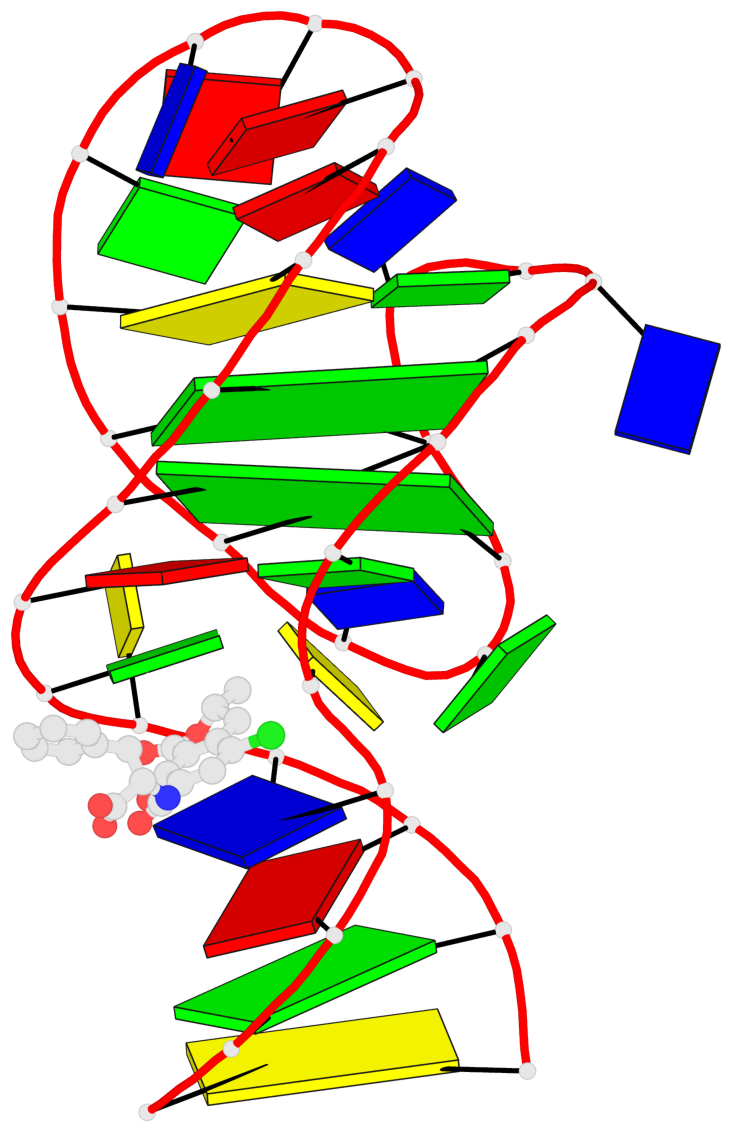
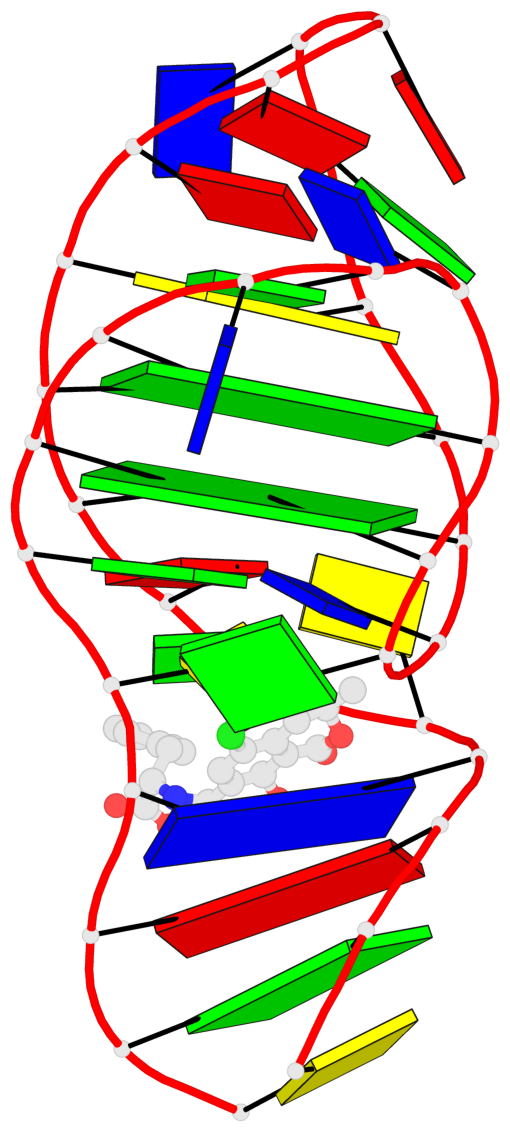
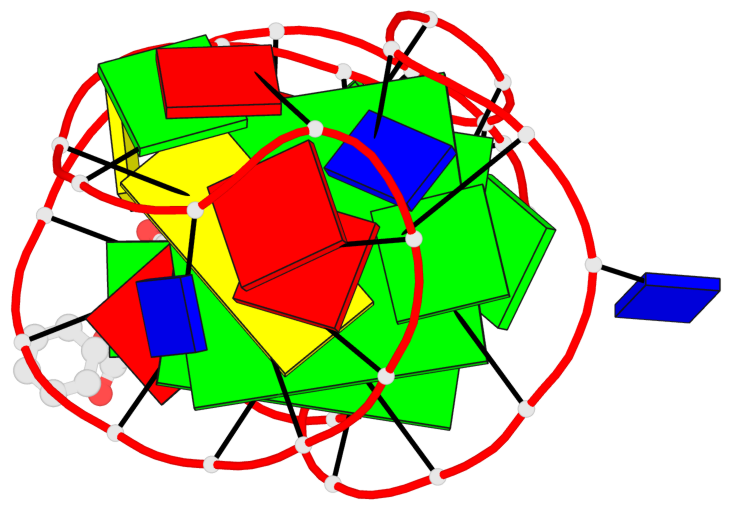
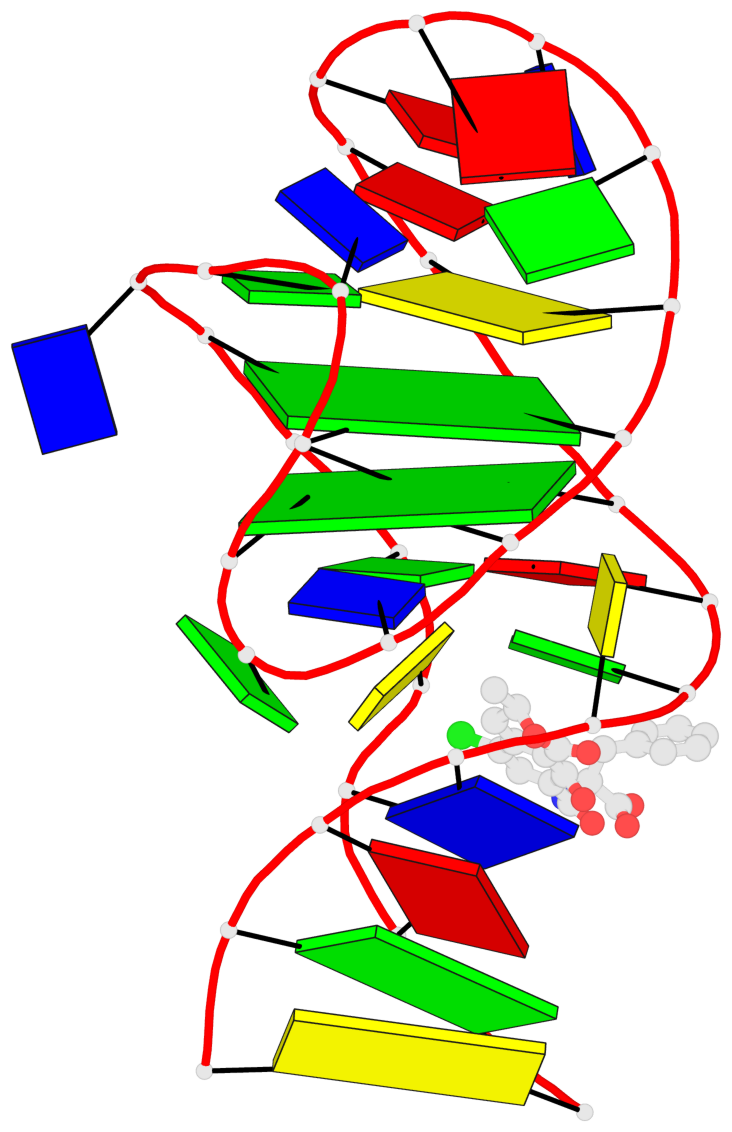
Detailed DSSR results for the G-quadruplex: PDB entry 7w9n
Created and maintained by Xiang-Jun Lu <xiangjun@x3dna.org>
Citation: Please cite the NAR'20 DSSR-PyMOL schematics paper and/or the NAR'15 DSSR method paper.
Summary information
- PDB id
- 7w9n
- Class
- DNA
- Method
- NMR
- Summary
- The structure of oba33-ota complex
- Reference
- Xu G, Zhao J, Yu H, Wang C, Huang Y, Zhao Q, Zhou X, Li C, Liu M (2022): "Structural Insights into the Mechanism of High-Affinity Binding of Ochratoxin A by a DNA Aptamer." J.Am.Chem.Soc., 144, 7731-7740. doi: 10.1021/jacs.2c00478.
- Abstract
- A 36-mer guanine (G)-rich DNA aptamer (OBA36) is able to distinguish one atomic difference between ochratoxin analogues A (OTA) and B (OTB), showing prominent recognition specificity and affinity among hundreds of aptamers for small molecules. Why OBA36 has >100-fold higher binding affinity to OTA than OTB remains a long-standing question due to the lack of high-resolution structure. Here we report the solution NMR structure of the aptamer-OTA complex. It was found that OTA binding induces the aptamer to fold into a well-defined unique duplex-quadruplex structural scaffold stabilized by Mg2+ and Na+ ions. OTA does not directly interact with the G-quadruplex, but specifically binds at the junction between the double helix and G-quadruplex through π-π stacking, halogen bonding (X-bond), and hydrophobic interaction. OTB has the same binding site as OTA but lacks the X-bond. The strong X-bond formed between the chlorine atom of OTA and the aromatic ring of C5 is the key to discriminating the strong binding toward OTA. The present research contributes to a deeper insight of aptamer molecular recognition, reveals structural basis of the high-affinity binding of aptamers, and provides a foundation for further aptamer engineering and applications.
- G4 notes
- 2 G-tetrads, 1 G4 helix, 1 G4 stem, 2(-Lw-Ln-Lw), chair(2+2), UDUD
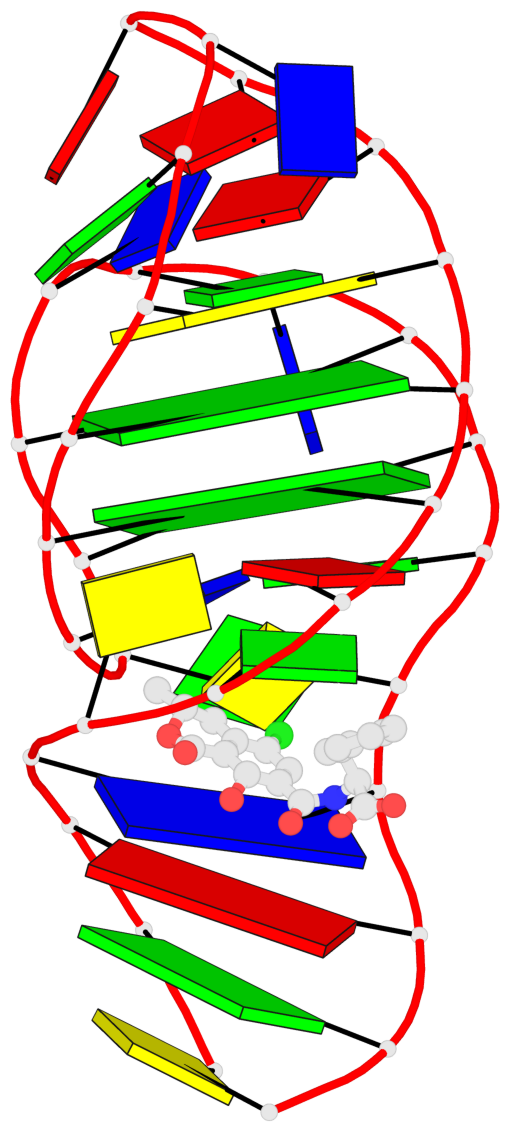
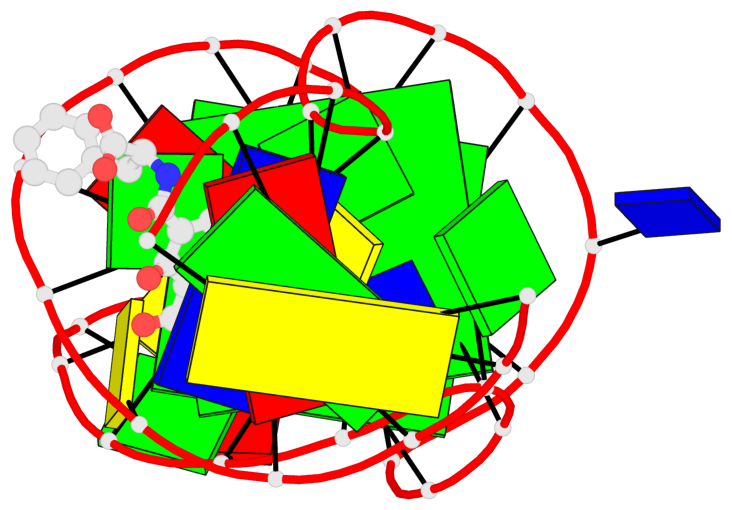
Base-block schematics in six views
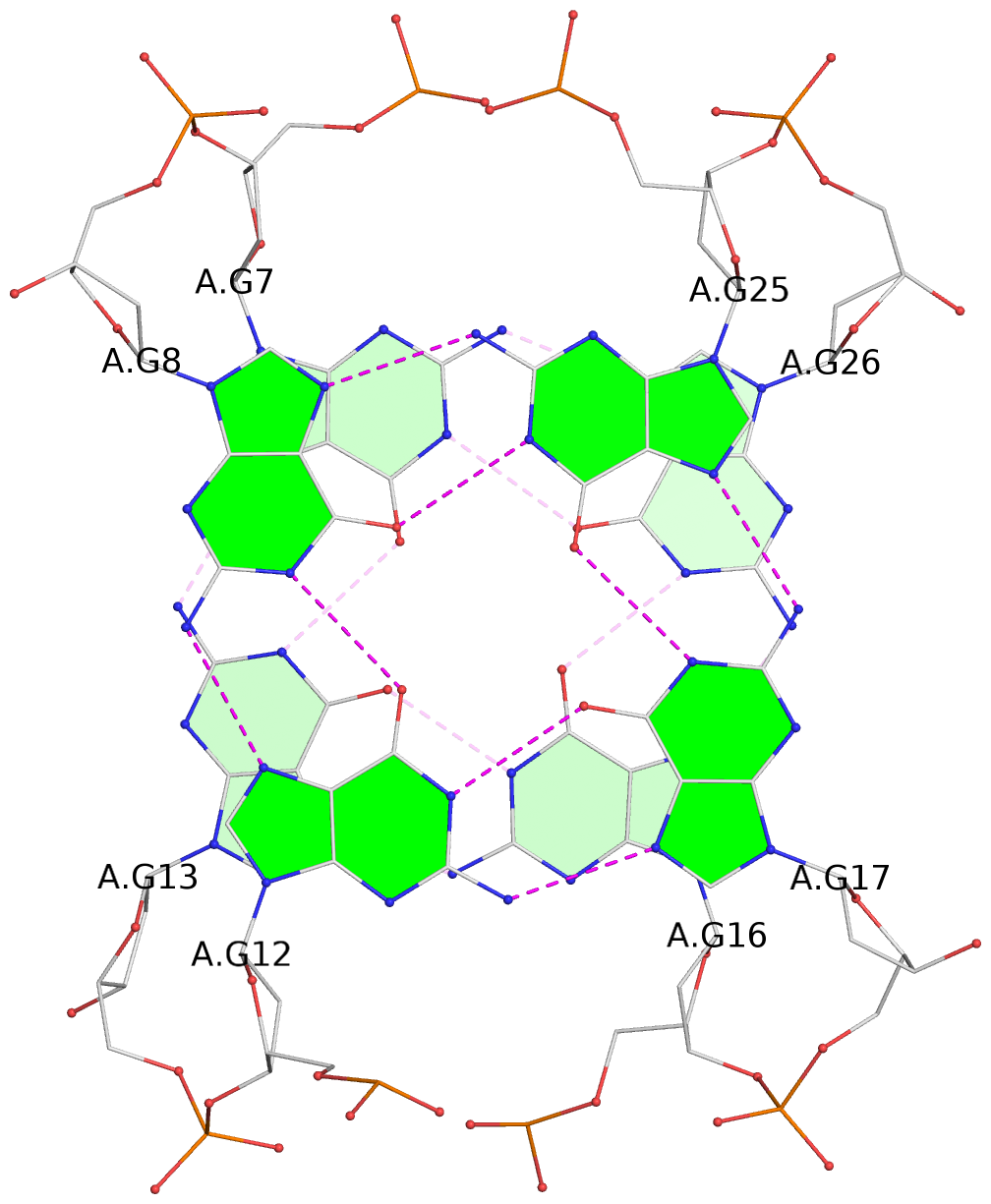
List of 2 G-tetrads
1 glyco-bond=s-s- sugar=..-- groove=wnwn planarity=0.315 type=other nts=4 GGGG A.DG7,A.DG13,A.DG16,A.DG26 2 glyco-bond=-s-s sugar=---- groove=wnwn planarity=0.152 type=planar nts=4 GGGG A.DG8,A.DG12,A.DG17,A.DG25
List of 1 G4-helix
In DSSR, a G4-helix is defined by stacking interactions of G-tetrads, regardless of backbone connectivity, and may contain more than one G4-stem.
Helix#1, 2 G-tetrad layers, INTRA-molecular, with 1 stem
List of 1 G4-stem
In DSSR, a G4-stem is defined as a G4-helix with backbone connectivity. Bulges are also allowed along each of the four strands.