Detailed DSSR results for the G-quadruplex: PDB entry 6k3y
Created and maintained by Xiang-Jun Lu <xiangjun@x3dna.org>
Citation: Please cite the NAR'20 DSSR-PyMOL schematics paper and/or the NAR'15 DSSR method paper.
Summary information
- PDB id
- 6k3y
- Class
- DNA
- Method
- NMR
- Summary
- G-quadruplex complex with cyclic dinucleotide 3'-3' cgamp
- Reference
- Winnerdy FR, Das P, Heddi B, Phan AT (2019): "Solution Structures of a G-Quadruplex Bound to Linear- and Cyclic-Dinucleotides." J.Am.Chem.Soc., 141, 18038-18047. doi: 10.1021/jacs.9b05642.
- Abstract
- Cyclic dinucleotides have emerged as important secondary messengers and cell signaling molecules that regulate several cell responses. A guanine-deficit G-quadruplex structure formation by a sequence containing (4n - 1) guanines, n denoting the number of G-tetrad layers, was previously reported. Here, a (4n - 1) G-quadruplex structure is shown to be capable of binding guanine-containing dinucleotides in micromolar affinity. The guanine base of the dinucleotides interacts with a vacant G-triad, forming four additional Hoogsteen hydrogen bonds to complete a G-tetrad. Solution structures of two complexes, both comprised of a (4n - 1) G-quadruplex structure, one bound to a linear dinucleotide (d(AG)) and the other to a cyclic dinucleotide (cGAMP), are solved using NMR spectroscopy. The latter suggests sufficiently strong interaction between the guanine base of the dinucleotide and the vacant G-triad, which acts as an anchor point of binding. The binding interfaces from the two solution structures provide useful information for specific ligand design. The results also infer that other guanine-containing metabolites of a similar size have the capability of binding G-quadruplexes, potentially affecting the expression of the metabolites and functionality of the bound G-quadruplexes.
- G4 notes
- 2 G-tetrads, 1 G4 helix, 1 G4 stem, 2(-P-P-P), parallel(4+0), UUUU
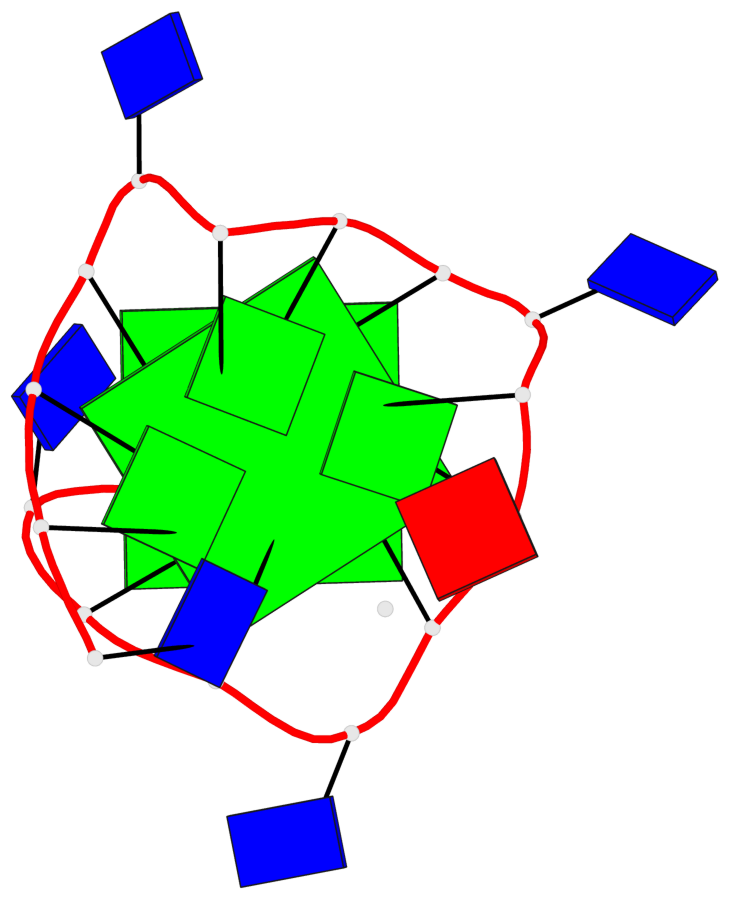
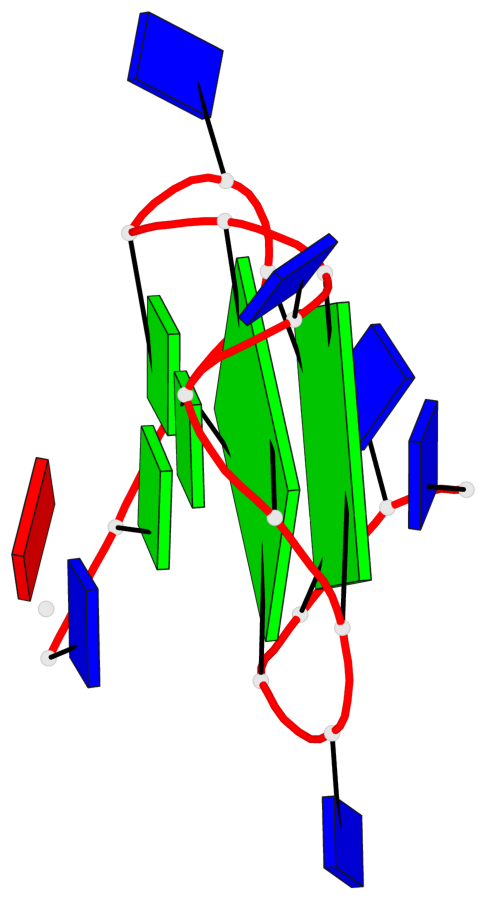
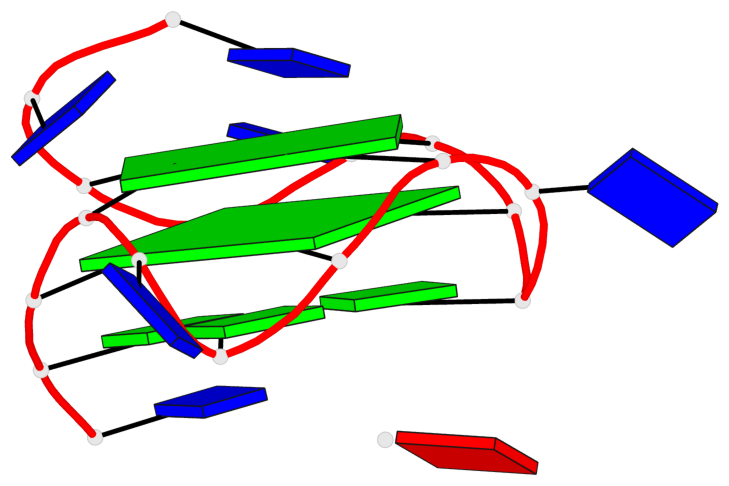
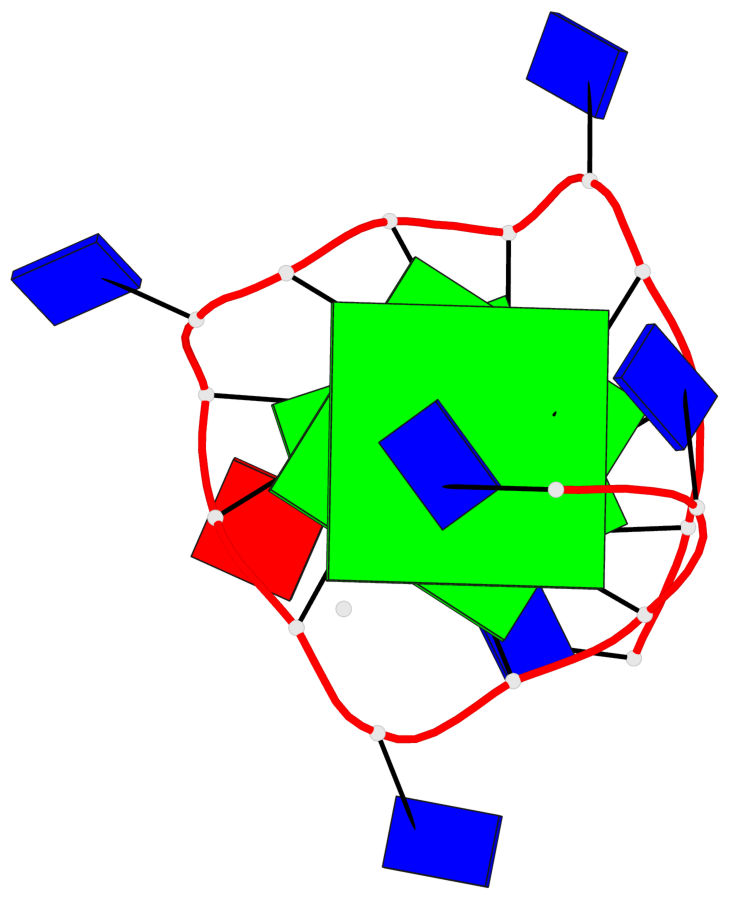
Base-block schematics in six views
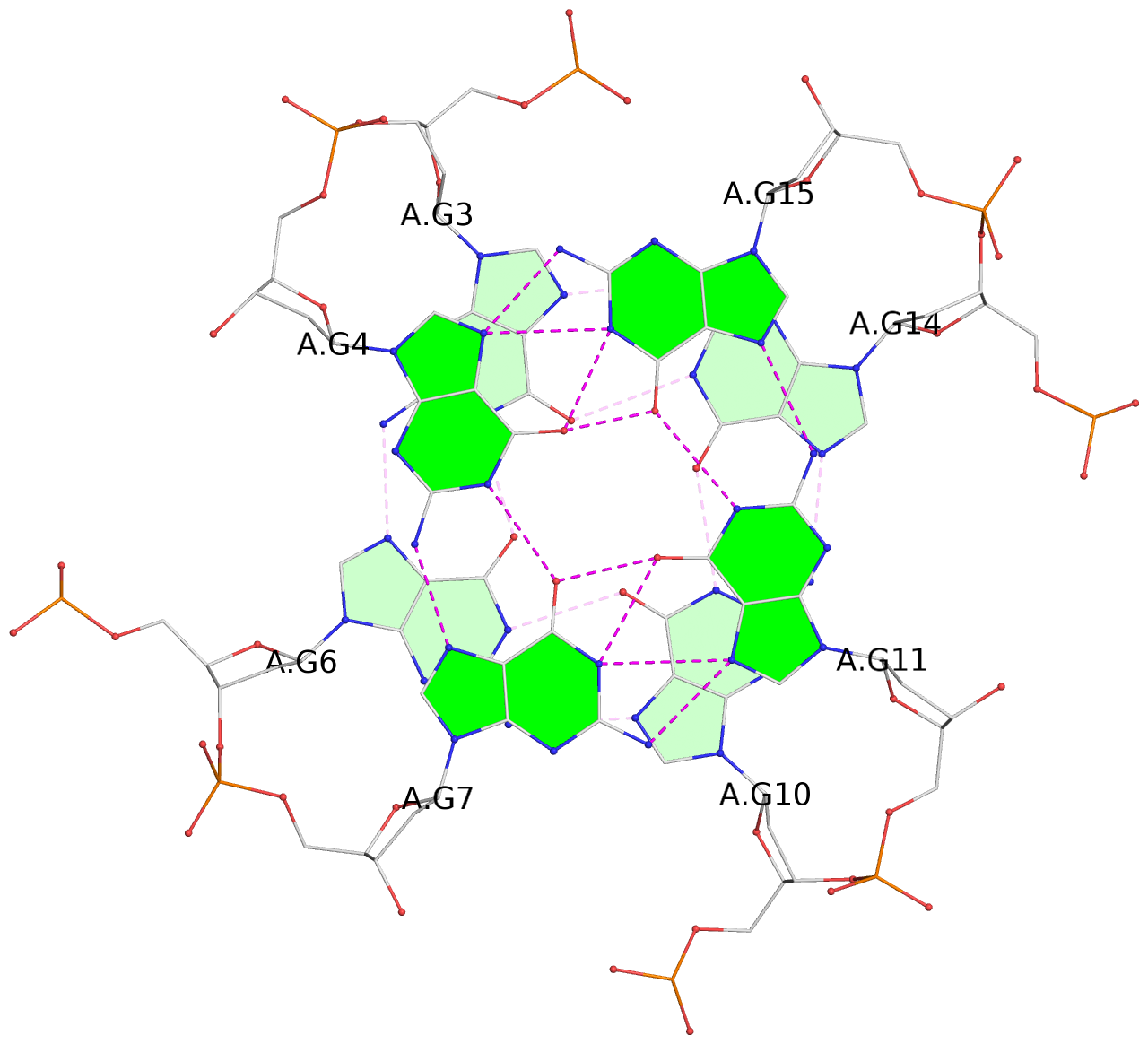
List of 2 G-tetrads
1 glyco-bond=---- sugar=---- groove=---- planarity=0.085 type=planar nts=4 GGGG A.DG3,A.DG6,A.DG10,A.DG14 2 glyco-bond=---- sugar=---- groove=---- planarity=0.081 type=planar nts=4 GGGG A.DG4,A.DG7,A.DG11,A.DG15
List of 1 G4-helix
In DSSR, a G4-helix is defined by stacking interactions of G-tetrads, regardless of backbone connectivity, and may contain more than one G4-stem.
Helix#1, 2 G-tetrad layers, INTRA-molecular, with 1 stem
List of 1 G4-stem
In DSSR, a G4-stem is defined as a G4-helix with backbone connectivity. Bulges are also allowed along each of the four strands.