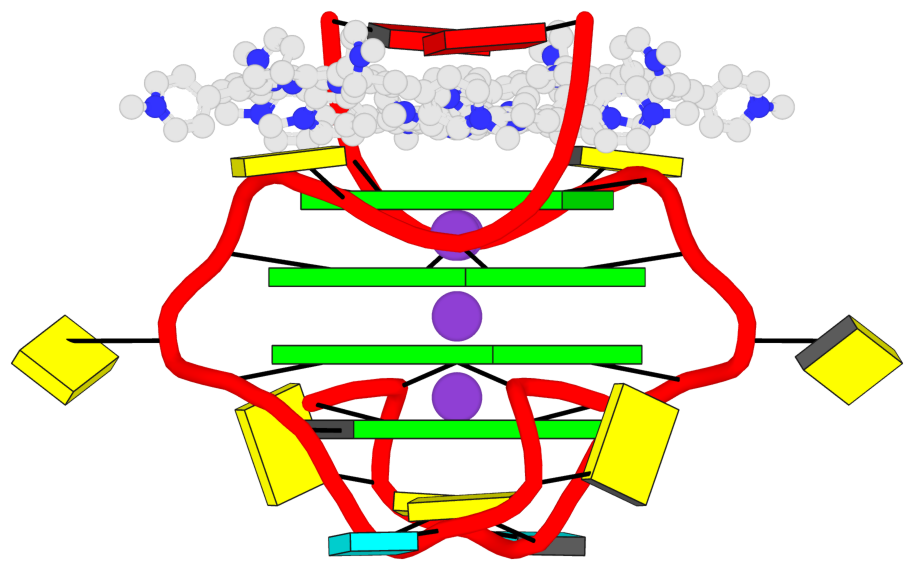
DSSR-enabled G4 identification/annotation: PDB entry 6jjh
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 6jjh
- Class
- RNA
- Method
- X-ray (1.74 Å)
- Summary
- Crystal structure of a two-quartet RNA parallel g-quadruplex complexed with the porphyrin tmpyp4
- Reference
- Zhang Y, El Omari K, Duman R, Liu S, Haider S, Wagner A, Parkinson GN, Wei D (2020): "Native de novo structural determinations of non-canonical nucleic acid motifs by X-ray crystallography at long wavelengths." Nucleic Acids Res., 48, 9886-9898. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa439.
- Abstract
- Obtaining phase information remains a formidable challenge for nucleic acid structure determination. The introduction of an X-ray synchrotron beamline designed to be tunable to long wavelengths at Diamond Light Source has opened the possibility to native de novo structure determinations by the use of intrinsic scattering elements. This provides opportunities to overcome the limitations of introducing modifying nucleotides, often required to derive phasing information. In this paper, we build on established methods to generate new tools for nucleic acid structure determinations. We report on the use of (i) native intrinsic potassium single-wavelength anomalous dispersion methods (K-SAD), (ii) use of anomalous scattering elements integral to the crystallization buffer (extrinsic cobalt and intrinsic potassium ions), (iii) extrinsic bromine and intrinsic phosphorus SAD to solve complex nucleic acid structures. Using the reported methods we solved the structures of (i) Pseudorabies virus (PRV) RNA G-quadruplex and ligand complex, (ii) PRV DNA G-quadruplex, and (iii) an i-motif of human telomeric sequence. Our results highlight the utility of using intrinsic scattering as a pathway to solve and determine non-canonical nucleic acid motifs and reveal the variability of topology, influence of ligand binding, and glycosidic angle rearrangements seen between RNA and DNA G-quadruplexes of the same sequence.
- G4 notes
- 4 G-tetrads, 1 G4 helix, 2 G4 stems, 1 G4 coaxial stack, UUUU, parallel, 4+0, coaxial interfaces: 3'/5'
Cartoon-block schematics in six views (download the tarball)
List of 4 G-tetrads
1 glyco-bond=ssss sugar=3333 groove=---- planarity=0.103 type=planar -- nts=4 GGGG 1:B.G1,2:B.G6,2:B.G1,1:B.G6 2 glyco-bond=---- sugar=---- groove=---- planarity=0.127 type=planar -- nts=4 GGGG 1:B.G2,1:B.G7,2:B.G2,2:B.G7 3 glyco-bond=---- sugar=-3-3 groove=---- planarity=0.124 type=planar -- nts=4 GGGG 1:B.G9,1:B.G12,2:B.G9,2:B.G12 4 glyco-bond=---- sugar=-3-3 groove=---- planarity=0.063 type=planar -- nts=4 GGGG 1:B.G10,1:B.G13,2:B.G10,2:B.G13
List of 1 G4-helix
In DSSR, a G4-helix is defined by stacking interactions of G-tetrads, regardless of backbone connectivity, and may contain more than one G4-stem.
Helix#1, 4 G-tetrads, inter-molecular, with 2 stems
List of 2 G4-stems
In DSSR, a G4-stem is defined as a G4-helix with backbone connectivity. Bulges are also allowed along each of the four strands.
Stem#1, 2 G-tetrads, 2 loops, inter-molecular, UUUU, parallel, 4+0
Stem#2, 2 G-tetrads, 2 loops, inter-molecular, UUUU, parallel, 4+0
List of 1 G4 coaxial stack
1 G4 helix#1 contains 2 G4 stems: [#1,#2] [3'/5']