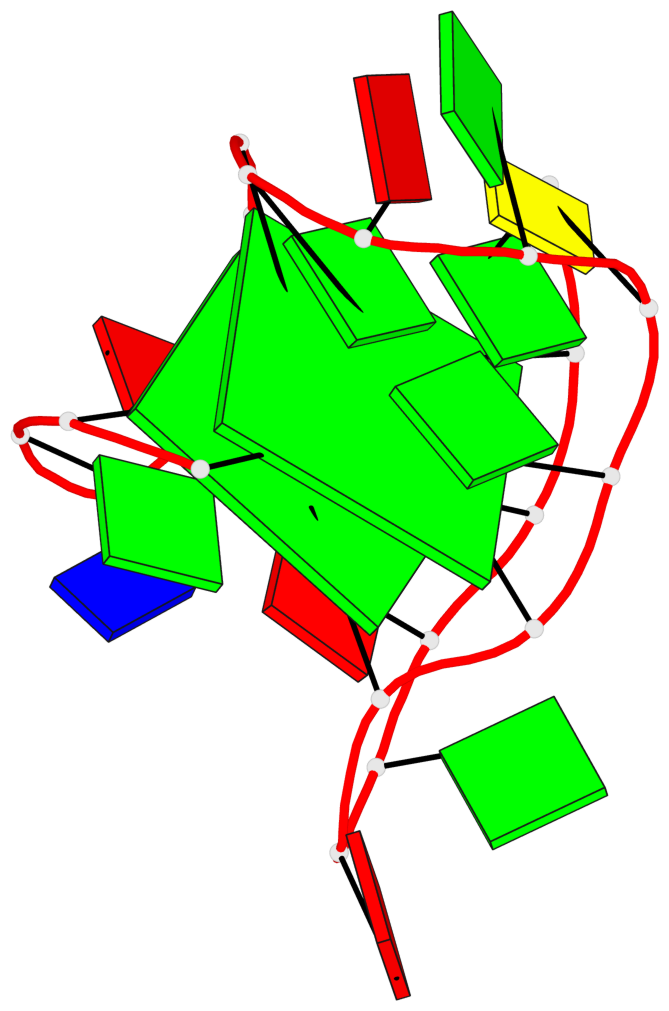
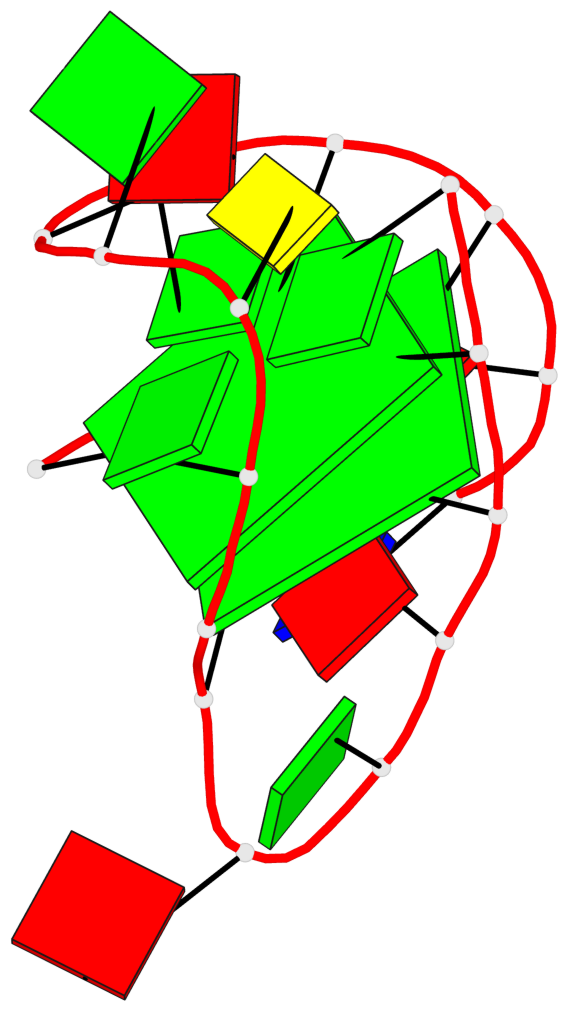
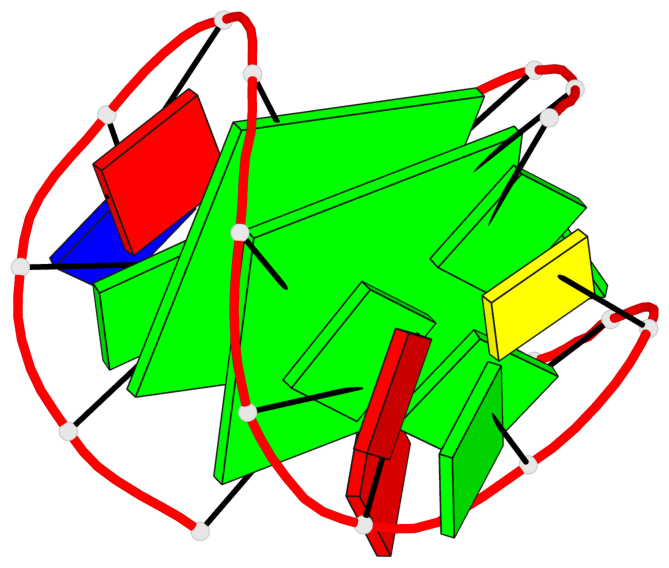
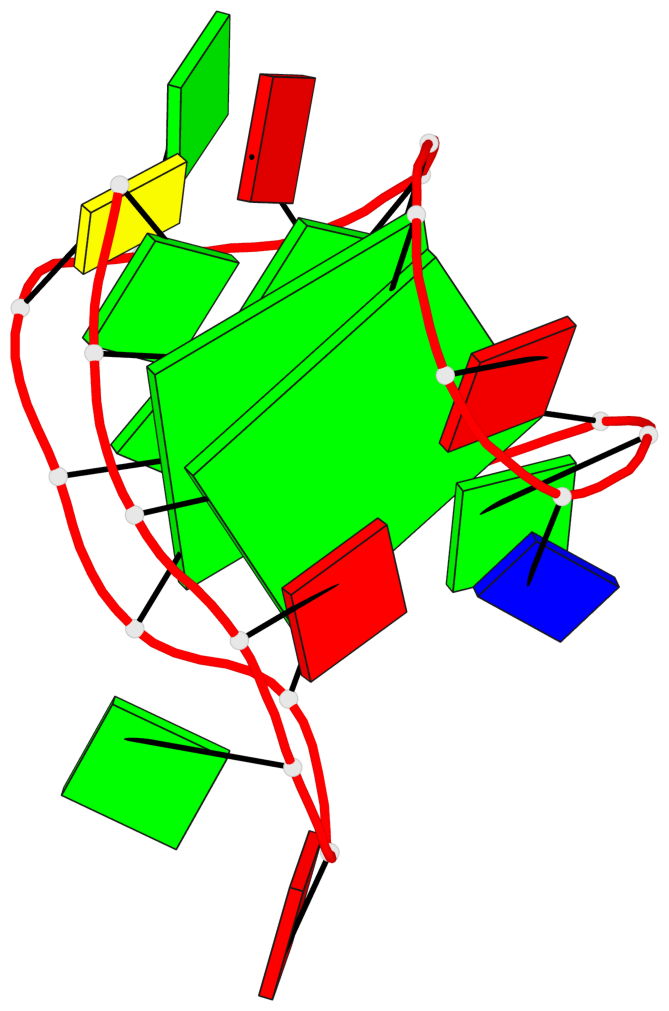
Detailed DSSR results for the G-quadruplex: PDB entry 6gzn
Created and maintained by Xiang-Jun Lu <xiangjun@x3dna.org>
Citation: Please cite the NAR'20 DSSR-PyMOL schematics paper and/or the NAR'15 DSSR method paper.
Summary information
- PDB id
- 6gzn
- Class
- DNA
- Method
- NMR
- Summary
- Adenine-driven structural switch from two- to three-quartet DNA g-quadruplex
- Reference
- Lenarcic Zivkovic M, Rozman J, Plavec J (2018): "Adenine-Driven Structural Switch from a Two- to Three-Quartet DNA G-Quadruplex." Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl., 57, 15395-15399. doi: 10.1002/anie.201809328.
- Abstract
- A G-rich sequence found in the regulatory region of the RANKL gene, which is associated with homeostasis of bone metabolism, folds into a two-quartet basket-type G-quadruplex stabilized by A⋅G⋅A and G⋅G⋅G base-triads. Perusal of local structural features together with G/A-to-T modifications uncovered the critical role of A5 for the formation of a distinct antiparallel two-quartet topology and not the three-quartet topology that would be expected based on the sequence with four GGG-tracts alone. The structural changes induced by the A5-to-T5 modification include a switch in orientation and relative positions of G-strands that together with anti to syn reorientation of G12 provide insights into the complexity of the interactions that influence the folding of G-rich DNA. Understanding the impact of loop residues on the stability and formation of G-quadruplexes advances our knowledge and ability to predict structures adopted by G-rich sequences, which are involved in regulatory mechanisms in the cell, and may also facilitate drug design.
- G4 notes
- 2 G-tetrads, 1 G4 helix, 1 G4 stem, 2(-LwD+Ln), basket(2+2), UDDU
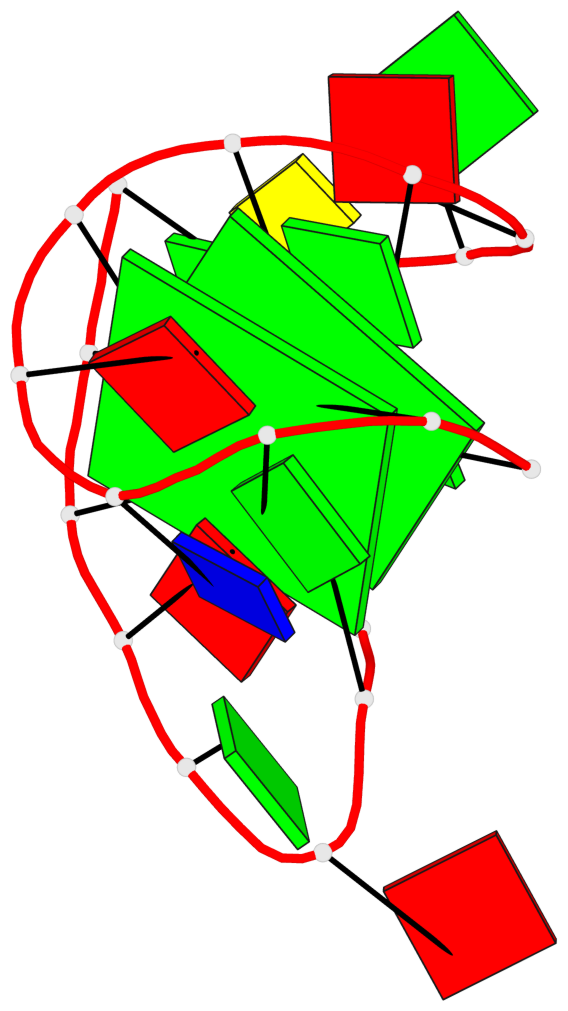
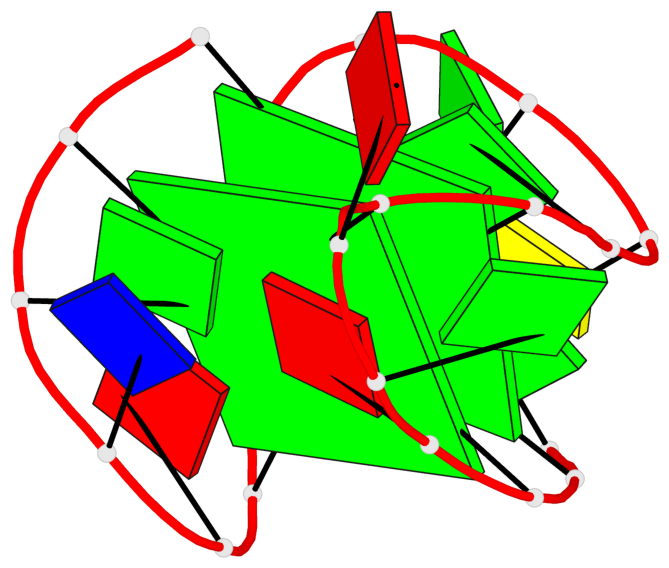
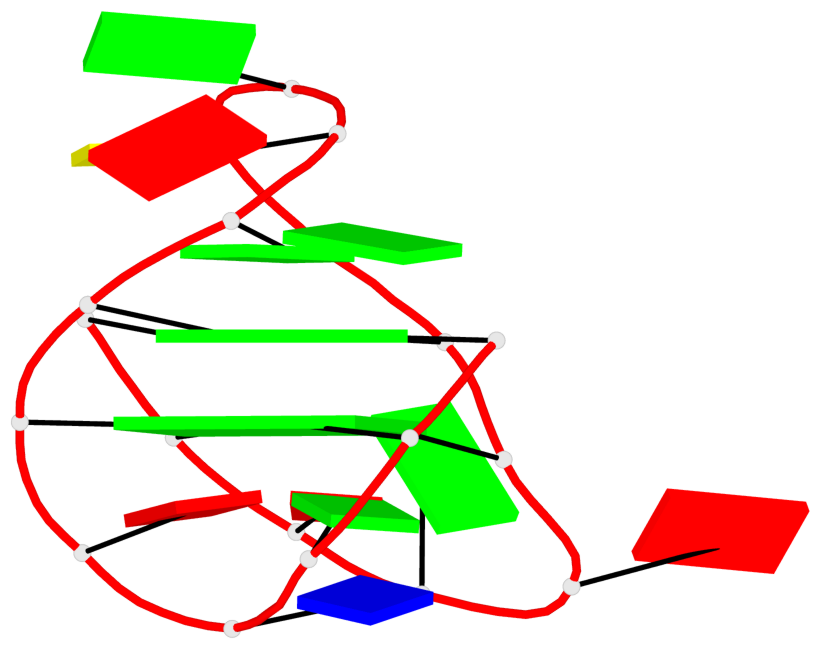
Base-block schematics in six views
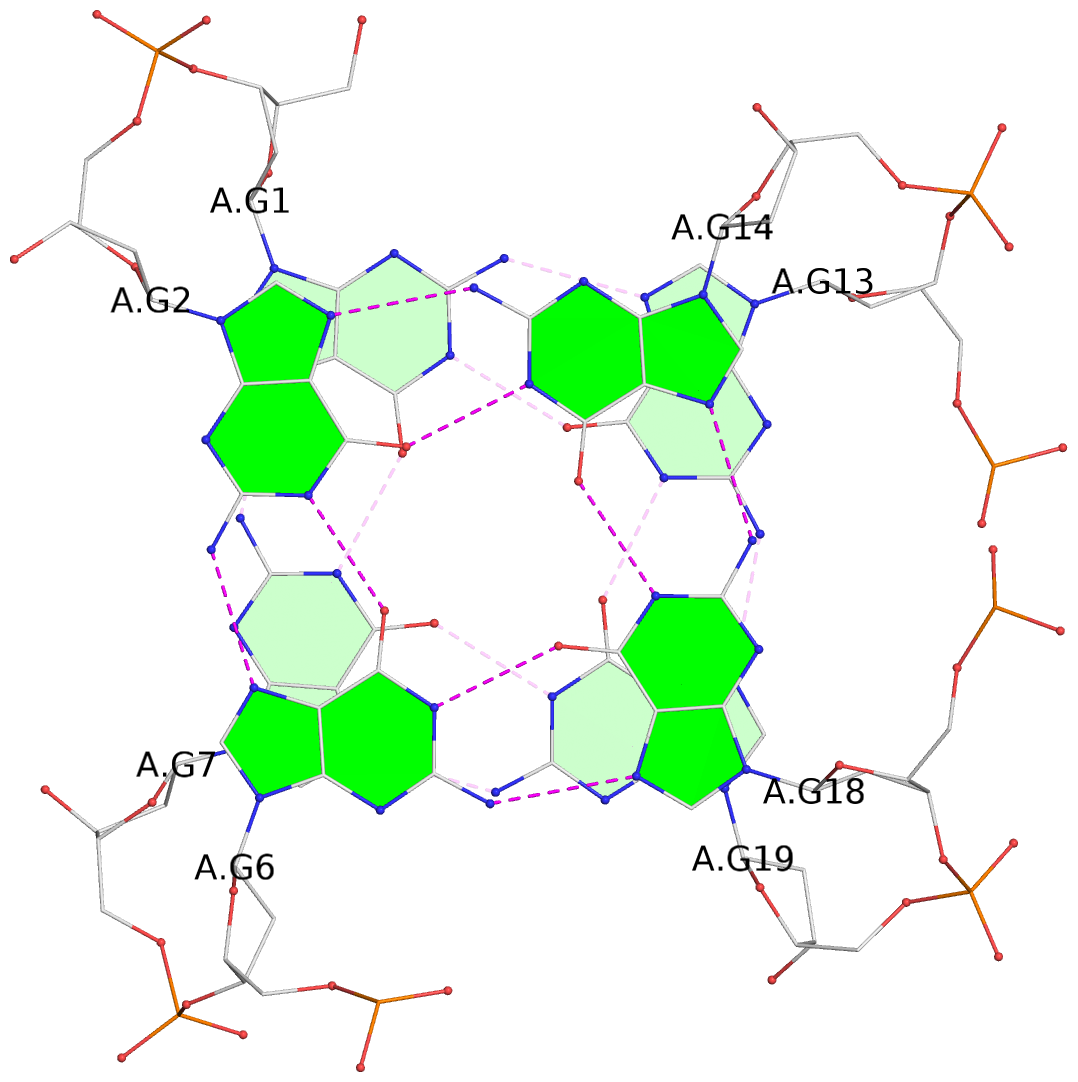
List of 2 G-tetrads
1 glyco-bond=s--s sugar=---- groove=w-n- planarity=0.086 type=planar nts=4 GGGG A.DG1,A.DG7,A.DG19,A.DG13 2 glyco-bond=-ss- sugar=---- groove=w-n- planarity=0.129 type=planar nts=4 GGGG A.DG2,A.DG6,A.DG18,A.DG14
List of 1 G4-helix
In DSSR, a G4-helix is defined by stacking interactions of G-tetrads, regardless of backbone connectivity, and may contain more than one G4-stem.
Helix#1, 2 G-tetrad layers, INTRA-molecular, with 1 stem
List of 1 G4-stem
In DSSR, a G4-stem is defined as a G4-helix with backbone connectivity. Bulges are also allowed along each of the four strands.