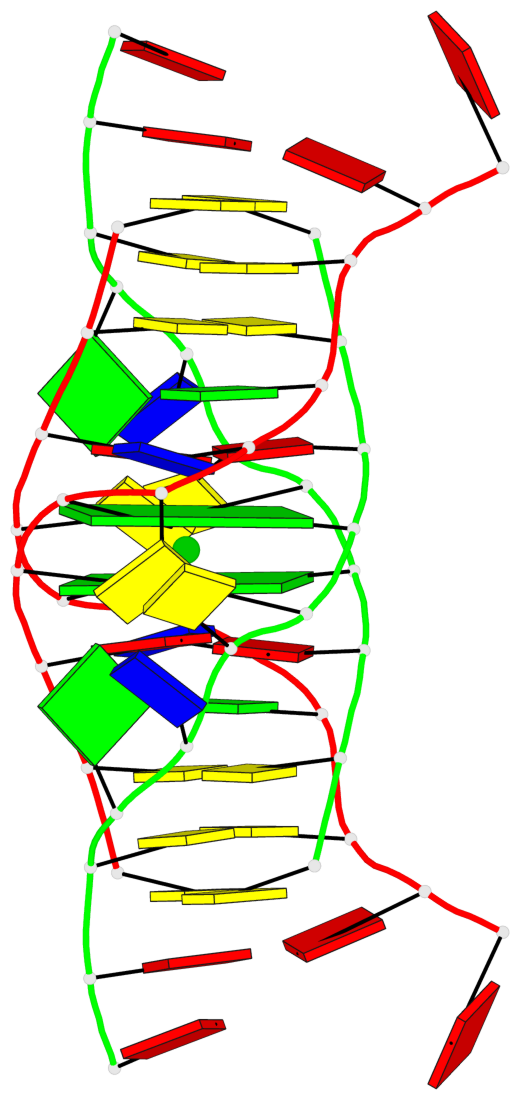
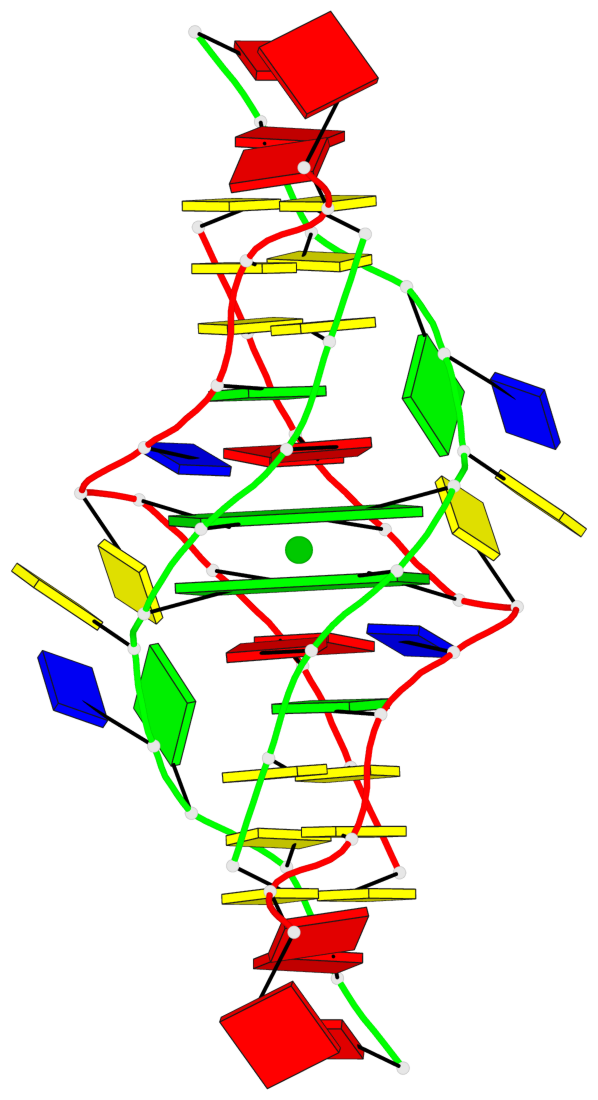
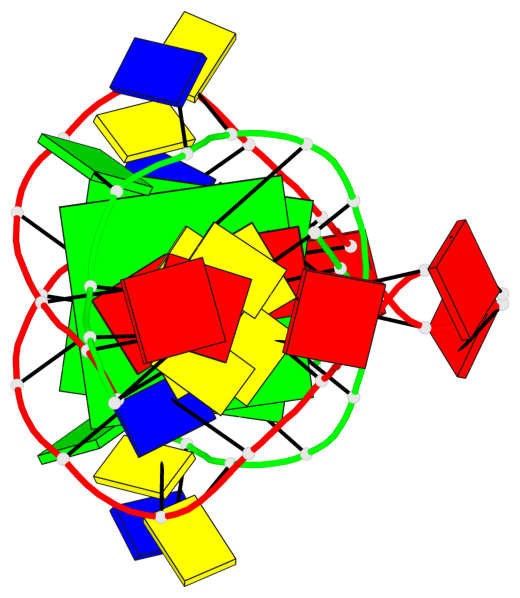
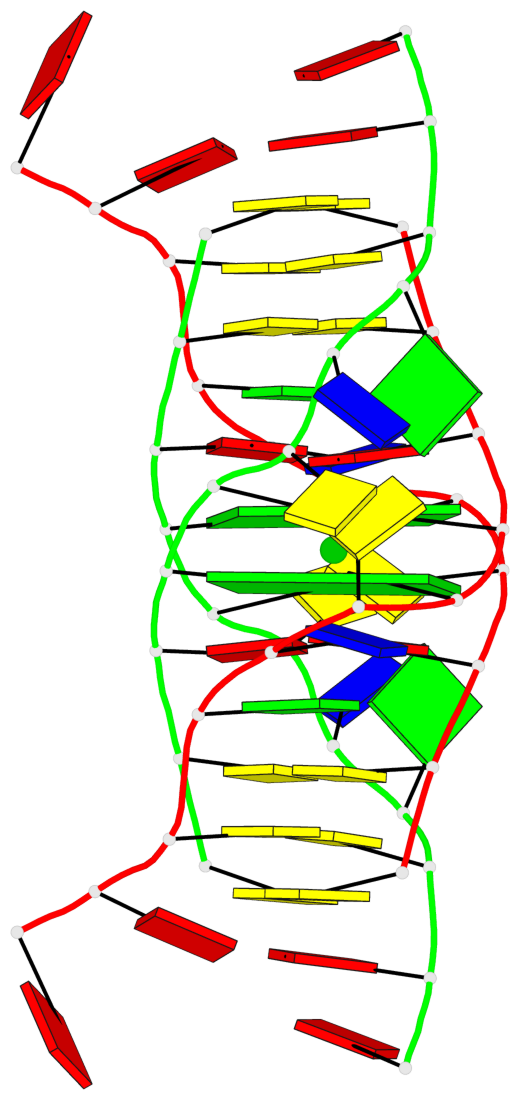
Detailed DSSR results for the G-quadruplex: PDB entry 6tzq
Created and maintained by Xiang-Jun Lu <xiangjun@x3dna.org>
Citation: Please cite the NAR'20 DSSR-PyMOL schematics paper and/or the NAR'15 DSSR method paper.
Summary information
- PDB id
- 6tzq
- Class
- DNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.29 Å)
- Summary
- A DNA g-quadruplex-i-motif hybrid
- Reference
- Chu B, Zhang D, Paukstelis PJ (2019): "A DNA G-quadruplex/i-motif hybrid." Nucleic Acids Res., 47, 11921-11930. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz1008.
- Abstract
- DNA can form many structures beyond the canonical Watson-Crick double helix. It is now clear that noncanonical structures are present in genomic DNA and have biological functions. G-rich G-quadruplexes and C-rich i-motifs are the most well-characterized noncanonical DNA motifs that have been detected in vivo with either proscribed or postulated biological roles. Because of their independent sequence requirements, these structures have largely been considered distinct types of quadruplexes. Here, we describe the crystal structure of the DNA oligonucleotide, d(CCAGGCTGCAA), that self-associates to form a quadruplex structure containing two central antiparallel G-tetrads and six i-motif C-C+ base pairs. Solution studies suggest a robust structural motif capable of assembling as a tetramer of individual strands or as a dimer when composed of tandem repeats. This hybrid structure highlights the growing structural diversity of DNA and suggests that biological systems may harbor many functionally important non-duplex structures.
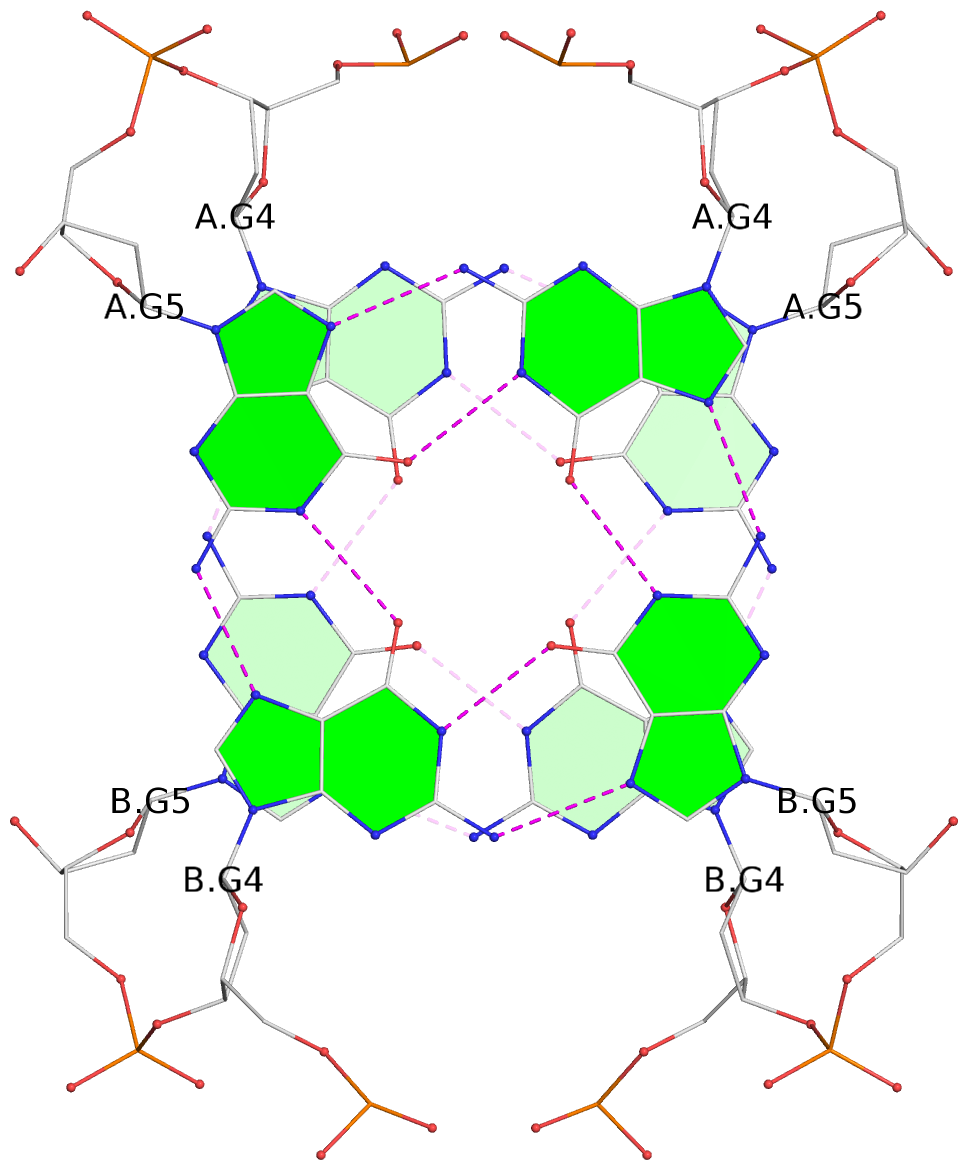
- G4 notes
- 2 G-tetrads, 1 G4 helix, 1 G4 stem, (2+2), UDUD
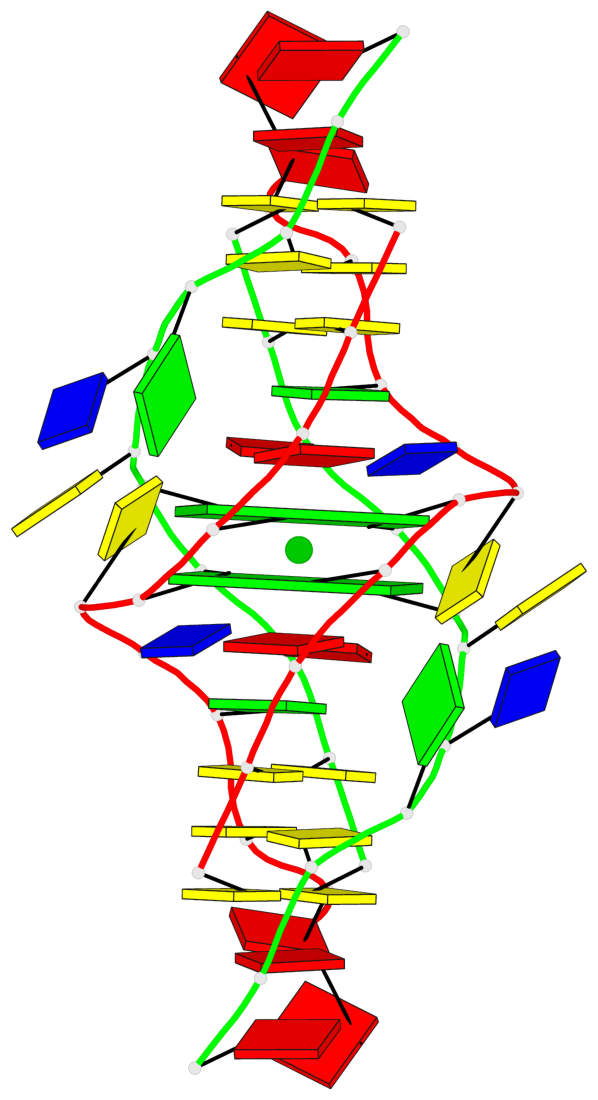
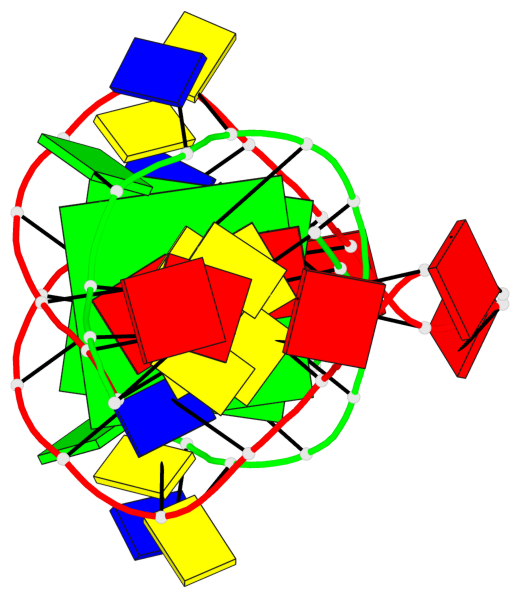
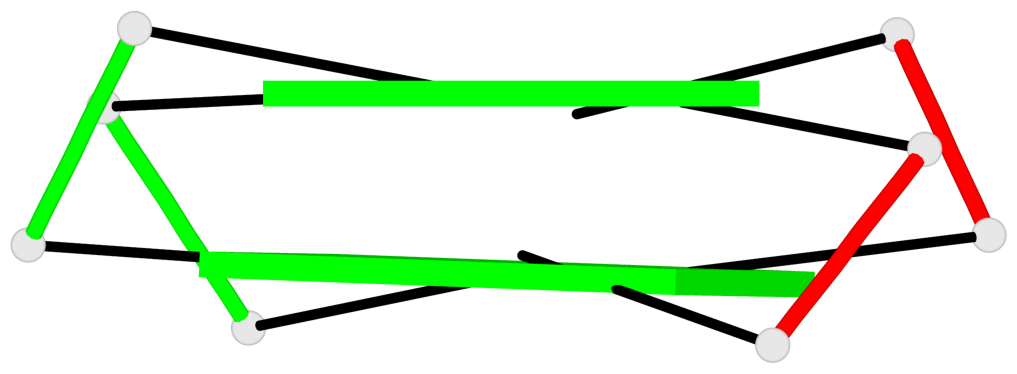
Base-block schematics in six views
List of 2 G-tetrads
1 glyco-bond=s-s- sugar=---- groove=wnwn planarity=0.289 type=other nts=4 GGGG 1:A.DG4,2:B.DG5,1:B.DG4,2:A.DG5 2 glyco-bond=-s-s sugar=---- groove=wnwn planarity=0.289 type=other nts=4 GGGG 1:A.DG5,2:B.DG4,1:B.DG5,2:A.DG4
List of 1 G4-helix
In DSSR, a G4-helix is defined by stacking interactions of G-tetrads, regardless of backbone connectivity, and may contain more than one G4-stem.
Helix#1, 2 G-tetrad layers, inter-molecular, with 1 stem
List of 1 G4-stem
In DSSR, a G4-stem is defined as a G4-helix with backbone connectivity. Bulges are also allowed along each of the four strands.