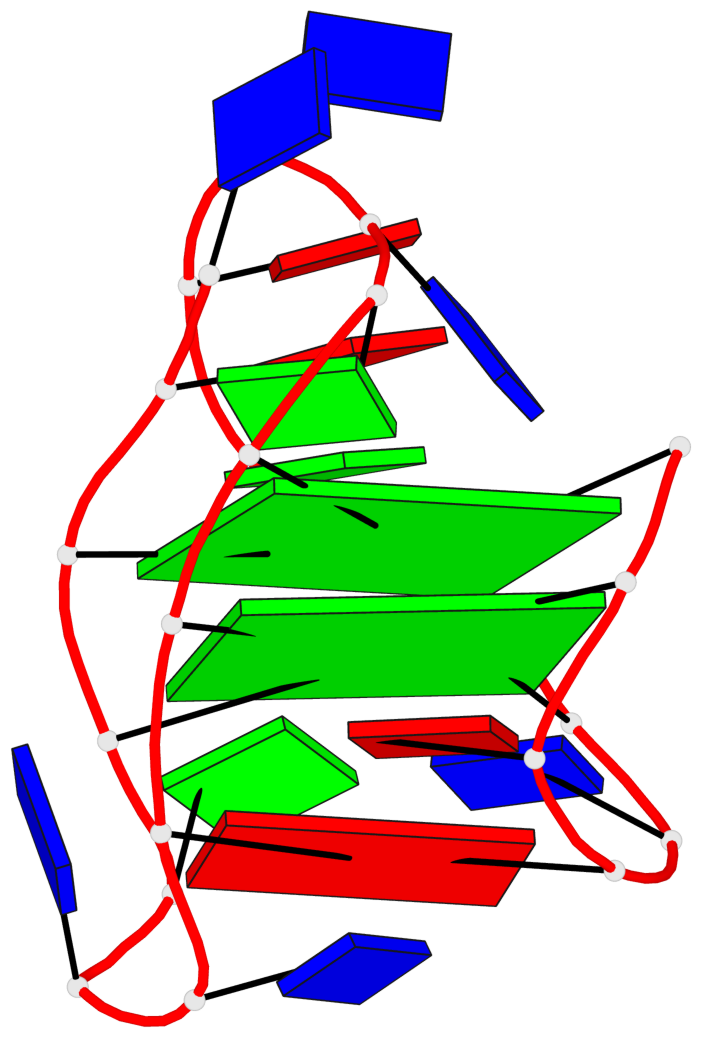
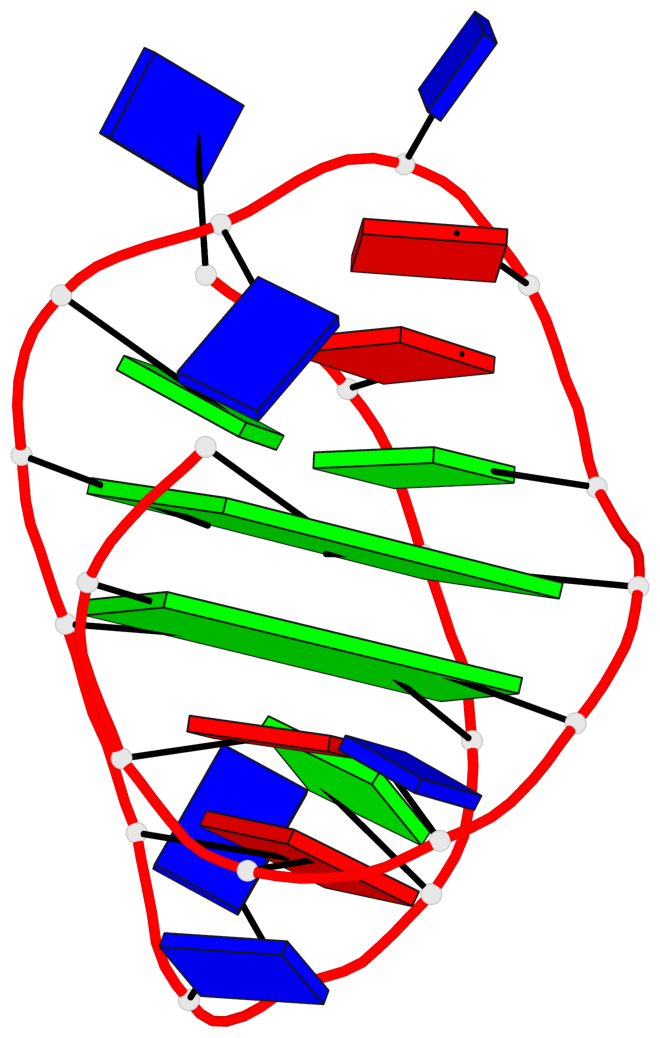
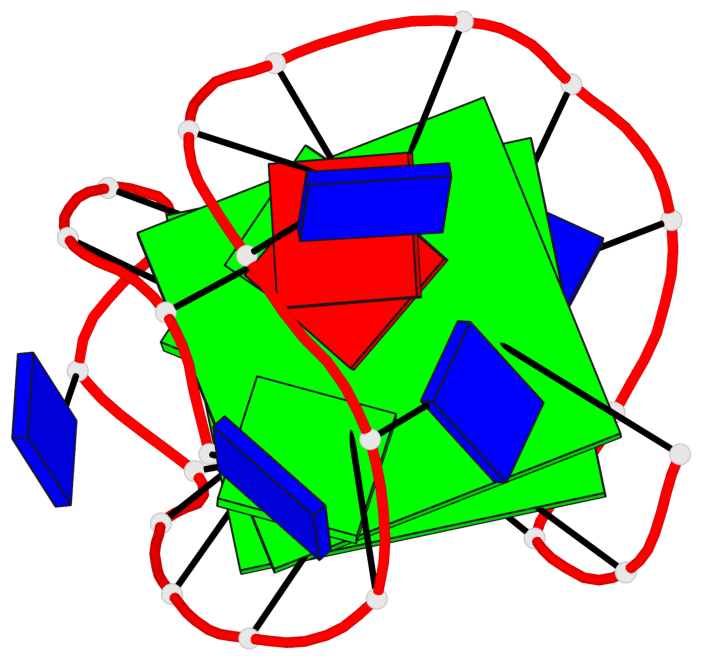
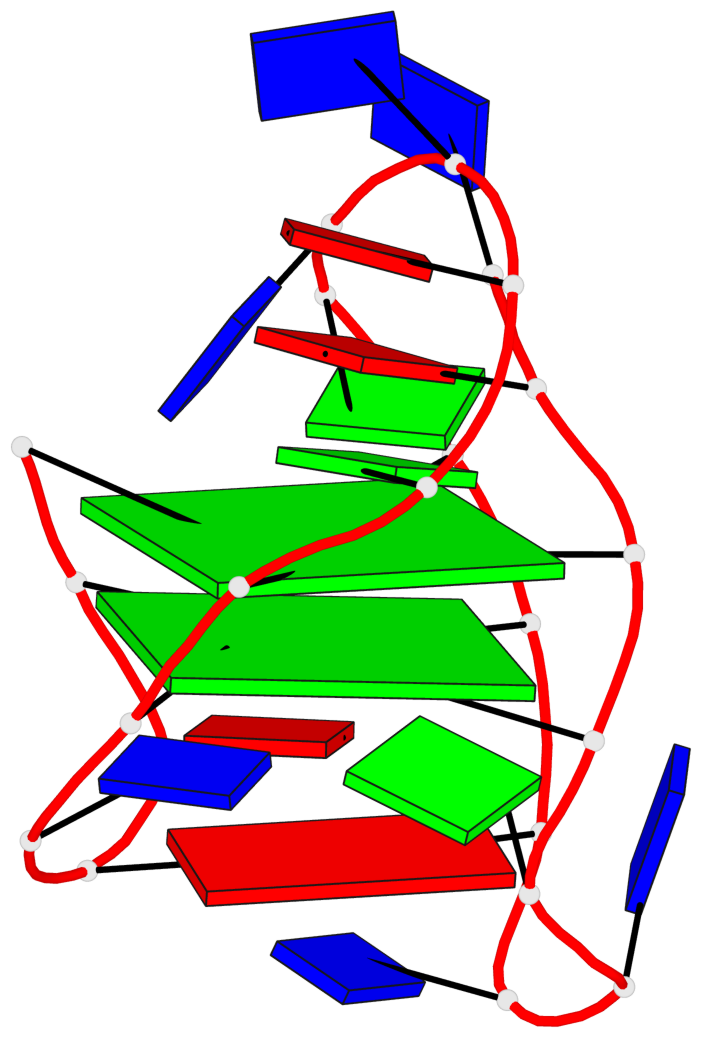
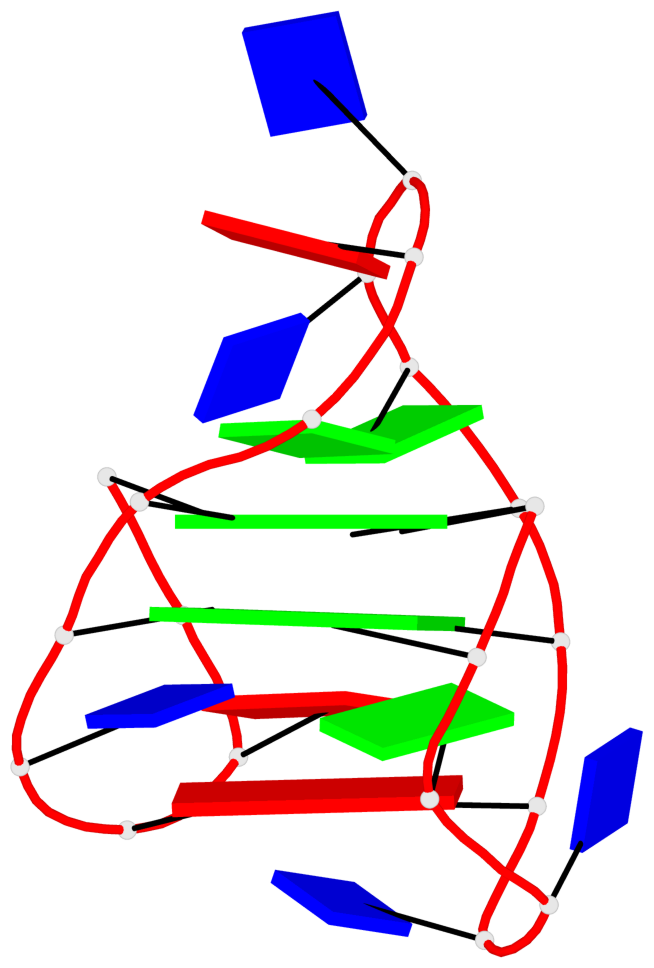
Detailed DSSR results for the G-quadruplex: PDB entry 8jih
Created and maintained by Xiang-Jun Lu <xiangjun@x3dna.org>
Citation: Please cite the NAR'20 DSSR-PyMOL schematics paper and/or the NAR'15 DSSR method paper.
Summary information
- PDB id
- 8jih
- Class
- DNA
- Method
- NMR
- Summary
- Human telomere two-quartet g-quadruplex at ph 5.0
- Reference
- Galer P, Wang B, Plavec J, Sket P (2023): "Unveiling the structural mechanism of a G-quadruplex pH-Driven switch." Biochimie, 214, 73-82. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2023.08.002.
- Abstract
- The human telomere oligonucleotide, d[TAGGG(TTAGGG)2TTAGG] (TAGGG), can adopt two distinct 2-G-quartet G-quadruplex structures at pH 7.0 and 5.0, referred to as the TD and KDH+ forms, respectively. By using a combination of NMR and computational techniques, we determined high-resolution structures of both forms, which revealed unique loop architectures, base triples, and base pairs that play a crucial role in the pH-driven structural transformation of TAGGG. Our study demonstrated that TAGGG represents a reversible pH-driven switch system where the stability and pH-induced structural transformation of the G-quadruplexes are influenced by the terminal residues and base triples. Gaining insight into the factors that regulate the formation of G-quadruplexes and their pH-sensitive structural equilibrium holds great potential for the rational design of novel DNA based pH-driven switches. These advancements in understanding create exciting opportunities for applications in the field of nanotechnology, specifically in the development of bio-nano-motors.
- G4 notes
- 2 G-tetrads, 1 G4 helix, 1 G4 stem, 2(+LnD-Lw), basket(2+2), UUDD
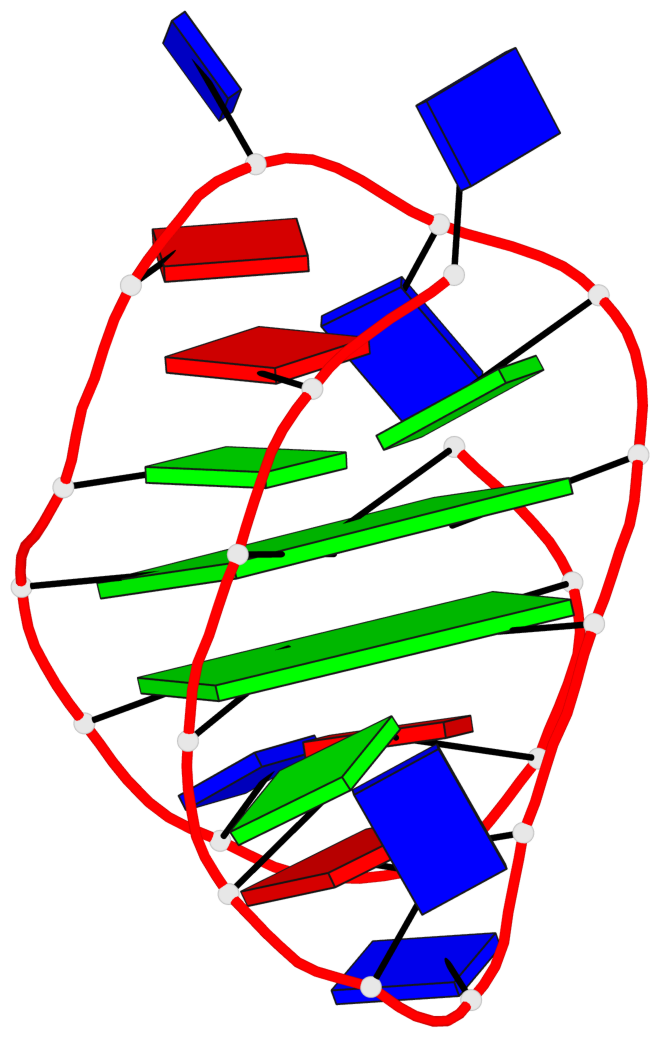
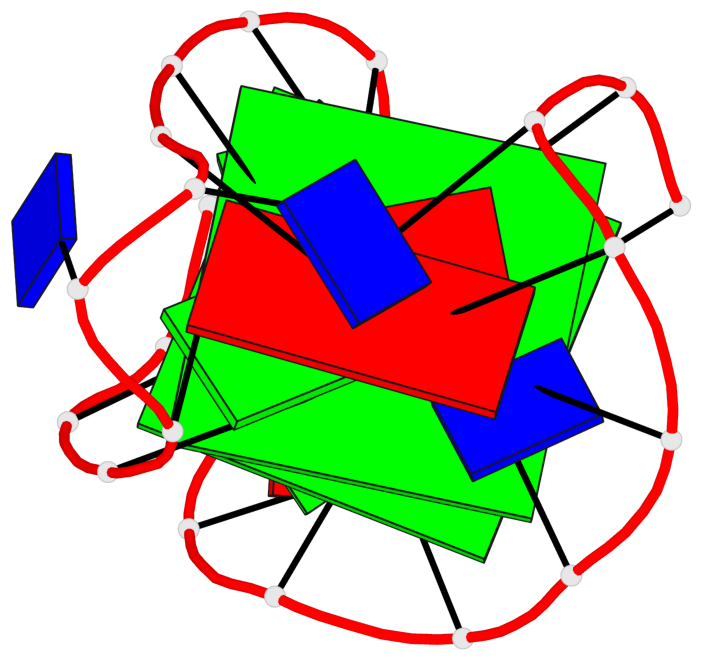
Base-block schematics in six views
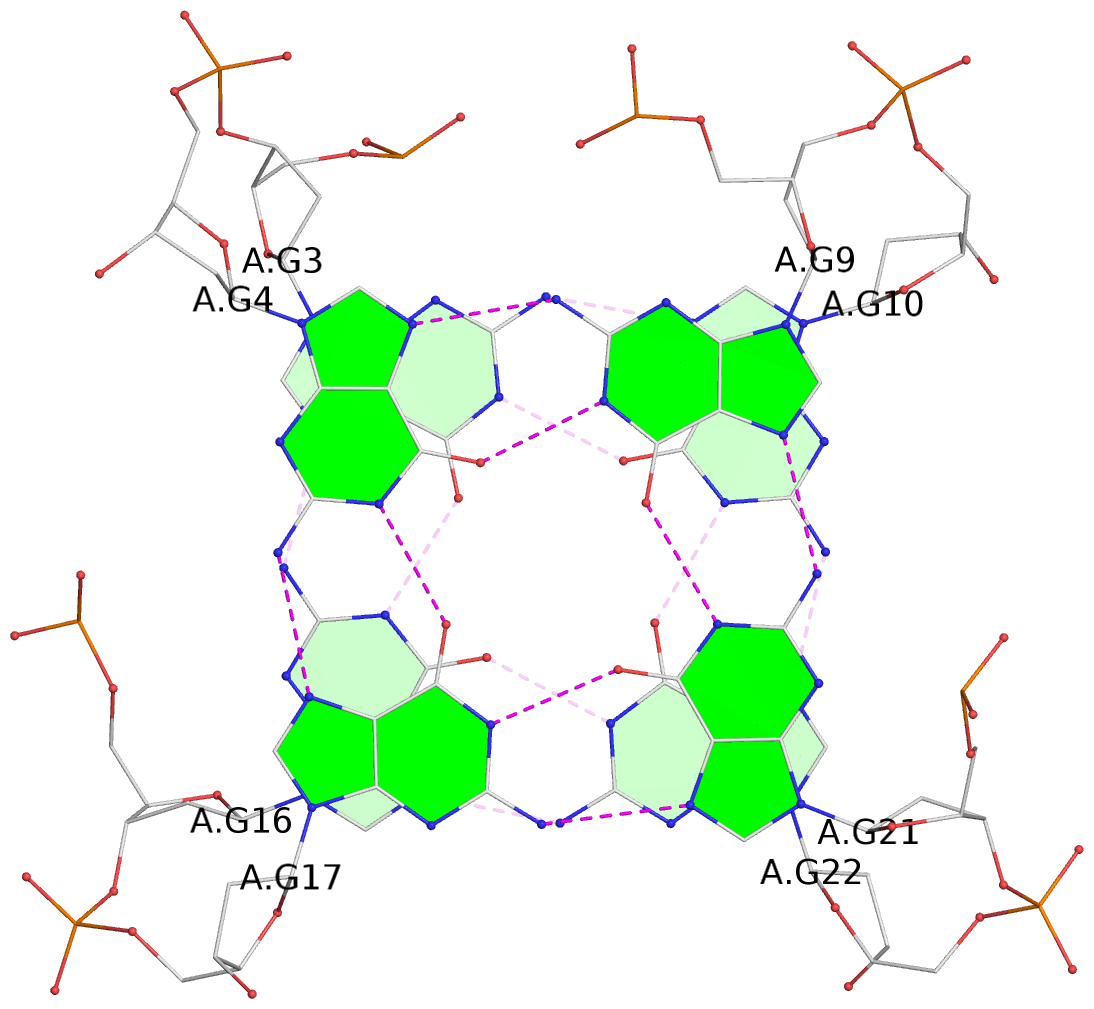
List of 2 G-tetrads
1 glyco-bond=ss-- sugar=---- groove=-w-n planarity=0.226 type=other nts=4 GGGG A.DG3,A.DG16,A.DG22,A.DG10 2 glyco-bond=--ss sugar=---- groove=-w-n planarity=0.123 type=planar nts=4 GGGG A.DG4,A.DG17,A.DG21,A.DG9
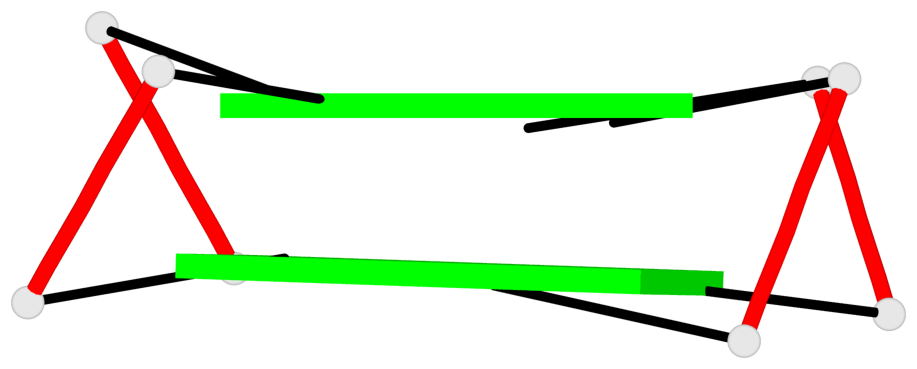
List of 1 G4-helix
In DSSR, a G4-helix is defined by stacking interactions of G-tetrads, regardless of backbone connectivity, and may contain more than one G4-stem.
Helix#1, 2 G-tetrad layers, INTRA-molecular, with 1 stem
List of 1 G4-stem
In DSSR, a G4-stem is defined as a G4-helix with backbone connectivity. Bulges are also allowed along each of the four strands.