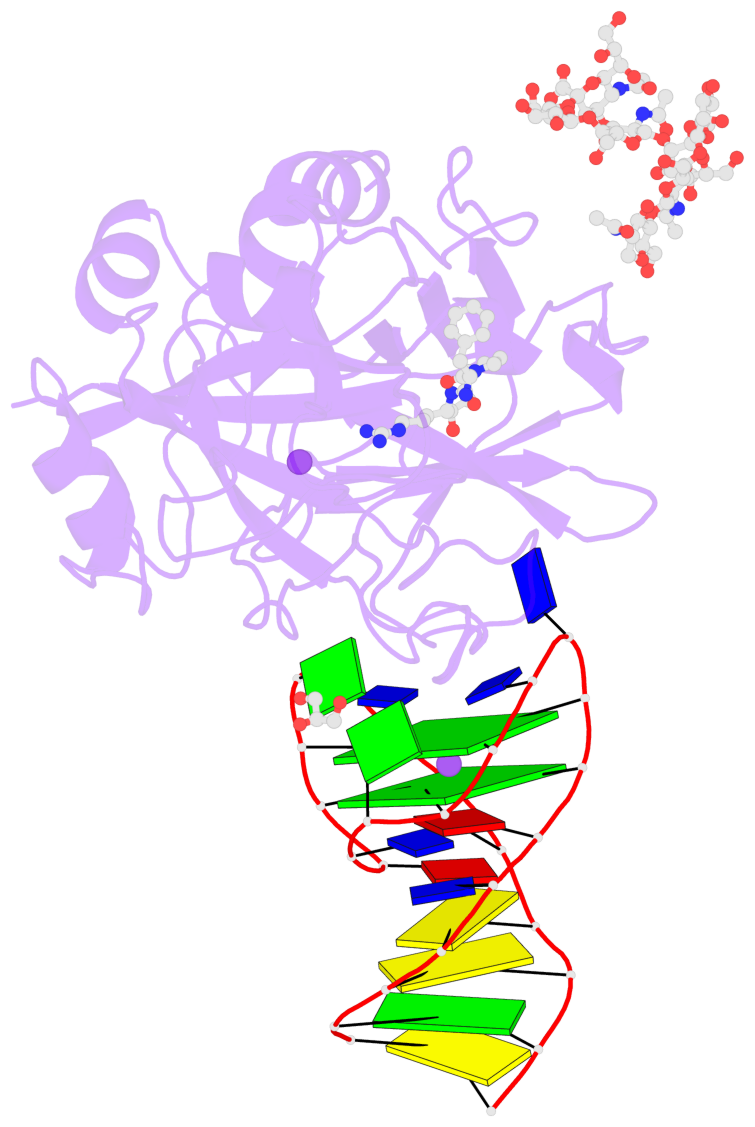
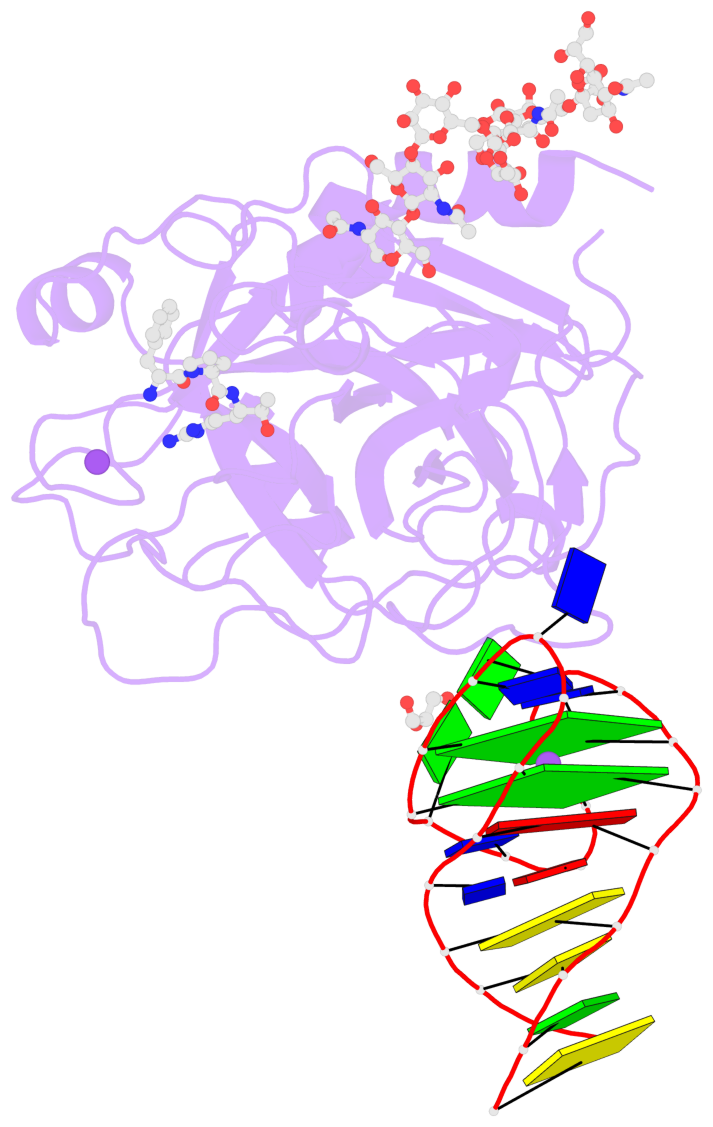
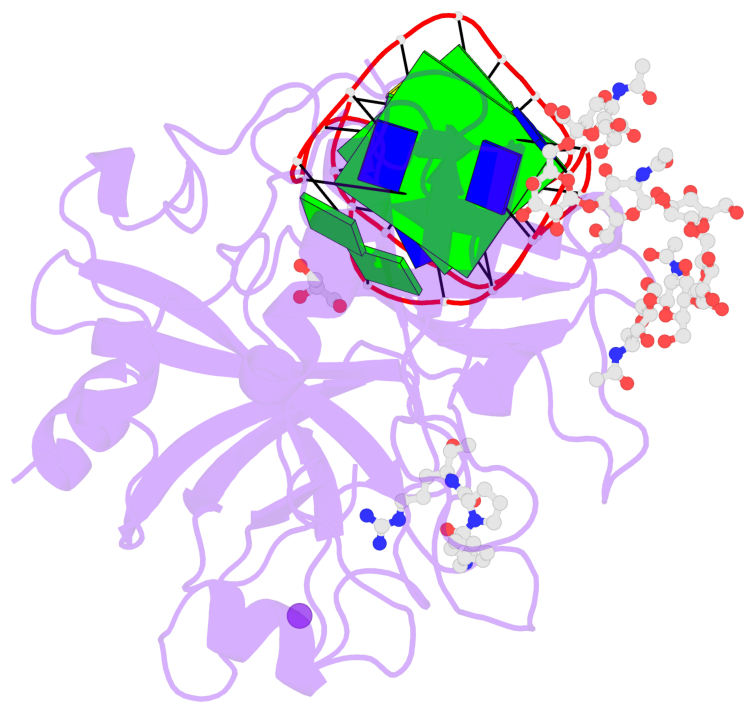
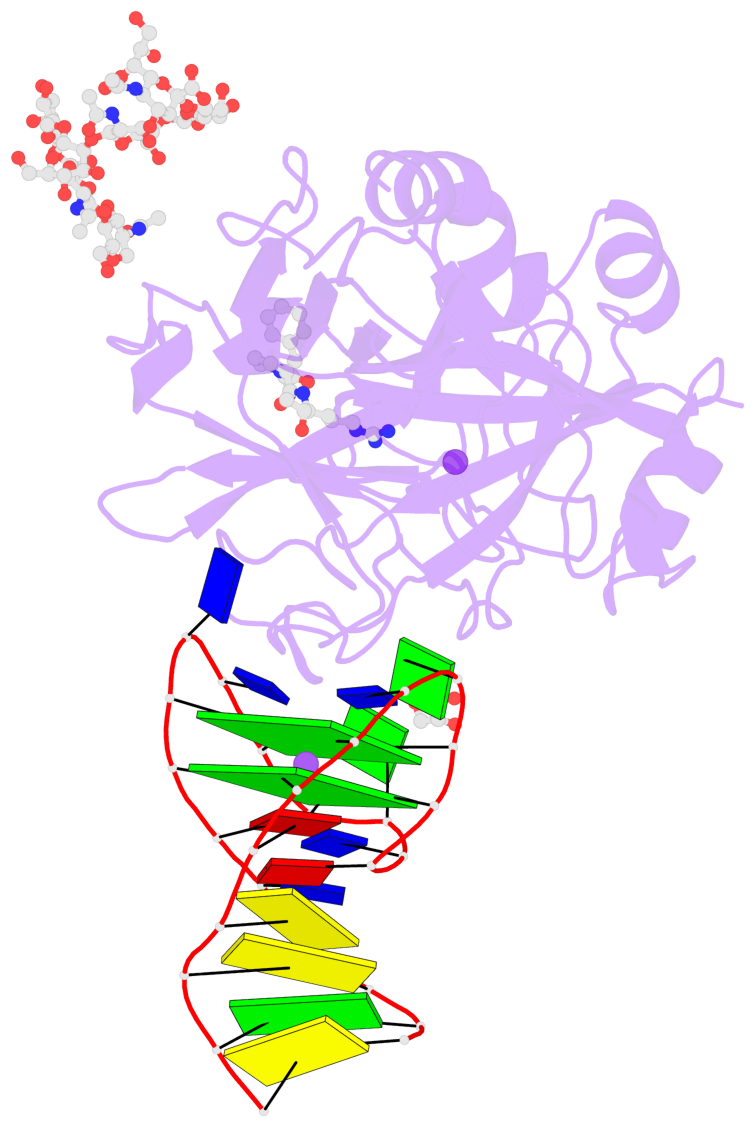
Detailed DSSR results for the G-quadruplex: PDB entry 6gn7
Created and maintained by Xiang-Jun Lu <xiangjun@x3dna.org>
Citation: Please cite the NAR'20 DSSR-PyMOL schematics paper and/or the NAR'15 DSSR method paper.
Summary information
- PDB id
- 6gn7
- Class
- hydrolase
- Method
- X-ray (2.8 Å)
- Summary
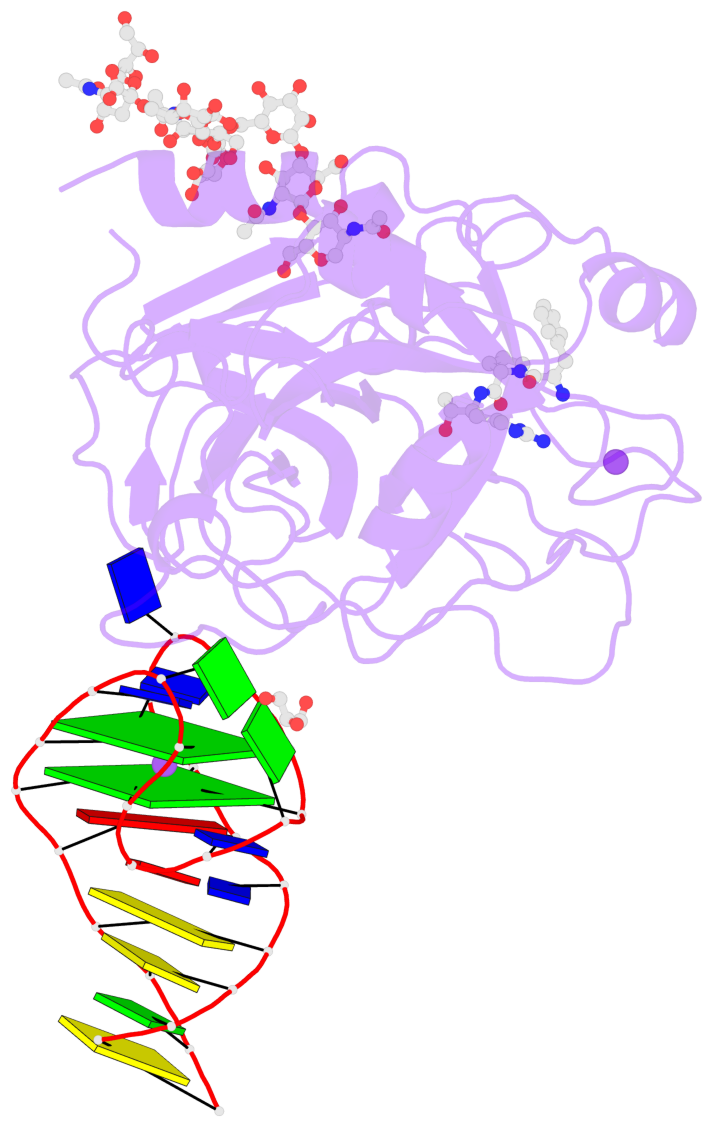
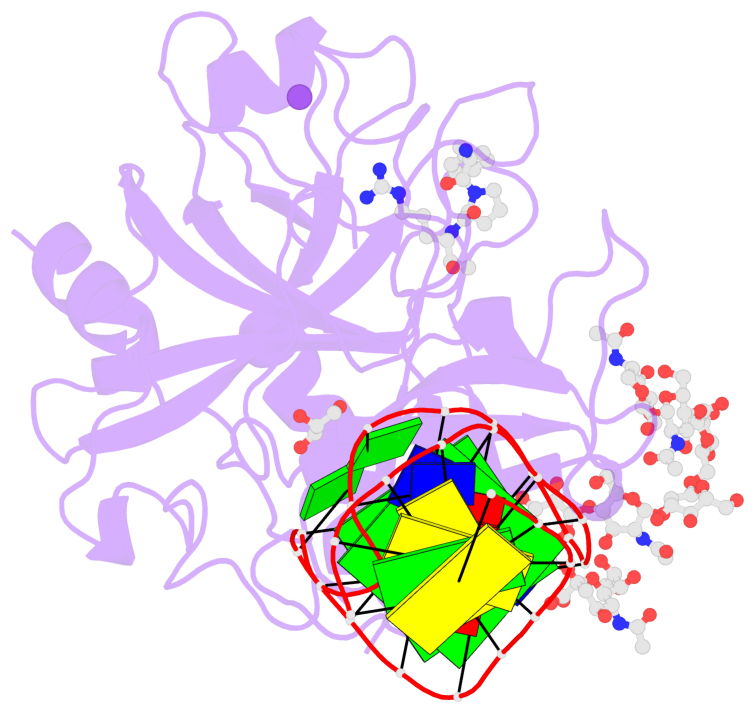
- X-ray structure of the complex between human alpha thrombin and nu172, a duplex-quadruplex 26-mer DNA aptamer, in the presence of sodium ions.
- Reference
- Troisi R, Napolitano V, Spiridonova V, Russo Krauss I, Sica F (2018): "Several structural motifs cooperate in determining the highly effective anti-thrombin activity of NU172 aptamer." Nucleic Acids Res., 46, 12177-12185. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky990.
- Abstract
- Despite aptamers are very promising alternative to antibodies, very few of them are under clinical trials or are used as drugs. Among them, NU172 is currently in Phase II as anticoagulant in heart disease treatments. It inhibits thrombin activity much more effectively than TBA, the best-known thrombin binding aptamer. The crystal structure of thrombin-NU172 complex reveals a bimodular duplex/quadruplex architecture for the aptamer, which binds thrombin exosite I through a highly complementary surface involving all three loops of the G-quadruplex module. Although the duplex domain does not interact directly with thrombin, the features of the duplex/quadruplex junction and the solution data on two newly designed NU172 mutants indicate that the duplex moiety is important for the optimization of the protein-ligand interaction and for the inhibition of the enzyme activity. Our work discloses the structural features determining the inhibition of thrombin by NU172 and put the basis for the design of mutants with improved properties.
- G4 notes
- 2 G-tetrads, 1 G4 helix, 1 G4 stem, 2(+Ln+Lw+Ln), chair(2+2), UDUD
Base-block schematics in six views
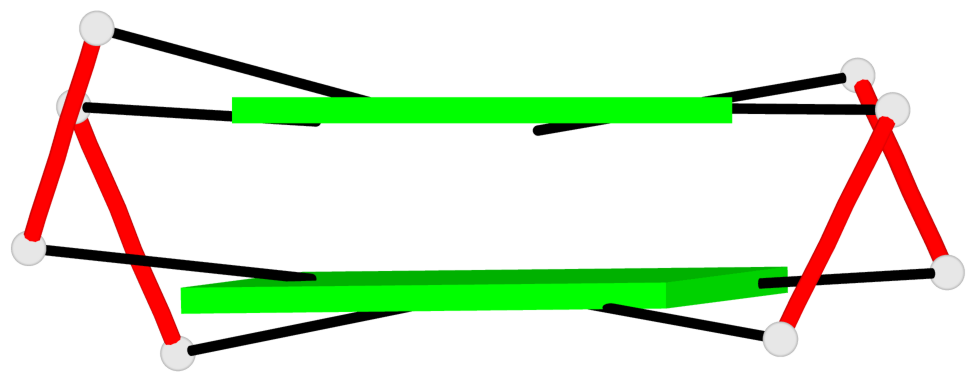
List of 2 G-tetrads
1 glyco-bond=s-s- sugar=---- groove=wnwn planarity=0.256 type=other nts=4 GGGG E.DG7,E.DG21,E.DG16,E.DG12 2 glyco-bond=-s-s sugar=--.- groove=wnwn planarity=0.217 type=other nts=4 GGGG E.DG8,E.DG20,E.DG17,E.DG11
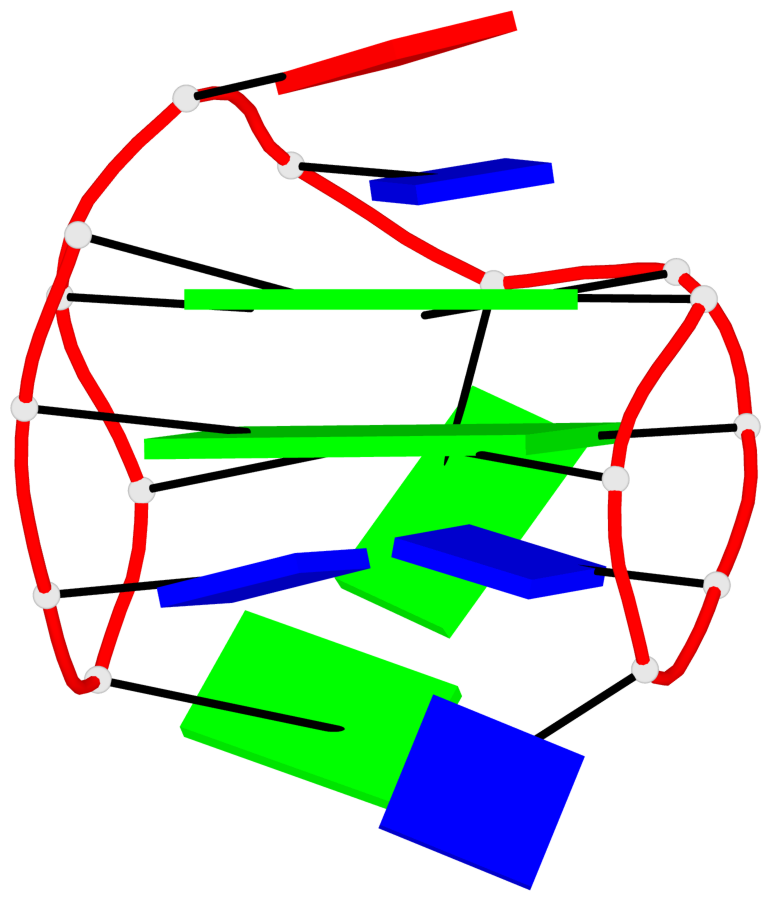
List of 1 G4-helix
In DSSR, a G4-helix is defined by stacking interactions of G-tetrads, regardless of backbone connectivity, and may contain more than one G4-stem.
Helix#1, 2 G-tetrad layers, INTRA-molecular, with 1 stem
List of 1 G4-stem
In DSSR, a G4-stem is defined as a G4-helix with backbone connectivity. Bulges are also allowed along each of the four strands.